The circular economy focuses on resource efficiency by promoting reuse, recycling, and regeneration to minimize waste and environmental impact, contrasting with the linear economy's traditional 'take-make-dispose' model. Businesses adopting circular practices benefit from reduced costs, enhanced sustainability, and long-term economic growth. Explore how transitioning to a circular economy can drive innovation and resilience in global markets.
Why it is important
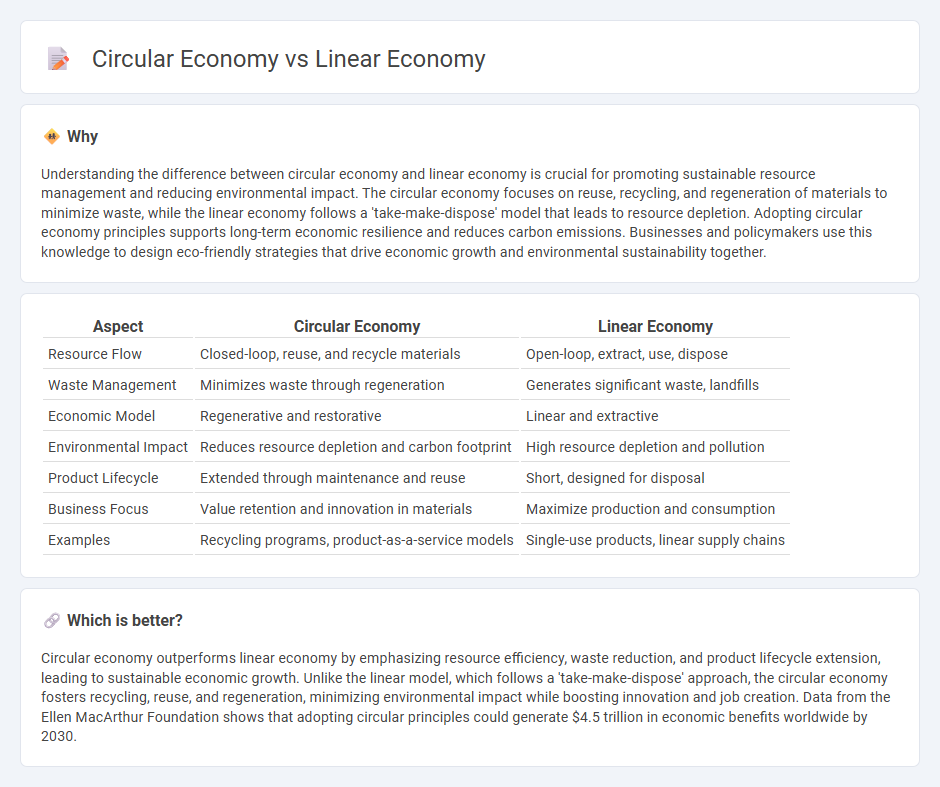
Understanding the difference between circular economy and linear economy is crucial for promoting sustainable resource management and reducing environmental impact. The circular economy focuses on reuse, recycling, and regeneration of materials to minimize waste, while the linear economy follows a 'take-make-dispose' model that leads to resource depletion. Adopting circular economy principles supports long-term economic resilience and reduces carbon emissions. Businesses and policymakers use this knowledge to design eco-friendly strategies that drive economic growth and environmental sustainability together.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Circular Economy | Linear Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Resource Flow | Closed-loop, reuse, and recycle materials | Open-loop, extract, use, dispose |
| Waste Management | Minimizes waste through regeneration | Generates significant waste, landfills |
| Economic Model | Regenerative and restorative | Linear and extractive |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces resource depletion and carbon footprint | High resource depletion and pollution |
| Product Lifecycle | Extended through maintenance and reuse | Short, designed for disposal |
| Business Focus | Value retention and innovation in materials | Maximize production and consumption |
| Examples | Recycling programs, product-as-a-service models | Single-use products, linear supply chains |
Which is better?
Circular economy outperforms linear economy by emphasizing resource efficiency, waste reduction, and product lifecycle extension, leading to sustainable economic growth. Unlike the linear model, which follows a 'take-make-dispose' approach, the circular economy fosters recycling, reuse, and regeneration, minimizing environmental impact while boosting innovation and job creation. Data from the Ellen MacArthur Foundation shows that adopting circular principles could generate $4.5 trillion in economic benefits worldwide by 2030.
Connection
Circular economy and linear economy are connected through their contrasting approaches to resource management, with the linear economy following a 'take-make-dispose' model, leading to waste generation, while the circular economy emphasizes recycling, reuse, and regeneration to minimize resource depletion. Transitioning from a linear to a circular economy involves redesigning products and processes to close material loops, thereby reducing environmental impact and enhancing economic sustainability. Effective integration of circular principles in traditionally linear systems fosters innovation, resource efficiency, and long-term economic resilience.
Key Terms
Resource extraction
Linear economy relies heavily on continuous resource extraction, leading to depletion of finite natural resources and environmental degradation. Circular economy minimizes resource extraction by emphasizing reuse, recycling, and sustainable design to create closed-loop systems that reduce waste. Explore how circular strategies can transform resource management and promote long-term environmental sustainability.
Waste generation
Linear economy generates significant waste due to its take-make-dispose model, leading to resource depletion and environmental pollution. Circular economy minimizes waste by promoting reuse, recycling, and sustainable resource management, enhancing material longevity and reducing landfill impact. Explore the benefits and strategies of circular economy to transform waste management effectively.
Product lifecycle
The linear economy follows a "take-make-dispose" model where raw materials are transformed into products and discarded after use, leading to significant waste and resource depletion. In contrast, the circular economy emphasizes product lifecycle extension through reuse, remanufacturing, recycling, and sustainable design, thereby reducing environmental impact and conserving resources. Discover how shifting to circular economy practices can innovate product lifecycle management and foster sustainability.
Source and External Links
Linear Economy: The Model of the Throwaway Society - The linear economy operates on a "Take-Make-Dispose" principle, emphasizing high resource consumption, short product lifecycles, and significant environmental impacts due to waste and pollution.
What is a Linear Economy? - A linear economy is a traditional system where raw materials are extracted, manufactured into products, consumed, and then discarded as waste, leading to resource depletion and environmental challenges.
Linear Economy Definition - Characterized by the "take-make-waste" model, the linear economy focuses on high production and consumption rates, resulting in excessive waste and environmental degradation without regard for long-term sustainability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com