Soft saving emphasizes gradual accumulation of financial resources through consistent, low-risk investments focused on long-term stability and wealth preservation. Soft spending prioritizes controlled and mindful expenditures aimed at enhancing quality of life without compromising future financial security. Explore how balancing soft saving and soft spending strategies can optimize your economic well-being.
Why it is important
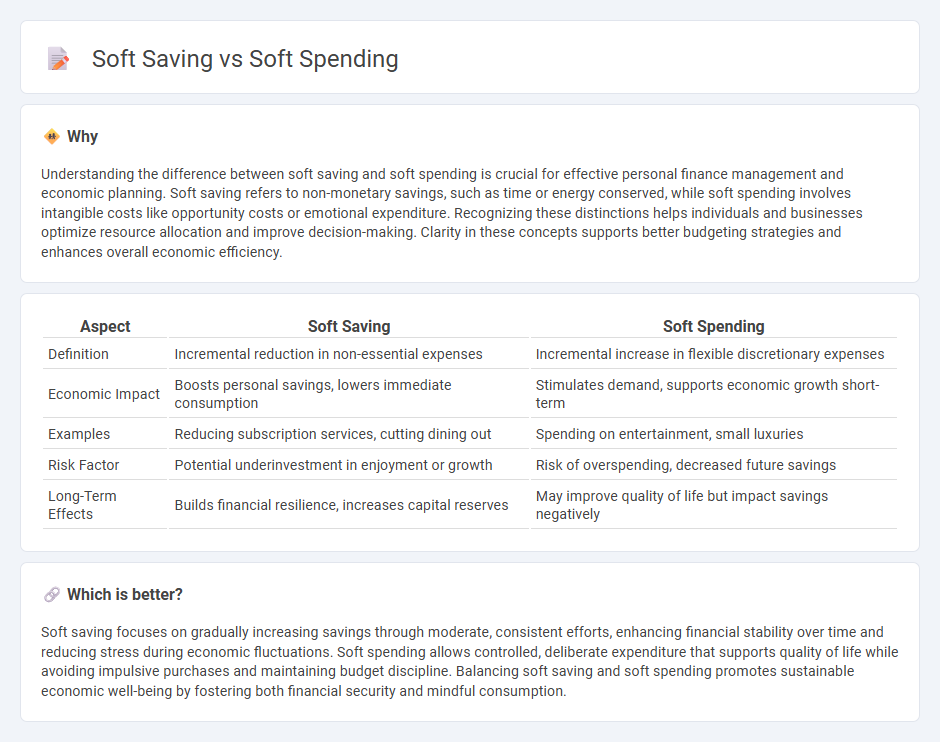
Understanding the difference between soft saving and soft spending is crucial for effective personal finance management and economic planning. Soft saving refers to non-monetary savings, such as time or energy conserved, while soft spending involves intangible costs like opportunity costs or emotional expenditure. Recognizing these distinctions helps individuals and businesses optimize resource allocation and improve decision-making. Clarity in these concepts supports better budgeting strategies and enhances overall economic efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Soft Saving | Soft Spending |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Incremental reduction in non-essential expenses | Incremental increase in flexible discretionary expenses |
| Economic Impact | Boosts personal savings, lowers immediate consumption | Stimulates demand, supports economic growth short-term |
| Examples | Reducing subscription services, cutting dining out | Spending on entertainment, small luxuries |
| Risk Factor | Potential underinvestment in enjoyment or growth | Risk of overspending, decreased future savings |
| Long-Term Effects | Builds financial resilience, increases capital reserves | May improve quality of life but impact savings negatively |
Which is better?
Soft saving focuses on gradually increasing savings through moderate, consistent efforts, enhancing financial stability over time and reducing stress during economic fluctuations. Soft spending allows controlled, deliberate expenditure that supports quality of life while avoiding impulsive purchases and maintaining budget discipline. Balancing soft saving and soft spending promotes sustainable economic well-being by fostering both financial security and mindful consumption.
Connection
Soft saving encourages gradual accumulation of funds by reducing impulsive expenditures, while soft spending focuses on mindful consumption that aligns with financial goals. Both strategies promote a balanced economy by enhancing personal financial stability, leading to increased consumer confidence and sustained economic growth. This interconnected approach helps mitigate market volatility and supports long-term investment opportunities.
Key Terms
Disposable Income
Soft spending refers to non-essential expenses that provide comfort or convenience, while soft saving focuses on incremental increases in disposable income by reducing these discretionary costs. Disposable income, the amount of money left after taxes and necessary expenses, plays a critical role in managing soft spending and soft saving habits. Explore how balancing these strategies can optimize your financial health and disposable income management.
Consumption
Soft spending emphasizes flexible, non-essential consumption that enhances lifestyle without significant financial commitment, often involving discretionary purchases like dining out or entertainment. In contrast, soft saving highlights gradual, less rigid financial accumulation strategies that prioritize small, consistent savings over time to support future consumption needs. Explore more about the balance between soft spending and soft saving to optimize your consumption habits and financial well-being.
Liquidity
Soft spending emphasizes moderate expenditure to maintain liquidity without depleting immediate cash flow, ensuring financial flexibility in uncertain markets. Soft saving involves reserving liquid assets incrementally, prioritizing accessibility and minimal risk over high returns, supporting short-term financial stability. Explore strategies to balance soft spending and soft saving for optimal liquidity management.
Source and External Links
What Is Soft Saving? - AAA - Soft spending, as part of the soft saving approach, involves prioritizing present enjoyment--such as hobbies, travel, and experiences--alongside meeting immediate needs and saving modestly for the future, aiming for a balance between financial security and quality of life.
The 'Soft Savings' Trend: What CFP(r) Professionals Should Know - The soft spending trend places value on present-day expenses like experiences and self-care, treating them as investments in well-being while maintaining an overall focus on future financial security, reflecting shifting priorities especially among younger generations.
The Purposes and Beneficiaries of Party "Soft Money" - In campaign finance, "soft money" refers to unregulated donations to political parties primarily spent on electioneering ads rather than direct voter mobilization, with the majority of contributions coming from business interests.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com