Girl math focuses on practical budgeting and everyday financial decisions, emphasizing intuitive spending habits and value assessment. Student math involves abstract problem-solving and theoretical concepts, concentrating on numeric accuracy and formula application. Explore deeper insights into how these approaches influence economic understanding and personal finance skills.
Why it is important
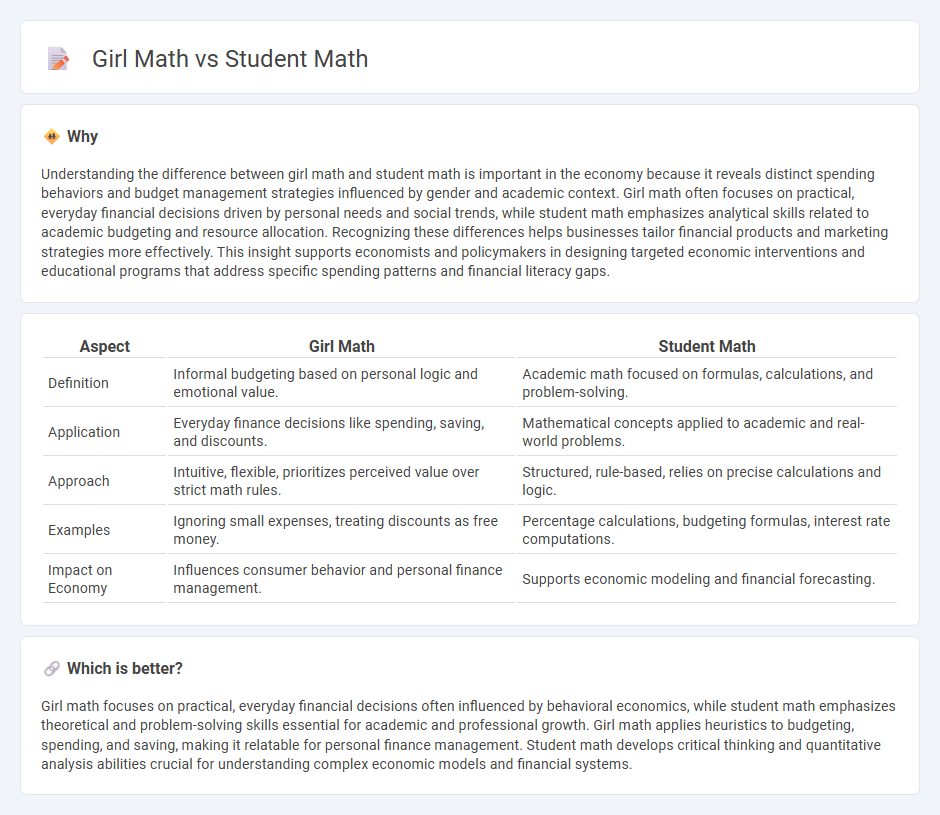
Understanding the difference between girl math and student math is important in the economy because it reveals distinct spending behaviors and budget management strategies influenced by gender and academic context. Girl math often focuses on practical, everyday financial decisions driven by personal needs and social trends, while student math emphasizes analytical skills related to academic budgeting and resource allocation. Recognizing these differences helps businesses tailor financial products and marketing strategies more effectively. This insight supports economists and policymakers in designing targeted economic interventions and educational programs that address specific spending patterns and financial literacy gaps.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Girl Math | Student Math |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Informal budgeting based on personal logic and emotional value. | Academic math focused on formulas, calculations, and problem-solving. |
| Application | Everyday finance decisions like spending, saving, and discounts. | Mathematical concepts applied to academic and real-world problems. |
| Approach | Intuitive, flexible, prioritizes perceived value over strict math rules. | Structured, rule-based, relies on precise calculations and logic. |
| Examples | Ignoring small expenses, treating discounts as free money. | Percentage calculations, budgeting formulas, interest rate computations. |
| Impact on Economy | Influences consumer behavior and personal finance management. | Supports economic modeling and financial forecasting. |
Which is better?
Girl math focuses on practical, everyday financial decisions often influenced by behavioral economics, while student math emphasizes theoretical and problem-solving skills essential for academic and professional growth. Girl math applies heuristics to budgeting, spending, and saving, making it relatable for personal finance management. Student math develops critical thinking and quantitative analysis abilities crucial for understanding complex economic models and financial systems.
Connection
Girl Math and Student Math both explore cognitive approaches to economic decision-making and budgeting, highlighting how individuals rationalize spending and saving behaviors. These concepts reveal psychological patterns that influence financial literacy, emphasizing gender and age-related differences in interpreting value and managing resources. Understanding these relationships enhances economic education by tailoring strategies to diverse mental models of money management.
Key Terms
Opportunity Cost
Student math emphasizes calculating opportunity cost by comparing quantifiable academic outcomes, such as grades and study time efficiency. Girl math often frames opportunity cost in practical, everyday scenarios, like budgeting or decision-making, blending emotional value with financial implications. Explore how these distinct perspectives shape decision-making strategies in various contexts.
Budgeting
Student math emphasizes strict numerical calculations and algebraic concepts to manage budgets, focusing on exact figures and cost analysis. Girl math, often characterized by intuitive spending strategies and mental accounting, highlights creative budgeting techniques and prioritization based on personal values. Discover more effective budgeting approaches by exploring the contrasts and applications of student math and girl math.
Consumer Behavior
Student math emphasizes logical problem-solving and numerical accuracy, often applied in academic contexts, while girl math explores consumer behavior through a playful, relatable lens highlighting spending habits and mental accounting. Consumer behavior in girl math involves understanding psychological triggers, budgeting strategies, and emotional purchasing influences that differ from traditional financial models. Discover more about how these perspectives transform insights into consumer decision-making and spending patterns.
Source and External Links
First In Math - An online math practice tool using gaming to build math skills and engagement for K-8 students.
Prodigy Math - A free math learning game that practices standards-aligned skills, supported by teacher and parent tools.
ST Math - A K-8 supplemental math program using visual, game-based learning grounded in neuroscience to build conceptual understanding.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com