Shrinkflation occurs when companies reduce product size or quantity while maintaining the same price, effectively increasing the cost per unit for consumers. Greedflation refers to price hikes driven by companies exploiting market power or increased profits rather than genuine cost increases. Explore how these phenomena impact inflation dynamics and consumer spending patterns.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between shrinkflation and greedflation is crucial for accurate economic analysis and consumer protection. Shrinkflation involves reducing product size while maintaining price, subtly impacting purchasing power and inflation measurements. Greedflation occurs when businesses increase prices beyond cost rises to boost profits, affecting market fairness and economic stability. Recognizing these distinctions helps policymakers devise targeted interventions and safeguards against inflationary pressures.
Comparison Table
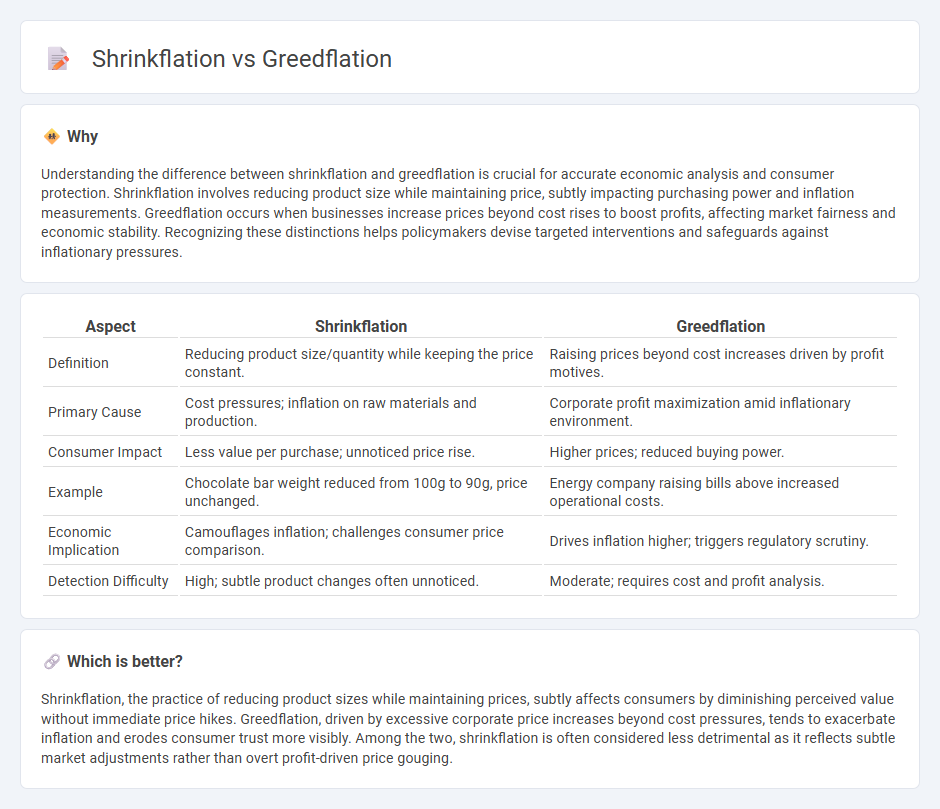
| Aspect | Shrinkflation | Greedflation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reducing product size/quantity while keeping the price constant. | Raising prices beyond cost increases driven by profit motives. |
| Primary Cause | Cost pressures; inflation on raw materials and production. | Corporate profit maximization amid inflationary environment. |
| Consumer Impact | Less value per purchase; unnoticed price rise. | Higher prices; reduced buying power. |
| Example | Chocolate bar weight reduced from 100g to 90g, price unchanged. | Energy company raising bills above increased operational costs. |
| Economic Implication | Camouflages inflation; challenges consumer price comparison. | Drives inflation higher; triggers regulatory scrutiny. |
| Detection Difficulty | High; subtle product changes often unnoticed. | Moderate; requires cost and profit analysis. |
Which is better?
Shrinkflation, the practice of reducing product sizes while maintaining prices, subtly affects consumers by diminishing perceived value without immediate price hikes. Greedflation, driven by excessive corporate price increases beyond cost pressures, tends to exacerbate inflation and erodes consumer trust more visibly. Among the two, shrinkflation is often considered less detrimental as it reflects subtle market adjustments rather than overt profit-driven price gouging.
Connection
Shrinkflation and greedflation are interconnected economic phenomena impacting consumer prices and purchasing power. Shrinkflation involves reducing product sizes while keeping prices constant, often masking inflation, whereas greedflation reflects businesses deliberately raising prices to increase profit margins beyond cost pressures. Both contribute to rising living costs and erode consumer confidence, highlighting challenges in inflation measurement and economic policy.
Key Terms
Profit Margins
Greedflation refers to price increases driven by companies exploiting market power to boost profit margins beyond cost pressures, while shrinkflation involves reducing product size or quantity to maintain prices and protect profits. Both strategies aim to maximize profitability amidst inflationary environments but differ in consumer perception and impact on brand trust. Explore detailed analyses to understand how these pricing tactics influence long-term profit margins and consumer behavior.
Pricing Strategies
Greedflation occurs when companies raise prices excessively beyond cost increases to maximize profits, while shrinkflation involves reducing product size or quantity while maintaining prices to mask inflation effects. Both pricing strategies impact consumer perception and purchasing power differently, influencing market dynamics and brand loyalty. Explore how these tactics shape economic behavior and affect your spending choices.
Consumer Purchasing Power
Greedflation, driven by excessive corporate profit margins, and shrinkflation, where product sizes decrease while prices remain constant, both erode consumer purchasing power by increasing the effective cost of goods. These inflationary pressures reduce household budgets and limit the ability to acquire essential goods and services. Explore how understanding the nuances of greedflation versus shrinkflation can help consumers better navigate rising costs and protect their financial well-being.
Source and External Links
What is greedflation - and is it driving higher prices? - Greedflation is the idea that corporations exploit inflation to create excessive profits by raising prices beyond cost increases, though some economists argue inflation is primarily due to supply shortages rather than corporate greed.
What is greedflation: The viral financial term explained - Greedflation refers to corporations intentionally increasing prices to boost profits, contributing to inflation and affecting costs of essentials like education and family goods globally, with debates ongoing about its current impact and regulation.
Greedflation in the US and UK | NEB Digest - U.S. President Biden has focused on tackling greedflation, linking corporate price gouging to rising inflation, a concern also present in the UK due to market concentration and monopoly power in sectors like energy and food raising prices for lower-income households.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com