Greenflation refers to the rising costs associated with the transition to environmentally sustainable energy and production methods, driven by increased demand for raw materials like lithium and cobalt. Skimpflation occurs when companies reduce the quality or quantity of goods and services to cope with rising expenses without raising prices significantly. Explore the nuances of greenflation and skimpflation to understand their distinct impacts on the global economy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between greenflation and skimpflation is crucial for policymakers and investors to develop effective economic strategies that balance environmental goals with consumer welfare. Greenflation refers to inflation driven by increased costs of eco-friendly goods and services, while skimpflation involves reduced product quality or service levels as a response to rising costs. Accurate identification helps in tailoring fiscal policies and inflation control measures to either support sustainable development or maintain consumer satisfaction. This distinction impacts decisions on taxation, subsidies, and supply chain adjustments vital for economic stability.
Comparison Table
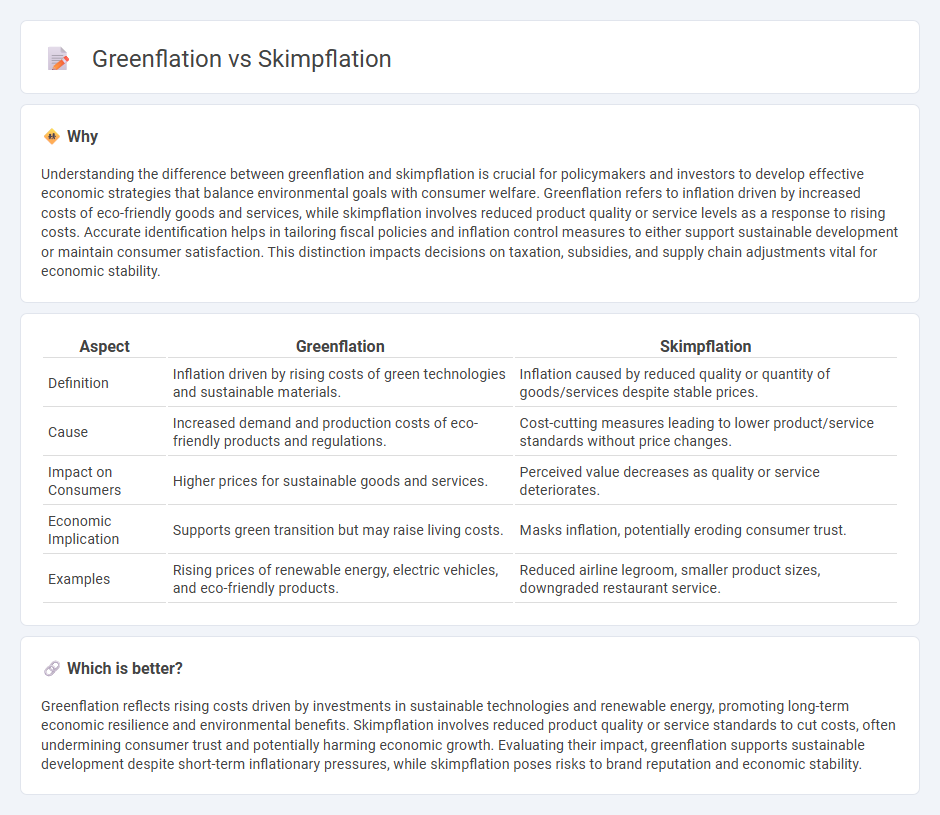
| Aspect | Greenflation | Skimpflation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inflation driven by rising costs of green technologies and sustainable materials. | Inflation caused by reduced quality or quantity of goods/services despite stable prices. |
| Cause | Increased demand and production costs of eco-friendly products and regulations. | Cost-cutting measures leading to lower product/service standards without price changes. |
| Impact on Consumers | Higher prices for sustainable goods and services. | Perceived value decreases as quality or service deteriorates. |
| Economic Implication | Supports green transition but may raise living costs. | Masks inflation, potentially eroding consumer trust. |
| Examples | Rising prices of renewable energy, electric vehicles, and eco-friendly products. | Reduced airline legroom, smaller product sizes, downgraded restaurant service. |
Which is better?
Greenflation reflects rising costs driven by investments in sustainable technologies and renewable energy, promoting long-term economic resilience and environmental benefits. Skimpflation involves reduced product quality or service standards to cut costs, often undermining consumer trust and potentially harming economic growth. Evaluating their impact, greenflation supports sustainable development despite short-term inflationary pressures, while skimpflation poses risks to brand reputation and economic stability.
Connection
Greenflation and skimpflation are connected through their impact on consumer prices and economic behavior during periods of rising costs. Greenflation occurs when the transition to environmentally sustainable practices increases production expenses, leading to higher prices for eco-friendly goods and services. Skimpflation, on the other hand, arises when companies reduce product quality or service levels to offset increased costs, affecting consumer satisfaction and overall market dynamics.
Key Terms
Consumer Experience
Skimpflation refers to the reduction in product quality or quantity while maintaining prices, directly affecting consumer satisfaction and perceived value. Greenflation involves rising prices driven by the increased costs of sustainable and eco-friendly production methods, impacting consumer purchasing power and experience. Explore how these inflation types shape modern consumer behavior and market trends to better understand their implications.
Environmental Policy
Skimpflation refers to the reduction in product quality or quantity as businesses try to cut costs, often impacting consumer satisfaction, while greenflation involves rising prices driven by environmental policies encouraging sustainable practices and carbon reduction. Environmental policies aimed at mitigating climate change contribute to greenflation by increasing production costs for carbon-intensive goods and incentivizing renewable energy adoption. Explore how evolving environmental regulations shape inflation dynamics and consumer markets.
Production Costs
Skimpflation occurs when businesses reduce product quality or quantity to offset rising production costs without increasing prices, whereas greenflation reflects the increased expenses linked to adopting environmentally friendly materials and sustainable energy sources. Both phenomena impact supply chain management and consumer pricing strategies, influencing inflation dynamics in various industries. Explore how these cost pressures uniquely affect your sector by learning more about skimpflation and greenflation.
Source and External Links
Beyond Inflation Numbers: Shrinkflation and Skimpflation - Skimpflation is when businesses maintain prices but reduce product or service quality, such as customers performing tasks previously done by staff, to remain profitable during inflation.
Shrinkflation - Wikipedia - Skimpflation refers to a reduction in product quality through reformulation or cheaper ingredients, distinct from shrinkflation, which is reducing package size at the same price point.
Inflation, Shrinkflation, Skimpflation, and Excuseflation: What You Need to Know - Skimpflation occurs when companies cut back on the quality or features of a product while keeping prices unchanged, often as a response to cost pressures rather than raising consumer prices.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com