Dark pool routing enables institutional investors to execute large trades anonymously away from public exchanges, reducing market impact and information leakage. Exchange routing, by contrast, involves placing orders directly on public stock exchanges, ensuring transparency and immediate price discovery. Explore the advantages and challenges of both methods to optimize your trading strategy.
Why it is important
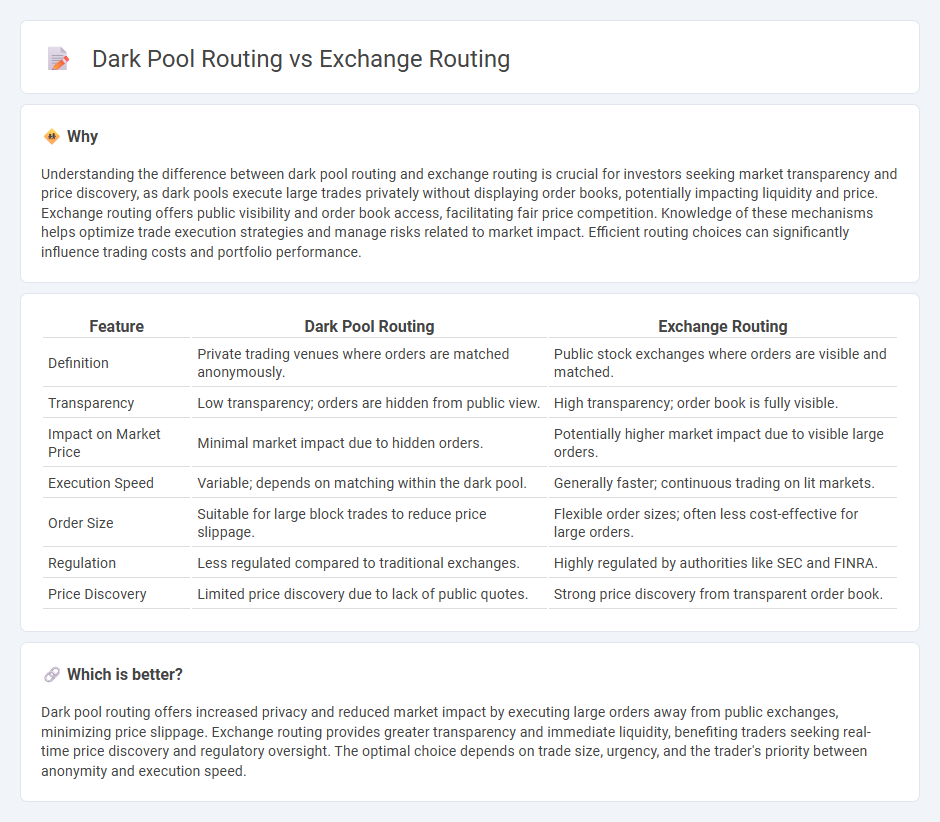
Understanding the difference between dark pool routing and exchange routing is crucial for investors seeking market transparency and price discovery, as dark pools execute large trades privately without displaying order books, potentially impacting liquidity and price. Exchange routing offers public visibility and order book access, facilitating fair price competition. Knowledge of these mechanisms helps optimize trade execution strategies and manage risks related to market impact. Efficient routing choices can significantly influence trading costs and portfolio performance.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Dark Pool Routing | Exchange Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Private trading venues where orders are matched anonymously. | Public stock exchanges where orders are visible and matched. |
| Transparency | Low transparency; orders are hidden from public view. | High transparency; order book is fully visible. |
| Impact on Market Price | Minimal market impact due to hidden orders. | Potentially higher market impact due to visible large orders. |
| Execution Speed | Variable; depends on matching within the dark pool. | Generally faster; continuous trading on lit markets. |
| Order Size | Suitable for large block trades to reduce price slippage. | Flexible order sizes; often less cost-effective for large orders. |
| Regulation | Less regulated compared to traditional exchanges. | Highly regulated by authorities like SEC and FINRA. |
| Price Discovery | Limited price discovery due to lack of public quotes. | Strong price discovery from transparent order book. |
Which is better?
Dark pool routing offers increased privacy and reduced market impact by executing large orders away from public exchanges, minimizing price slippage. Exchange routing provides greater transparency and immediate liquidity, benefiting traders seeking real-time price discovery and regulatory oversight. The optimal choice depends on trade size, urgency, and the trader's priority between anonymity and execution speed.
Connection
Dark pool routing and exchange routing connect through order execution strategies where dark pool routing directs large, non-displayed orders to private trading venues to minimize market impact, while exchange routing sends orders to public exchanges for transparency and price discovery. Both methods rely on algorithms that optimize trade execution by analyzing market liquidity, price, and order size. Integrating these routing techniques helps institutional investors balance stealth with competitive pricing in their trading activities.
Key Terms
Order Flow
Exchange routing directs orders to public stock exchanges such as NYSE or NASDAQ, ensuring transparency and regulated price discovery. Dark pool routing sends orders to private liquidity venues where trades occur anonymously, minimizing market impact and preserving order confidentiality. Explore deeper into how each routing method influences order flow and trading strategies.
Liquidity
Exchange routing targets lit markets with transparent order books, providing visible liquidity and potentially tighter spreads for trading. Dark pool routing seeks hidden liquidity by matching orders within private venues, minimizing market impact and reducing information leakage. Explore the differences in liquidity access and trading strategies to optimize your order execution.
Market Transparency
Exchange routing offers high market transparency by executing orders on public exchanges where trade details are readily visible to all participants, promoting fair price discovery. Dark pool routing, in contrast, operates within private, non-transparent venues that shield trade sizes and prices, potentially reducing market impact but limiting visibility. Explore the nuances of these routing types to understand their impact on trading strategies and market transparency.
Source and External Links
Mail routing in Exchange Server - Learn Microsoft - Exchange Server routes messages by calculating the least-cost path through IP site links and connectors, considering message size limits and hop counts to determine the optimal routing path for delivery within or outside the organization.
Transport routing in Exchange hybrid deployments - Learn Microsoft - In Exchange hybrid deployments, inbound and outbound message routing is handled by on-premises and Exchange Online servers, with routing decisions based on mail recipient location and MX records to direct messages appropriately.
Part 4: RabbitMQ Exchanges, routing keys and bindings - CloudAMQP - Exchanges in messaging systems like RabbitMQ route messages to queues using routing keys and binding patterns, enabling selective message delivery based on matching routing rules.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com