Friendshoring focuses on relocating supply chains to allied nations to enhance geopolitical stability and reduce risks, while onshoring emphasizes bringing production back to a company's home country to boost local employment and control. Both strategies aim to secure supply chains but differ in terms of geographic and political considerations. Explore further to understand how these approaches impact global trade and economic resilience.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between friendshoring and onshoring is crucial for optimizing supply chain resilience and geopolitical risk management. Friendshoring focuses on relocating production to allied countries, enhancing security and collaboration, while onshoring involves bringing manufacturing back to the domestic country, promoting local economic growth and job creation. Businesses can leverage these strategies to mitigate disruptions from global conflicts and trade restrictions. Clear knowledge supports informed decisions that balance cost, security, and economic impact.
Comparison Table
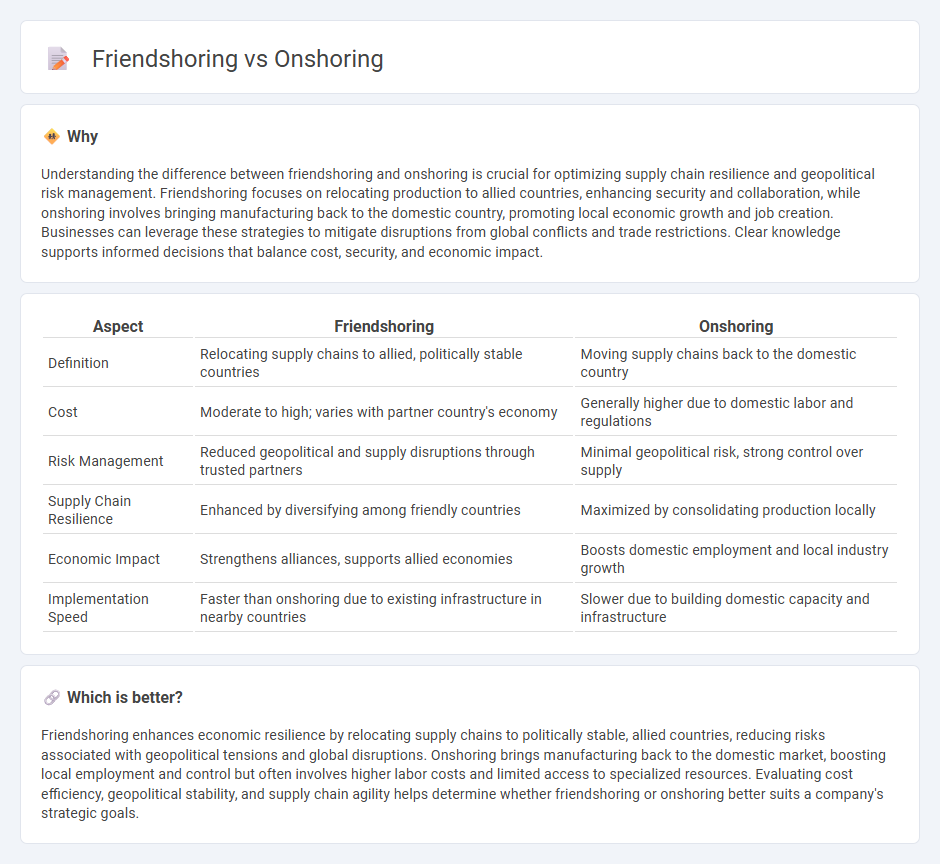
| Aspect | Friendshoring | Onshoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Relocating supply chains to allied, politically stable countries | Moving supply chains back to the domestic country |
| Cost | Moderate to high; varies with partner country's economy | Generally higher due to domestic labor and regulations |
| Risk Management | Reduced geopolitical and supply disruptions through trusted partners | Minimal geopolitical risk, strong control over supply |
| Supply Chain Resilience | Enhanced by diversifying among friendly countries | Maximized by consolidating production locally |
| Economic Impact | Strengthens alliances, supports allied economies | Boosts domestic employment and local industry growth |
| Implementation Speed | Faster than onshoring due to existing infrastructure in nearby countries | Slower due to building domestic capacity and infrastructure |
Which is better?
Friendshoring enhances economic resilience by relocating supply chains to politically stable, allied countries, reducing risks associated with geopolitical tensions and global disruptions. Onshoring brings manufacturing back to the domestic market, boosting local employment and control but often involves higher labor costs and limited access to specialized resources. Evaluating cost efficiency, geopolitical stability, and supply chain agility helps determine whether friendshoring or onshoring better suits a company's strategic goals.
Connection
Friendshoring and onshoring both aim to enhance supply chain resilience by relocating production closer to home or to politically aligned countries. These strategies reduce dependency on distant or unstable regions, thereby minimizing risks from geopolitical tensions and trade disruptions. Companies leveraging friendshoring and onshoring benefit from improved control, faster delivery times, and strengthened economic security.
Key Terms
Supply chain resilience
Onshoring enhances supply chain resilience by relocating production closer to the end market, reducing lead times and minimizing reliance on foreign suppliers, which mitigates risks from geopolitical disruptions. Friendshoring prioritizes sourcing from allied or politically stable countries, balancing cost efficiency with reduced vulnerability to international trade conflicts while maintaining diversified supply networks. Explore the strategic benefits of onshoring and friendshoring to optimize supply chain resilience in your business operations.
Geopolitical risk
Onshoring reduces geopolitical risk by relocating production closer to a company's home country, minimizing exposure to international trade conflicts and unstable foreign policies. Friendshoring involves sourcing from allied or politically stable countries, maintaining supply chain resilience while supporting trusted economic partners. Explore how strategic decisions between onshoring and friendshoring can safeguard your business from geopolitical disruptions.
Domestic production
Onshoring emphasizes shifting production back to domestic facilities to enhance supply chain resilience, reduce transportation costs, and support local economies. Friendshoring involves relocating manufacturing to politically stable and allied nations, balancing security with global diversification. Explore how these strategies impact domestic production and economic growth.
Source and External Links
Reshoring, nearshoring, friendshoring, onshoring, and ... - Onshoring is moving part or all of a business's operations, like manufacturing or services, back to a company's home country, allowing for easier management and control of processes while supporting local labor markets and minimizing foreign risks.
What Is Onshoring? - Onshoring is sourcing or relocating production operations within domestic borders, distinct from reshoring (returning production from abroad) and nearshoring (moving to nearby countries), and is often used to regain supply chain control and avoid rising foreign costs.
What Is Onshoring? - Onshoring involves bringing sourcing and manufacturing operations back to a company's home country--sometimes called reshoring--driven by factors like international trade tensions, logistical delays, government incentives, and the desire for greater quality control.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com