Resilient supply chains prioritize flexibility, local sourcing, and risk mitigation to withstand disruptions such as geopolitical tensions and natural disasters, unlike offshored supply chains that often focus on cost reduction through global outsourcing but face vulnerabilities from distant production hubs. Companies investing in resilient supply chains are better positioned to maintain continuous operations and meet shifting consumer demands during crises. Explore further to understand how businesses are balancing efficiency and robustness in their supply chain strategies.
Why it is important
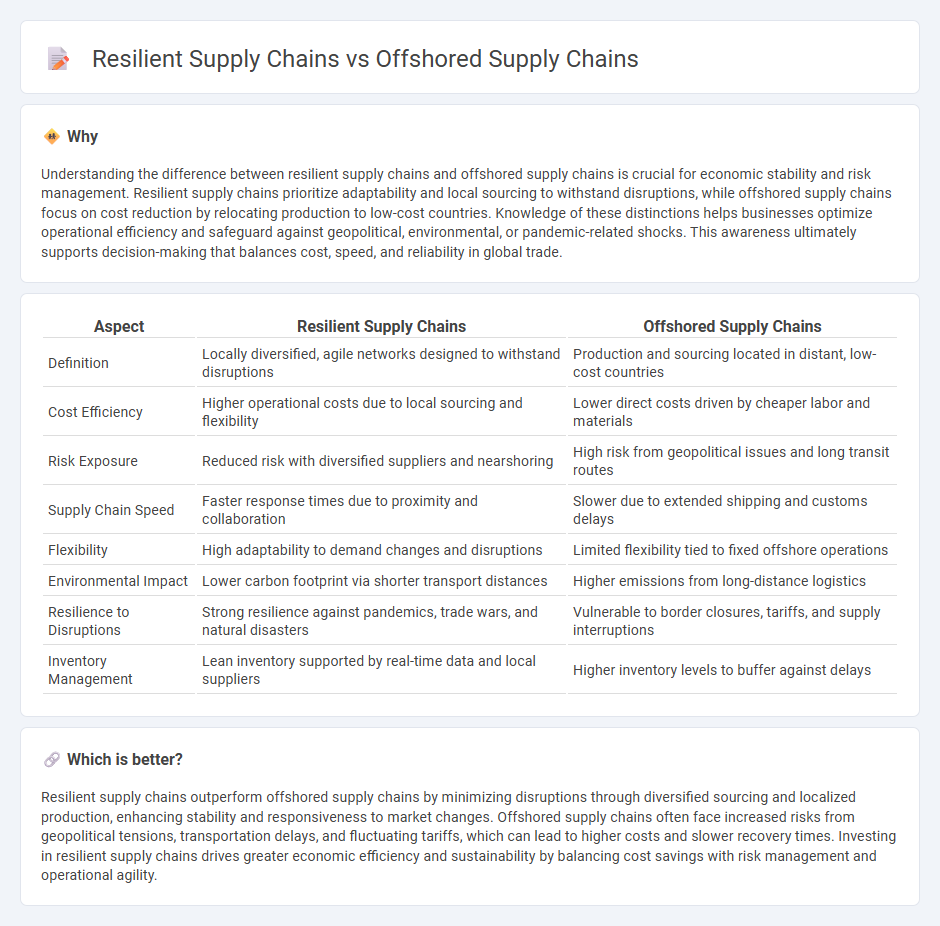
Understanding the difference between resilient supply chains and offshored supply chains is crucial for economic stability and risk management. Resilient supply chains prioritize adaptability and local sourcing to withstand disruptions, while offshored supply chains focus on cost reduction by relocating production to low-cost countries. Knowledge of these distinctions helps businesses optimize operational efficiency and safeguard against geopolitical, environmental, or pandemic-related shocks. This awareness ultimately supports decision-making that balances cost, speed, and reliability in global trade.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Resilient Supply Chains | Offshored Supply Chains |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Locally diversified, agile networks designed to withstand disruptions | Production and sourcing located in distant, low-cost countries |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher operational costs due to local sourcing and flexibility | Lower direct costs driven by cheaper labor and materials |
| Risk Exposure | Reduced risk with diversified suppliers and nearshoring | High risk from geopolitical issues and long transit routes |
| Supply Chain Speed | Faster response times due to proximity and collaboration | Slower due to extended shipping and customs delays |
| Flexibility | High adaptability to demand changes and disruptions | Limited flexibility tied to fixed offshore operations |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint via shorter transport distances | Higher emissions from long-distance logistics |
| Resilience to Disruptions | Strong resilience against pandemics, trade wars, and natural disasters | Vulnerable to border closures, tariffs, and supply interruptions |
| Inventory Management | Lean inventory supported by real-time data and local suppliers | Higher inventory levels to buffer against delays |
Which is better?
Resilient supply chains outperform offshored supply chains by minimizing disruptions through diversified sourcing and localized production, enhancing stability and responsiveness to market changes. Offshored supply chains often face increased risks from geopolitical tensions, transportation delays, and fluctuating tariffs, which can lead to higher costs and slower recovery times. Investing in resilient supply chains drives greater economic efficiency and sustainability by balancing cost savings with risk management and operational agility.
Connection
Resilient supply chains often incorporate strategic offshoring to balance cost-efficiency with risk management, enabling companies to quickly adapt to global disruptions. Offshored supply chains diversify sourcing locations, mitigating the impact of regional disturbances on production continuity. This interconnected approach enhances overall supply chain robustness by combining geographic flexibility with optimized resource allocation.
Key Terms
Globalization
Offshored supply chains optimize cost and efficiency by leveraging global labor markets and production hubs, yet introduce vulnerabilities through geopolitical risks and transportation delays. Resilient supply chains emphasize diversification, local sourcing, and adaptive capacity to withstand disruptions inherent in globalized networks. Explore how businesses balance globalization with supply chain resilience to sustain competitive advantage.
Risk mitigation
Offshored supply chains often face higher risks from geopolitical instability, transportation disruptions, and extended lead times, making risk mitigation complex and costly. Resilient supply chains emphasize diversification, local sourcing, and real-time monitoring to minimize vulnerabilities and ensure continuity during unexpected disruptions. Explore effective strategies to enhance supply chain resilience and safeguard your operations against global risks.
Diversification
Offshored supply chains often rely on cost advantages by concentrating production in specific regions, increasing vulnerability to disruptions such as geopolitical tensions and natural disasters. In contrast, resilient supply chains emphasize diversification by sourcing materials and manufacturing across multiple locations and suppliers, reducing risk and enhancing adaptability. Explore further insights on how strategic diversification strengthens supply chain resilience in a global market.
Source and External Links
Are We Seeing an End to the Age of Offshore Production? - Offshore supply chains, particularly for U.S. manufacturers, are decreasing as companies shift toward nearshoring and domestic production to reduce reliance on China, with Mexico becoming a favored nearshoring destination and offshore production expected to drop significantly in the next few years.
Keeping Offshore Assets Afloat - Offshore supply chains face unique challenges like limited storage and transport capacity, with logistics costs accounting for 10-15% of offshore facility operating costs, especially in sectors such as oil and gas where marine transport is predominant.
Supply Chain Road Map for Offshore Wind Energy in the U.S. - Developing a robust domestic offshore wind supply chain requires significant investment and infrastructure expansion with an expected timeline of 6-9 years, potentially creating thousands of jobs while still relying on some imports to meet targets.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com