Tokenization transforms physical or financial assets into digital tokens on a blockchain, enhancing liquidity and transparency. Asset-backed securities pool financial assets like loans or receivables to issue tradable securities, providing investors with predictable income streams. Explore how these financial instruments reshape investment strategies and market access.
Why it is important
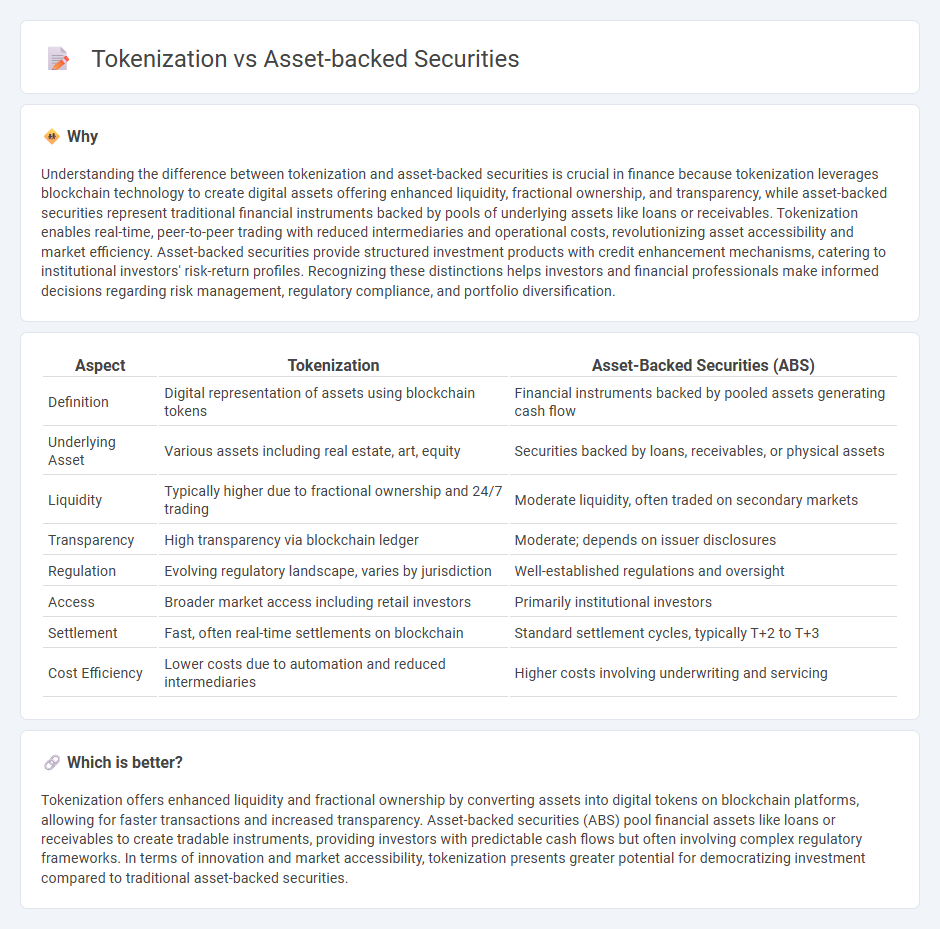
Understanding the difference between tokenization and asset-backed securities is crucial in finance because tokenization leverages blockchain technology to create digital assets offering enhanced liquidity, fractional ownership, and transparency, while asset-backed securities represent traditional financial instruments backed by pools of underlying assets like loans or receivables. Tokenization enables real-time, peer-to-peer trading with reduced intermediaries and operational costs, revolutionizing asset accessibility and market efficiency. Asset-backed securities provide structured investment products with credit enhancement mechanisms, catering to institutional investors' risk-return profiles. Recognizing these distinctions helps investors and financial professionals make informed decisions regarding risk management, regulatory compliance, and portfolio diversification.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Tokenization | Asset-Backed Securities (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital representation of assets using blockchain tokens | Financial instruments backed by pooled assets generating cash flow |
| Underlying Asset | Various assets including real estate, art, equity | Securities backed by loans, receivables, or physical assets |
| Liquidity | Typically higher due to fractional ownership and 24/7 trading | Moderate liquidity, often traded on secondary markets |
| Transparency | High transparency via blockchain ledger | Moderate; depends on issuer disclosures |
| Regulation | Evolving regulatory landscape, varies by jurisdiction | Well-established regulations and oversight |
| Access | Broader market access including retail investors | Primarily institutional investors |
| Settlement | Fast, often real-time settlements on blockchain | Standard settlement cycles, typically T+2 to T+3 |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower costs due to automation and reduced intermediaries | Higher costs involving underwriting and servicing |
Which is better?
Tokenization offers enhanced liquidity and fractional ownership by converting assets into digital tokens on blockchain platforms, allowing for faster transactions and increased transparency. Asset-backed securities (ABS) pool financial assets like loans or receivables to create tradable instruments, providing investors with predictable cash flows but often involving complex regulatory frameworks. In terms of innovation and market accessibility, tokenization presents greater potential for democratizing investment compared to traditional asset-backed securities.
Connection
Tokenization transforms traditional assets into digital tokens recorded on a blockchain, enhancing liquidity and transparency in asset-backed securities (ABS). Asset-backed securities utilize pools of underlying assets, which can be represented as tokenized digital units, enabling fractional ownership and easier transferability. This integration of tokenization with ABS reduces transaction costs and accelerates settlement times in financial markets.
Key Terms
Securitization
Asset-backed securities (ABS) represent financial instruments backed by pools of underlying assets such as loans or receivables, offering investors predictable cash flows through traditional securitization processes. Tokenization transforms these underlying assets into digital tokens on a blockchain, facilitating fractional ownership, enhanced liquidity, and transparent transaction records. Explore how combining traditional asset-backed securities with blockchain tokenization can revolutionize securitization practices and investor accessibility.
Blockchain
Asset-backed securities (ABS) represent financial instruments backed by pools of assets, traditionally managed through centralized processes, while tokenization leverages blockchain technology to digitize these assets, enhancing transparency, liquidity, and security. Blockchain ensures immutable records and smart contracts automate transactions, reducing intermediaries and operational costs in tokenized assets. Explore how blockchain revolutionizes asset-backed securities through tokenization for cutting-edge financial innovation.
Liquidity
Asset-backed securities (ABS) provide liquidity by pooling financial assets and selling claims to investors, enabling quicker capital recovery from assets like loans or receivables. Tokenization enhances liquidity further by converting ownership of assets into digital tokens on a blockchain, allowing for fractional ownership and 24/7 trading in secondary markets with reduced intermediaries. Explore how combining ABS and tokenization can revolutionize liquidity and market access.
Source and External Links
Asset-backed securities: Definition, types and examples - Asset-backed securities (ABS) are debt securities collateralized by pools of loans such as auto loans, mortgages, or credit card receivables, allowing institutions to raise funds by converting illiquid assets into liquid securities backed by contractual obligations to pay investors.
The ABCs of Asset-Backed Securities - ABS enable financing backed by diversified asset pools like auto loans and mortgages, often ranking senior to traditional debt and offering investor protections like tranching and overcollateralization to manage risk and improve liquidity.
Asset-backed security - Wikipedia - ABS convert pools of illiquid assets into tradable securities with structured risk/return profiles, allowing loan originators to free capital for new lending while transferring associated risks to investors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com