Slowbalization reflects a global economic trend where international trade and investment growth decelerate, emphasizing regional supply chains and reducing dependency on distant markets. Localization focuses on strengthening domestic industries and local markets to boost resilience and economic stability amid geopolitical uncertainties and disrupted global networks. Explore how these contrasting strategies shape the future of global commerce and economic policies.
Why it is important
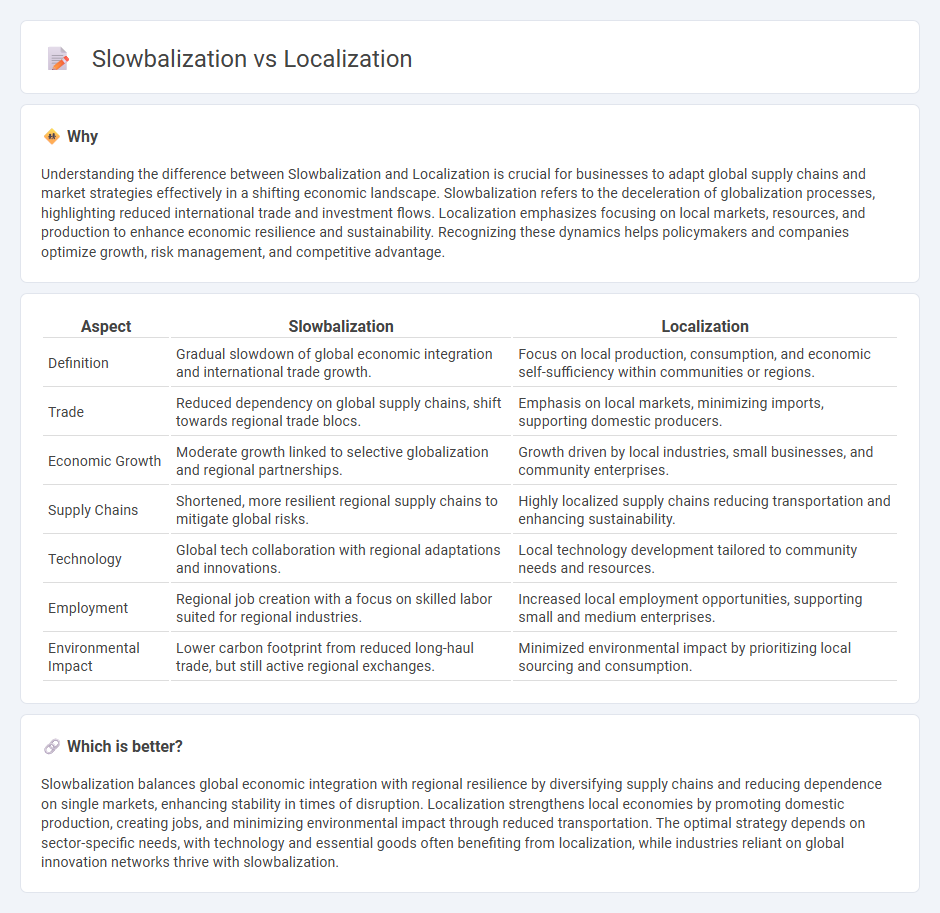
Understanding the difference between Slowbalization and Localization is crucial for businesses to adapt global supply chains and market strategies effectively in a shifting economic landscape. Slowbalization refers to the deceleration of globalization processes, highlighting reduced international trade and investment flows. Localization emphasizes focusing on local markets, resources, and production to enhance economic resilience and sustainability. Recognizing these dynamics helps policymakers and companies optimize growth, risk management, and competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Slowbalization | Localization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Gradual slowdown of global economic integration and international trade growth. | Focus on local production, consumption, and economic self-sufficiency within communities or regions. |
| Trade | Reduced dependency on global supply chains, shift towards regional trade blocs. | Emphasis on local markets, minimizing imports, supporting domestic producers. |
| Economic Growth | Moderate growth linked to selective globalization and regional partnerships. | Growth driven by local industries, small businesses, and community enterprises. |
| Supply Chains | Shortened, more resilient regional supply chains to mitigate global risks. | Highly localized supply chains reducing transportation and enhancing sustainability. |
| Technology | Global tech collaboration with regional adaptations and innovations. | Local technology development tailored to community needs and resources. |
| Employment | Regional job creation with a focus on skilled labor suited for regional industries. | Increased local employment opportunities, supporting small and medium enterprises. |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint from reduced long-haul trade, but still active regional exchanges. | Minimized environmental impact by prioritizing local sourcing and consumption. |
Which is better?
Slowbalization balances global economic integration with regional resilience by diversifying supply chains and reducing dependence on single markets, enhancing stability in times of disruption. Localization strengthens local economies by promoting domestic production, creating jobs, and minimizing environmental impact through reduced transportation. The optimal strategy depends on sector-specific needs, with technology and essential goods often benefiting from localization, while industries reliant on global innovation networks thrive with slowbalization.
Connection
Slowbalization and localization intersect by emphasizing regional supply chains and reducing dependence on global networks to enhance economic resilience. This shift encourages investment in local industries, fostering sustainable growth and mitigating risks associated with global disruptions. Businesses increasingly prioritize localized production to optimize efficiency and meet evolving consumer preferences.
Key Terms
Supply Chains
Localization emphasizes reshoring production and sourcing materials from nearby suppliers to reduce costs, enhance responsiveness, and mitigate risks in supply chains. Slowbalization reflects a shift towards regional trade hubs and diversified sourcing strategies to balance efficiency with resilience amid global uncertainties. Explore how these contrasting approaches reshape global supply chains and impact business strategies.
Trade Barriers
Localization emphasizes reducing trade barriers by promoting domestic production and protecting local industries, which can lead to increased tariffs and quotas to shield national markets. Slowbalization, characterized by a gradual slowdown in global trade growth, often results in moderate trade barriers as countries balance economic interdependence with strategic autonomy. Explore the detailed impacts of each approach on international trade dynamics and market access.
Regional Integration
Localization emphasizes strengthening local economies by prioritizing domestic production and consumption, reducing dependence on global supply chains. Slowbalization reflects a strategic shift towards regional integration, fostering trade agreements and cooperative frameworks within specific geographic areas to balance global interconnectivity and local resilience. Explore the dynamics of regional cooperation strategies and their impact on global trade to understand this evolving economic landscape.
Source and External Links
LOCALIZATION definition | Cambridge English Dictionary - Localization refers to the process of organizing business or industry activities locally rather than on a national or international scale, often involving cultural and language adaptations.
Localization (l10n): What It Is, and How to Build a Strategy? - This resource provides insights into the importance of localization, explaining it as adapting products to meet cultural, linguistic, legal, and other market requirements, and outlines a strategy to implement it.
What is localization? | Definition from TechTarget - Localization is the process of customizing a product to fit a specific market based on language, culture, expectations, and local standards, distinguishing it from mere translation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com