A soft landing in the economy refers to a scenario where growth slows down gradually, avoiding a recession and maintaining stable employment and inflation rates. In contrast, a slump involves a sharp economic downturn characterized by rising unemployment, decreased consumer spending, and contracting GDP. Explore more to understand how these divergent economic outcomes impact markets and policy decisions.
Why it is important
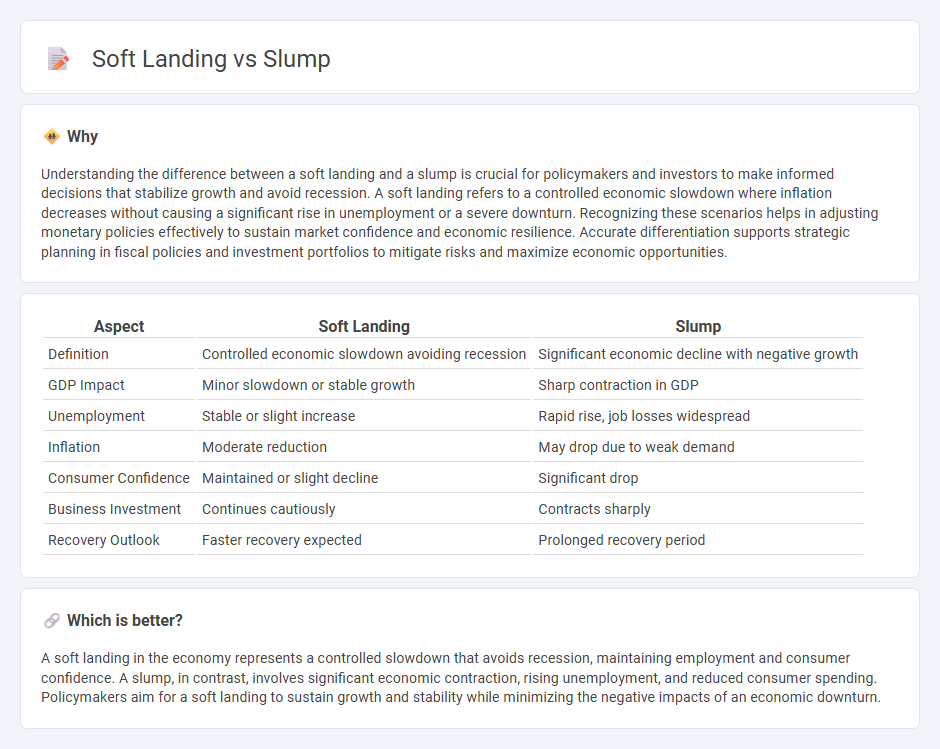
Understanding the difference between a soft landing and a slump is crucial for policymakers and investors to make informed decisions that stabilize growth and avoid recession. A soft landing refers to a controlled economic slowdown where inflation decreases without causing a significant rise in unemployment or a severe downturn. Recognizing these scenarios helps in adjusting monetary policies effectively to sustain market confidence and economic resilience. Accurate differentiation supports strategic planning in fiscal policies and investment portfolios to mitigate risks and maximize economic opportunities.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Soft Landing | Slump |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Controlled economic slowdown avoiding recession | Significant economic decline with negative growth |
| GDP Impact | Minor slowdown or stable growth | Sharp contraction in GDP |
| Unemployment | Stable or slight increase | Rapid rise, job losses widespread |
| Inflation | Moderate reduction | May drop due to weak demand |
| Consumer Confidence | Maintained or slight decline | Significant drop |
| Business Investment | Continues cautiously | Contracts sharply |
| Recovery Outlook | Faster recovery expected | Prolonged recovery period |
Which is better?
A soft landing in the economy represents a controlled slowdown that avoids recession, maintaining employment and consumer confidence. A slump, in contrast, involves significant economic contraction, rising unemployment, and reduced consumer spending. Policymakers aim for a soft landing to sustain growth and stability while minimizing the negative impacts of an economic downturn.
Connection
A soft landing in the economy refers to a gradual slowdown aimed at avoiding a severe recession, while a slump denotes a significant decline in economic activity characterized by high unemployment and reduced consumer spending. Policymakers strive for a soft landing to prevent the economy from slipping into a slump. Key indicators such as GDP growth rates, inflation levels, and unemployment figures help gauge the likelihood of transitioning from a soft landing to a slump.
Key Terms
Recession
A recession slump is characterized by a sharp and prolonged decline in economic activity, marked by significant drops in GDP, rising unemployment, and decreased consumer spending. A soft landing occurs when the economy slows down just enough to curb inflation without causing a severe contraction, maintaining steady growth and employment levels. Explore the key indicators and policy measures that distinguish a recession slump from a soft landing.
Monetary Policy
A monetary policy-induced slump occurs when aggressive interest rate hikes significantly reduce consumer spending and business investments, leading to a prolonged economic downturn and rising unemployment. In contrast, a soft landing is achieved by carefully calibrated monetary tightening that slows inflation without triggering a recession, maintaining stable growth and controlled inflation rates. Explore how central banks balance rate adjustments to steer economies toward soft landings rather than slumps.
Inflation
A slump refers to a deep and sustained economic downturn characterized by high unemployment and reduced consumer demand, often triggered by runaway inflation eroding purchasing power. A soft landing involves slowing inflation rates through monetary policy adjustments without tipping the economy into recession, balancing growth with price stability. Explore more to understand how inflation dynamics shape these contrasting economic outcomes.
Source and External Links
Slump (geology) - Wikipedia - In geology, a slump is a form of mass wasting where a coherent mass of loosely consolidated materials or rock slides a short distance down a slope, often along a concave-upward or planar surface.
SLUMP | definition in the Cambridge English Dictionary - As a verb, "slump" means to fall suddenly, such as when prices, values, or sales drop sharply, or to sit or fall in a loose, relaxed, or drooping way.
Slump - Etymology, Origin & Meaning - The word "slump" originates from the 1670s, probably from Scandinavian words meaning "to fall or sink suddenly," and later evolved to describe sudden declines in business or performance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com