Decentralized over-the-counter (OTC) trading enables direct peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries, enhancing privacy and reducing counterparty risk in cryptocurrency markets. Automated market makers (AMMs) utilize algorithmic liquidity pools to facilitate seamless asset swaps and maintain market efficiency on decentralized exchanges. Explore the key differences and benefits of both mechanisms to deepen your understanding of modern decentralized finance (DeFi) solutions.
Why it is important
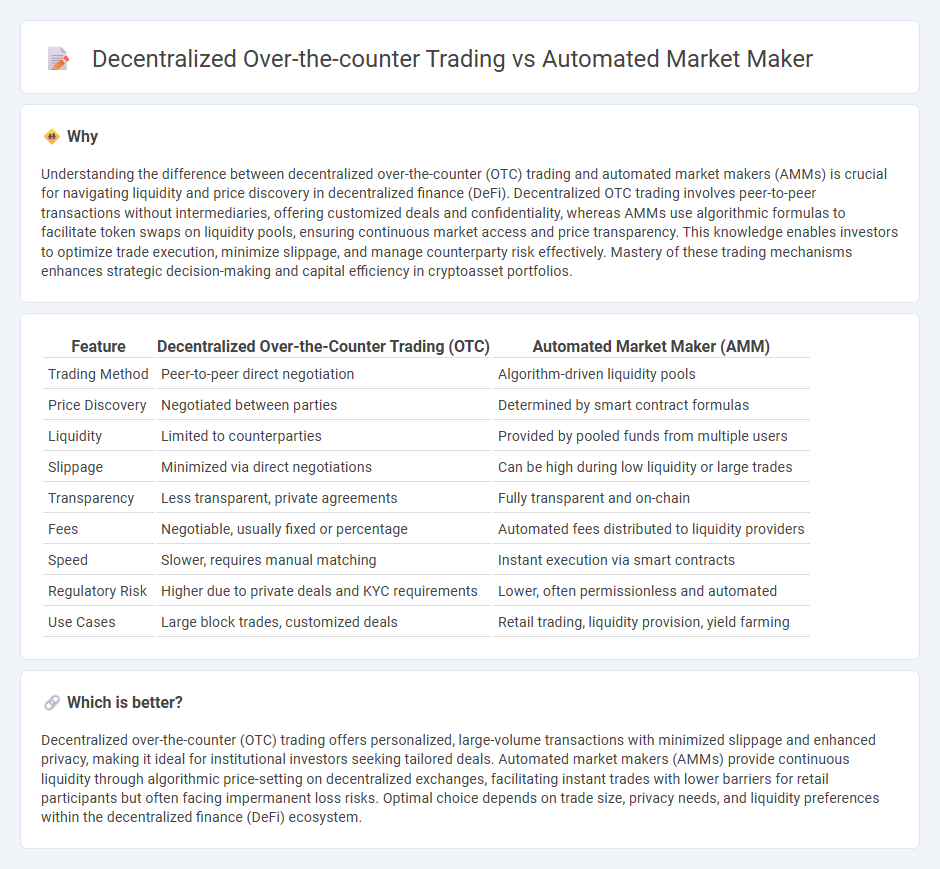
Understanding the difference between decentralized over-the-counter (OTC) trading and automated market makers (AMMs) is crucial for navigating liquidity and price discovery in decentralized finance (DeFi). Decentralized OTC trading involves peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries, offering customized deals and confidentiality, whereas AMMs use algorithmic formulas to facilitate token swaps on liquidity pools, ensuring continuous market access and price transparency. This knowledge enables investors to optimize trade execution, minimize slippage, and manage counterparty risk effectively. Mastery of these trading mechanisms enhances strategic decision-making and capital efficiency in cryptoasset portfolios.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Decentralized Over-the-Counter Trading (OTC) | Automated Market Maker (AMM) |
|---|---|---|
| Trading Method | Peer-to-peer direct negotiation | Algorithm-driven liquidity pools |
| Price Discovery | Negotiated between parties | Determined by smart contract formulas |
| Liquidity | Limited to counterparties | Provided by pooled funds from multiple users |
| Slippage | Minimized via direct negotiations | Can be high during low liquidity or large trades |
| Transparency | Less transparent, private agreements | Fully transparent and on-chain |
| Fees | Negotiable, usually fixed or percentage | Automated fees distributed to liquidity providers |
| Speed | Slower, requires manual matching | Instant execution via smart contracts |
| Regulatory Risk | Higher due to private deals and KYC requirements | Lower, often permissionless and automated |
| Use Cases | Large block trades, customized deals | Retail trading, liquidity provision, yield farming |
Which is better?
Decentralized over-the-counter (OTC) trading offers personalized, large-volume transactions with minimized slippage and enhanced privacy, making it ideal for institutional investors seeking tailored deals. Automated market makers (AMMs) provide continuous liquidity through algorithmic price-setting on decentralized exchanges, facilitating instant trades with lower barriers for retail participants but often facing impermanent loss risks. Optimal choice depends on trade size, privacy needs, and liquidity preferences within the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem.
Connection
Decentralized over-the-counter (OTC) trading enhances liquidity by enabling peer-to-peer asset exchanges without intermediaries, integrating seamlessly with Automated Market Makers (AMMs) that utilize smart contracts to provide continuous pricing and asset swaps. AMMs facilitate decentralized OTC markets by using algorithm-driven pools, reducing counterparty risk and improving price efficiency in real-time trading environments. The synergy between decentralized OTC trading and AMMs promotes transparency, lowers transaction costs, and supports broader access to diverse financial assets within blockchain ecosystems.
Key Terms
Liquidity Pool
Automated Market Makers (AMMs) utilize liquidity pools where users provide tokens to enable decentralized trading without intermediaries, ensuring continuous market liquidity and enabling instant asset swaps. Decentralized Over-the-Counter (OTC) trading, on the other hand, involves direct peer-to-peer transactions outside of order books, often lacking pooled liquidity but offering personalized negotiation and reduced slippage for large trades. Explore the dynamics of liquidity pools and their impact on decentralized trading efficiency to gain deeper insights.
Order Book
Automated Market Makers (AMMs) operate on decentralized exchanges using liquidity pools instead of traditional order books, enabling continuous token swaps with algorithmically determined prices. In contrast, decentralized over-the-counter (OTC) trading relies on peer-to-peer transactions often negotiated off-chain with an order book mechanism that records buy and sell offers to facilitate price discovery. Explore the distinct mechanisms and benefits of AMMs and decentralized OTC trading for a deeper understanding of decentralized finance.
Price Discovery
Automated market makers (AMMs) leverage algorithmic formulas to provide continuous liquidity and transparent price discovery, typically using liquidity pools on decentralized exchanges. Decentralized over-the-counter (OTC) trading allows direct peer-to-peer negotiations, enabling customized pricing but often lacks the same level of real-time market efficiency and price transparency. Explore the nuances of how these mechanisms impact price discovery and trading strategies in the evolving DeFi landscape.
Source and External Links
What is an Automated Market Maker (AMM)? AMMs explained - An automated market maker (AMM) is an autonomous protocol used by decentralized exchanges to facilitate crypto trades via liquidity pools and algorithmically determined prices, eliminating the need for waiting for a counterparty in trading.
What Is an Automated Market Maker (AMM)? - Gemini - AMMs use liquidity pools instead of order books, allowing users to trade directly against pooled tokens with prices set by mathematical formulas, thus keeping the DeFi ecosystem liquid 24/7.
Automated Market Makers (AMMs) Explained - Chainlink - AMMs commonly use constant function market makers like the constant product market maker (x*y=k), which maintains liquidity by ensuring the product of token quantities stays constant during trades.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com