Greenflation refers to rising prices driven by the increased costs of environmentally sustainable products and practices, impacting sectors like energy and agriculture. Shrinkflation occurs when product sizes are reduced while prices remain constant, subtly influencing consumer purchasing power. Explore deeper insights into how these phenomena affect global economic trends and consumer behavior.
Why it is important
Understanding greenflation and shrinkflation is crucial for accurately assessing economic inflation drivers and consumer price impacts. Greenflation refers to rising costs due to environmental policies and sustainable practices, while shrinkflation involves reducing product sizes to mask price increases. This knowledge helps policymakers design targeted fiscal strategies and businesses adjust pricing transparently. Consumers benefit by making informed purchasing decisions amidst evolving market conditions.
Comparison Table
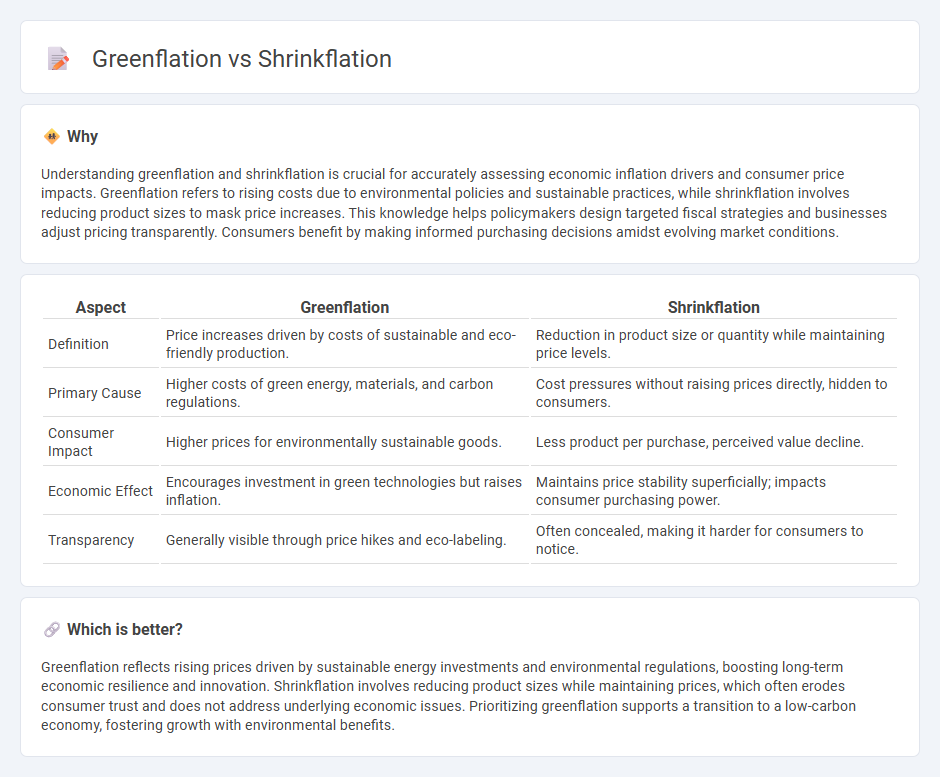
| Aspect | Greenflation | Shrinkflation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Price increases driven by costs of sustainable and eco-friendly production. | Reduction in product size or quantity while maintaining price levels. |
| Primary Cause | Higher costs of green energy, materials, and carbon regulations. | Cost pressures without raising prices directly, hidden to consumers. |
| Consumer Impact | Higher prices for environmentally sustainable goods. | Less product per purchase, perceived value decline. |
| Economic Effect | Encourages investment in green technologies but raises inflation. | Maintains price stability superficially; impacts consumer purchasing power. |
| Transparency | Generally visible through price hikes and eco-labeling. | Often concealed, making it harder for consumers to notice. |
Which is better?
Greenflation reflects rising prices driven by sustainable energy investments and environmental regulations, boosting long-term economic resilience and innovation. Shrinkflation involves reducing product sizes while maintaining prices, which often erodes consumer trust and does not address underlying economic issues. Prioritizing greenflation supports a transition to a low-carbon economy, fostering growth with environmental benefits.
Connection
Greenflation and shrinkflation are interconnected through rising production costs that drive price adjustments in consumer goods. Greenflation occurs as eco-friendly regulations and sustainable materials increase manufacturing expenses, while shrinkflation happens when companies reduce product sizes to maintain price points amid those cost pressures. Both phenomena reflect businesses' strategies to manage inflationary effects without directly raising prices, impacting overall economic inflation metrics.
Key Terms
Consumer Prices
Shrinkflation involves reducing product quantity or size while maintaining prices, subtly increasing the unit cost for consumers. Greenflation refers to the rise in prices driven by environmental regulations, renewable energy investments, and sustainable production costs impacting goods and services. Explore the detailed effects of shrinkflation and greenflation on consumer prices and purchasing power.
Production Costs
Shrinkflation reduces product size while maintaining price, driven by increasing raw material and packaging costs, forcing manufacturers to subtly pass on expenses without direct price hikes. Greenflation arises from integrating sustainable practices and eco-friendly materials into production, leading to higher operational costs due to investments in renewable energy, carbon compliance, and environmentally responsible sourcing. Explore the nuances of shrinkflation and greenflation to understand their distinct impacts on production costs and pricing strategies.
Inflation Drivers
Shrinkflation involves the reduction of product size or quantity while maintaining price, driving inflation by masking real price increases. Greenflation stems from higher production costs due to environmental regulations and sustainable sourcing, leading to increased prices in eco-friendly goods. Explore these inflation drivers in detail to understand their impact on the economy.
Source and External Links
Shrinkflation | EBSCO Research Starters - Shrinkflation is an economic phenomenon where companies reduce the size or quantity of a product while maintaining its price, acting as a hidden form of inflation to increase profits without obvious price hikes to consumers.
Shrinkflation - Wikipedia - Shrinkflation, also known as package downsizing, is when product size or quantity shrinks but the price stays the same, allowing manufacturers to manage rising production costs while maintaining sales and profitability.
The Unstoppable Rise of Shrinkflation - Shrinkflation has become a widespread cost-management strategy, accelerated by pandemic supply chain issues, with many common groceries shrinking in size while prices remain steady or slightly increased.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com