Ghost kitchen expansion drives significant growth in the virtual dining sector by leveraging low overhead and digital ordering platforms, boosting overall market efficiency. Local food hubs enhance community-based economies by facilitating direct farm-to-consumer distribution, promoting sustainability and reducing food miles. Explore how these contrasting models reshape economic landscapes and consumer habits in the evolving food industry.
Why it is important
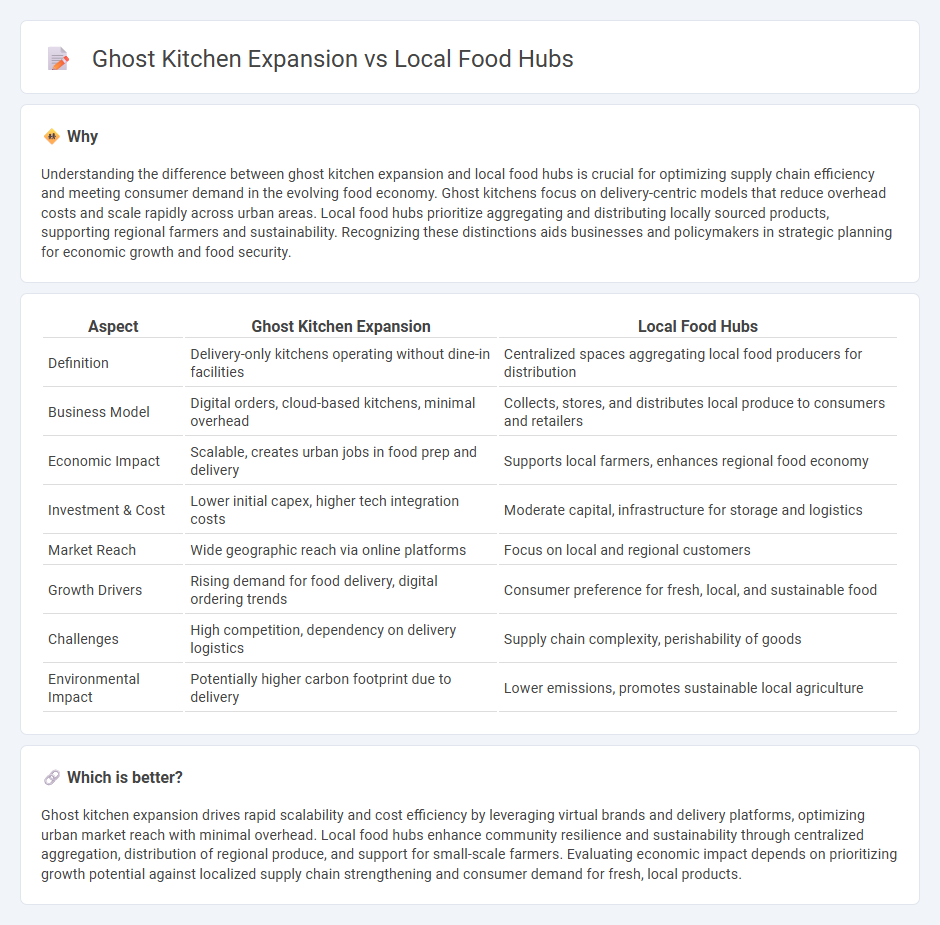
Understanding the difference between ghost kitchen expansion and local food hubs is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and meeting consumer demand in the evolving food economy. Ghost kitchens focus on delivery-centric models that reduce overhead costs and scale rapidly across urban areas. Local food hubs prioritize aggregating and distributing locally sourced products, supporting regional farmers and sustainability. Recognizing these distinctions aids businesses and policymakers in strategic planning for economic growth and food security.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ghost Kitchen Expansion | Local Food Hubs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Delivery-only kitchens operating without dine-in facilities | Centralized spaces aggregating local food producers for distribution |
| Business Model | Digital orders, cloud-based kitchens, minimal overhead | Collects, stores, and distributes local produce to consumers and retailers |
| Economic Impact | Scalable, creates urban jobs in food prep and delivery | Supports local farmers, enhances regional food economy |
| Investment & Cost | Lower initial capex, higher tech integration costs | Moderate capital, infrastructure for storage and logistics |
| Market Reach | Wide geographic reach via online platforms | Focus on local and regional customers |
| Growth Drivers | Rising demand for food delivery, digital ordering trends | Consumer preference for fresh, local, and sustainable food |
| Challenges | High competition, dependency on delivery logistics | Supply chain complexity, perishability of goods |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially higher carbon footprint due to delivery | Lower emissions, promotes sustainable local agriculture |
Which is better?
Ghost kitchen expansion drives rapid scalability and cost efficiency by leveraging virtual brands and delivery platforms, optimizing urban market reach with minimal overhead. Local food hubs enhance community resilience and sustainability through centralized aggregation, distribution of regional produce, and support for small-scale farmers. Evaluating economic impact depends on prioritizing growth potential against localized supply chain strengthening and consumer demand for fresh, local products.
Connection
Ghost kitchen expansion drives demand for efficient local food hubs by enabling rapid meal preparation and delivery in urban areas, reducing reliance on traditional restaurants. Local food hubs streamline supply chains by aggregating and distributing fresh, locally sourced ingredients to ghost kitchens, enhancing quality and sustainability. This synergy supports economic growth by creating new jobs and optimizing food distribution networks within the evolving food service industry.
Key Terms
Supply Chain
Local food hubs enhance supply chain efficiency by aggregating produce from multiple farmers, reducing transportation costs, and ensuring fresher, higher-quality products for consumers. Ghost kitchens streamline supply chains through centralized production and delivery operations, minimizing overhead and enabling rapid scaling to meet urban demand. Explore how these models transform food distribution and delivery logistics for a deeper understanding.
Market Access
Local food hubs improve market access by aggregating products from multiple small producers, enabling streamlined distribution to broader consumer bases and retail channels. Ghost kitchens expand market reach by minimizing overhead and leveraging digital platforms for delivery, allowing rapid scalability and penetration into urban food markets. Explore the comparative benefits of local food hubs and ghost kitchens in enhancing market access for food entrepreneurs.
Operational Efficiency
Local food hubs enhance operational efficiency by streamlining supply chains, reducing delivery times, and fostering direct relationships between producers and consumers. Ghost kitchens optimize kitchen utilization and lower overhead costs by focusing solely on delivery orders, enabling rapid scalability in urban areas. Explore the comparative advantages of these models to identify which operational strategy suits your business goals best.
Source and External Links
Food Hubs & Values-Based Supply Chains - Food hubs are business or organizations that aggregate, distribute, and market locally sourced food products, offering small to medium-scale farmers better market access and transportation efficiency, with a strong growth trend in the US, including around 20 hubs in California as of 2017.
Food Hubs - Healthy Food Access Portal - Food hubs serve as bridges between food producers and consumers to support local agricultural economies and provide fresh, affordable food; examples include the Common Market in Philadelphia and Corbin Hill Food Project in NYC, which tailor offerings to community needs.
Local Food Directories - Agricultural Marketing Service - USDA - USDA provides directories to find and list local food hubs, farmers markets, and producers to facilitate the marketing and distribution of local foods for both consumers and wholesale buyers across the US.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com