Retail algorithmic trading leverages automated systems and quantitative models to execute trades at high speed and frequency, optimizing market opportunities with minimal human intervention. Active investing relies on human judgment and fundamental analysis to make strategic decisions, focusing on long-term value creation and market trends. Explore the key differences and advantages of retail algorithmic trading compared to active investing to enhance your financial strategy.
Why it is important
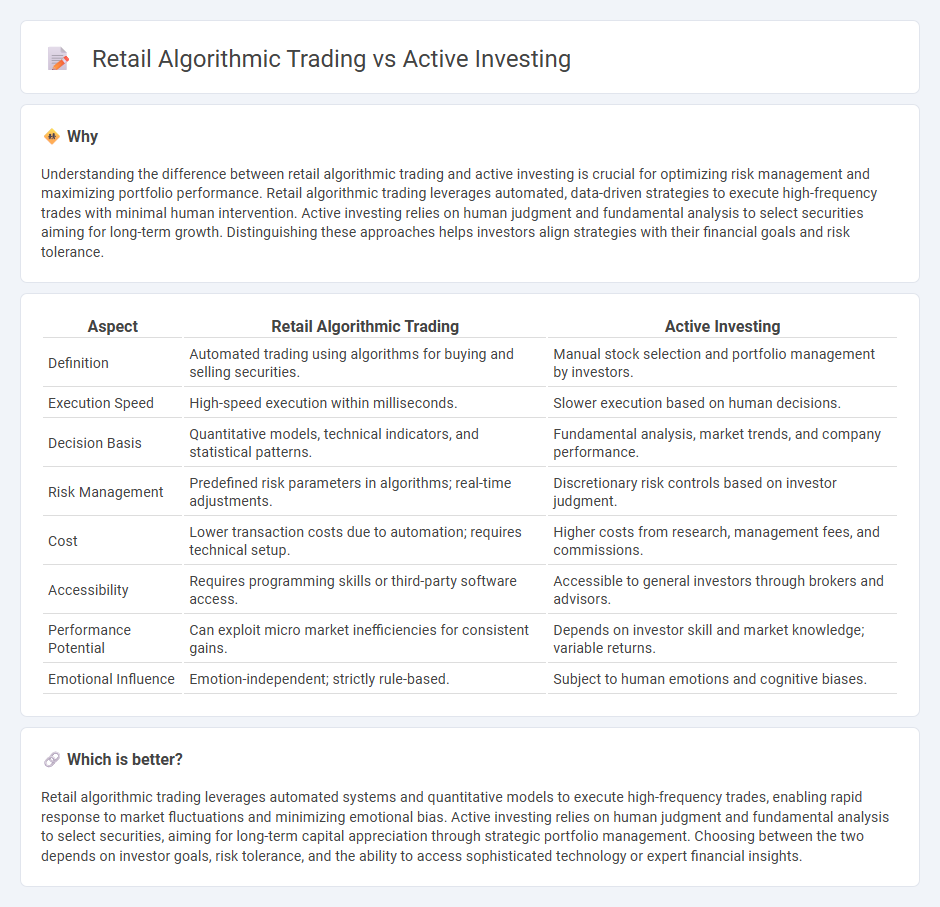
Understanding the difference between retail algorithmic trading and active investing is crucial for optimizing risk management and maximizing portfolio performance. Retail algorithmic trading leverages automated, data-driven strategies to execute high-frequency trades with minimal human intervention. Active investing relies on human judgment and fundamental analysis to select securities aiming for long-term growth. Distinguishing these approaches helps investors align strategies with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Retail Algorithmic Trading | Active Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated trading using algorithms for buying and selling securities. | Manual stock selection and portfolio management by investors. |
| Execution Speed | High-speed execution within milliseconds. | Slower execution based on human decisions. |
| Decision Basis | Quantitative models, technical indicators, and statistical patterns. | Fundamental analysis, market trends, and company performance. |
| Risk Management | Predefined risk parameters in algorithms; real-time adjustments. | Discretionary risk controls based on investor judgment. |
| Cost | Lower transaction costs due to automation; requires technical setup. | Higher costs from research, management fees, and commissions. |
| Accessibility | Requires programming skills or third-party software access. | Accessible to general investors through brokers and advisors. |
| Performance Potential | Can exploit micro market inefficiencies for consistent gains. | Depends on investor skill and market knowledge; variable returns. |
| Emotional Influence | Emotion-independent; strictly rule-based. | Subject to human emotions and cognitive biases. |
Which is better?
Retail algorithmic trading leverages automated systems and quantitative models to execute high-frequency trades, enabling rapid response to market fluctuations and minimizing emotional bias. Active investing relies on human judgment and fundamental analysis to select securities, aiming for long-term capital appreciation through strategic portfolio management. Choosing between the two depends on investor goals, risk tolerance, and the ability to access sophisticated technology or expert financial insights.
Connection
Retail algorithmic trading leverages automated strategies and data analytics to execute trades with precision and speed, enhancing decision-making for active investors. Active investing relies on timely market insights and dynamic portfolio adjustments, which algorithmic trading facilitates by processing vast datasets and identifying trends. This synergy enables individual investors to implement sophisticated trading tactics previously accessible predominantly to institutional players, optimizing returns and managing risks effectively.
Key Terms
Strategy
Active investing relies on fundamental analysis and market insights to select individual securities aiming for outperforming the market. Retail algorithmic trading utilizes pre-programmed algorithms and quantitative models to execute trades based on specific market conditions, reducing human emotion and increasing speed. Discover the nuances of these strategies to optimize your investment approach.
Risk Management
Active investing emphasizes human decision-making and experience to identify market opportunities while managing risk through diversified portfolios and ongoing analysis. Retail algorithmic trading uses automated systems to execute trades based on predefined risk parameters, minimizing emotional biases and enhancing precision. Explore how integrating both strategies can optimize risk management in your investment approach.
Order Execution
Active investing relies on human decision-making to optimize order execution, emphasizing market timing and price improvements through skilled negotiation. Retail algorithmic trading uses automated strategies to place orders rapidly, minimizing latency and slippage for precise market entry and exit points. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which method enhances your trading performance.
Source and External Links
Active management - Wikipedia - Active investing involves selecting investments to build a portfolio with the goal of outperforming the market, offering flexibility, customization to risk tolerance, and tax planning benefits, but it tends to be more expensive and less tax-efficient than passive strategies.
Active vs. Passive Investing Strategies | KAR - Active investing uses expert analysis to buy and sell stocks for potentially bigger rewards, providing flexibility to capitalize on undervalued stocks and manage taxes, especially beneficial when markets are volatile and quality company selection matters most.
Active vs. Passive Investing | FINRA.org - Active investing requires frequent buying and selling to exploit short-term opportunities and typically involves managing individual securities, contrasting with passive investing which aims to track market performance over the long term through buy-and-hold strategies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com