Dark pool routing offers institutional investors the ability to execute large trades privately, minimizing market impact and information leakage. Auction markets provide transparent price discovery by matching buy and sell orders openly on public exchanges, enhancing liquidity and fairness. Explore the differences between these trading venues to optimize your investment strategy.
Why it is important
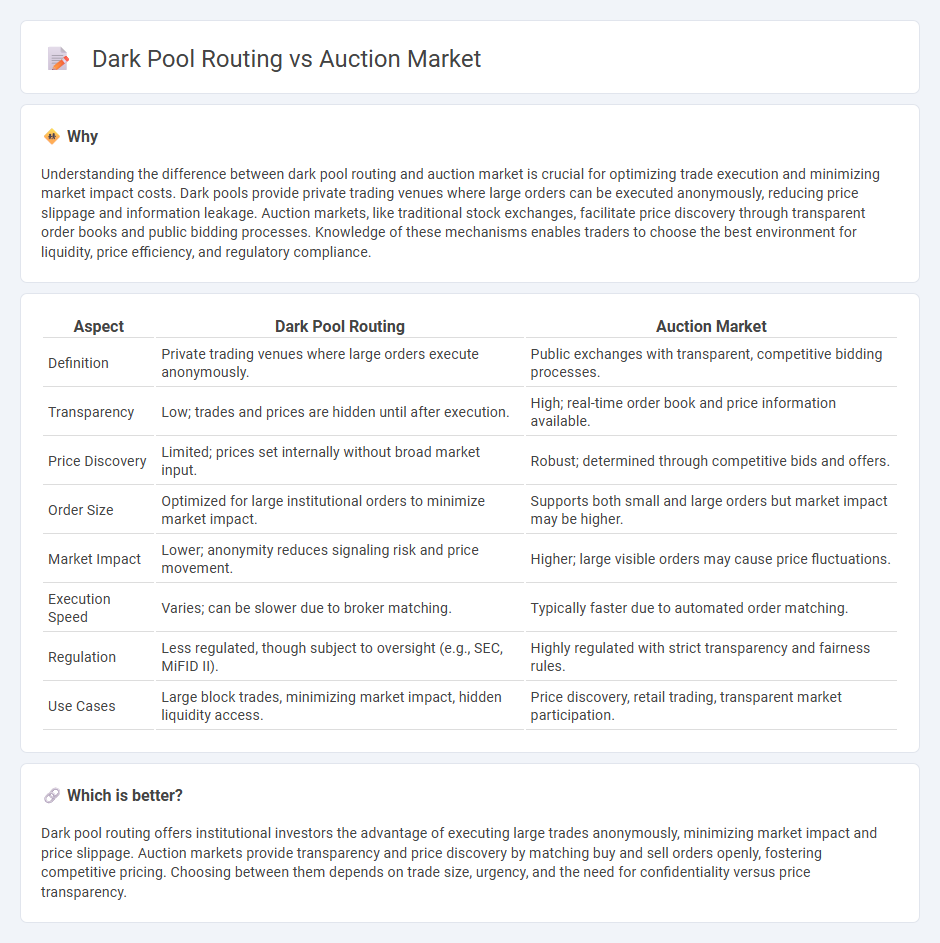
Understanding the difference between dark pool routing and auction market is crucial for optimizing trade execution and minimizing market impact costs. Dark pools provide private trading venues where large orders can be executed anonymously, reducing price slippage and information leakage. Auction markets, like traditional stock exchanges, facilitate price discovery through transparent order books and public bidding processes. Knowledge of these mechanisms enables traders to choose the best environment for liquidity, price efficiency, and regulatory compliance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dark Pool Routing | Auction Market |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Private trading venues where large orders execute anonymously. | Public exchanges with transparent, competitive bidding processes. |
| Transparency | Low; trades and prices are hidden until after execution. | High; real-time order book and price information available. |
| Price Discovery | Limited; prices set internally without broad market input. | Robust; determined through competitive bids and offers. |
| Order Size | Optimized for large institutional orders to minimize market impact. | Supports both small and large orders but market impact may be higher. |
| Market Impact | Lower; anonymity reduces signaling risk and price movement. | Higher; large visible orders may cause price fluctuations. |
| Execution Speed | Varies; can be slower due to broker matching. | Typically faster due to automated order matching. |
| Regulation | Less regulated, though subject to oversight (e.g., SEC, MiFID II). | Highly regulated with strict transparency and fairness rules. |
| Use Cases | Large block trades, minimizing market impact, hidden liquidity access. | Price discovery, retail trading, transparent market participation. |
Which is better?
Dark pool routing offers institutional investors the advantage of executing large trades anonymously, minimizing market impact and price slippage. Auction markets provide transparency and price discovery by matching buy and sell orders openly, fostering competitive pricing. Choosing between them depends on trade size, urgency, and the need for confidentiality versus price transparency.
Connection
Dark pool routing directs large institutional orders to private, non-transparent trading venues to minimize market impact and information leakage. Auction markets provide a structured environment for price discovery through competitive bidding, often serving as reference points for execution quality in dark pools. The interaction between dark pool routing and auction markets enhances liquidity and price efficiency by leveraging hidden order flow alongside transparent price formation mechanisms.
Key Terms
Transparency
Auction markets provide high transparency by displaying order books and trade details openly, allowing participants to gauge supply and demand effectively. Dark pool routing, in contrast, operates with limited transparency as trades occur off-exchange without public disclosure until after execution, aiming to minimize market impact. Explore how transparency in trading venues influences execution quality and market fairness.
Price Discovery
Auction markets enhance price discovery by aggregating buy and sell orders transparently, allowing market participants to see real-time price formation. Dark pool routing, conversely, obscures order flow to minimize market impact but can impede efficient price discovery due to limited visibility. Explore further to understand how each mechanism influences trading strategies and market transparency.
Liquidity
Auction markets provide transparent price discovery by aggregating buy and sell orders in a centralized order book, fostering liquidity through visible bids and asks. Dark pool routing, in contrast, offers private trading venues where large orders can execute without immediate market impact, preserving liquidity but reducing transparency. Explore the nuances of liquidity in different trading environments to optimize your market strategy.
Source and External Links
Auction markets: What is it, types, Importance, Example, FAQ | POEMS - An auction market is where buyers and sellers compete by submitting bids and offers, with prices determined by these competitive interactions, enabling transparent, efficient trading of assets like stocks, bonds, and commodities.
AUCTION MARKET: Easy explanation. - YouTube - The auction market works by matching buyers' bid prices and sellers' ask prices, completing transactions at the point where these prices meet, a method used in exchanges like the NYSE and CME.
What is Auction Market? Definition of Auction ... - The Economic Times - An auction market is one where buyers and sellers simultaneously place ambitious bids and offers, with trades executed at prices where bid and offer match, reflecting the highest price a buyer will pay and the lowest price a seller will accept.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com