Friendshoring involves relocating supply chains to trusted countries with strong political and economic ties to reduce risks associated with outsourcing, which typically focuses on cost efficiency by sourcing from low-cost regions. This strategic shift enhances supply chain resilience and geopolitical stability while balancing operational expenses. Explore the differences and impacts of friendshoring versus outsourcing to understand how businesses adapt to evolving global economic challenges.
Why it is important
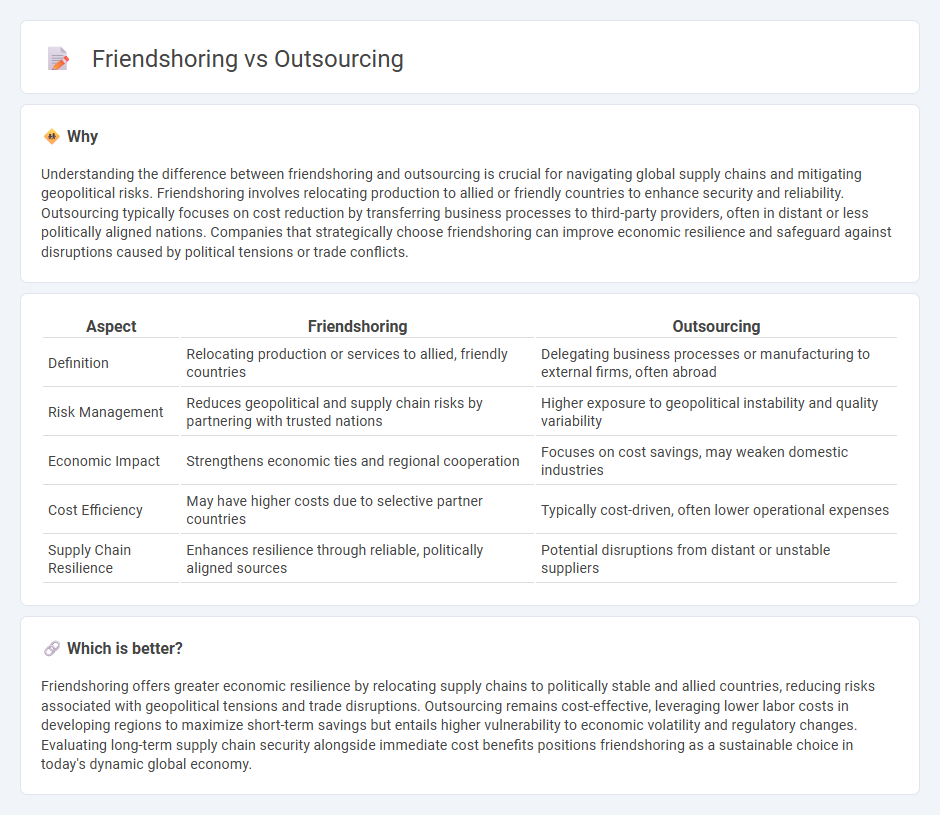
Understanding the difference between friendshoring and outsourcing is crucial for navigating global supply chains and mitigating geopolitical risks. Friendshoring involves relocating production to allied or friendly countries to enhance security and reliability. Outsourcing typically focuses on cost reduction by transferring business processes to third-party providers, often in distant or less politically aligned nations. Companies that strategically choose friendshoring can improve economic resilience and safeguard against disruptions caused by political tensions or trade conflicts.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Friendshoring | Outsourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Relocating production or services to allied, friendly countries | Delegating business processes or manufacturing to external firms, often abroad |
| Risk Management | Reduces geopolitical and supply chain risks by partnering with trusted nations | Higher exposure to geopolitical instability and quality variability |
| Economic Impact | Strengthens economic ties and regional cooperation | Focuses on cost savings, may weaken domestic industries |
| Cost Efficiency | May have higher costs due to selective partner countries | Typically cost-driven, often lower operational expenses |
| Supply Chain Resilience | Enhances resilience through reliable, politically aligned sources | Potential disruptions from distant or unstable suppliers |
Which is better?
Friendshoring offers greater economic resilience by relocating supply chains to politically stable and allied countries, reducing risks associated with geopolitical tensions and trade disruptions. Outsourcing remains cost-effective, leveraging lower labor costs in developing regions to maximize short-term savings but entails higher vulnerability to economic volatility and regulatory changes. Evaluating long-term supply chain security alongside immediate cost benefits positions friendshoring as a sustainable choice in today's dynamic global economy.
Connection
Friendshoring and outsourcing both involve relocating business processes to external countries but differ in strategic intent; friendshoring prioritizes partnerships with politically and economically aligned nations to reduce supply chain risks, while traditional outsourcing focuses primarily on cost reduction. These strategies impact global trade dynamics by influencing supply chain resilience and operational efficiency across industries such as manufacturing and technology. Companies adopting friendshoring often reassess outsourcing relationships to balance cost advantages with geopolitical stability and compliance requirements.
Key Terms
Comparative Advantage
Outsourcing capitalizes on cost efficiency by delegating tasks to external suppliers, often in low-wage countries, while friendshoring prioritizes geopolitical stability and trust by relocating supply chains to allied nations. Comparative advantage in outsourcing emphasizes reduced labor costs and operational expenses, whereas friendshoring leverages strategic partnerships and shared regulatory frameworks to mitigate risks. Explore deeper insights into how shifting global dynamics reshape supply chain strategies.
Supply Chain
Outsourcing in supply chain management involves delegating production processes to third-party vendors, often in distant countries to leverage cost advantages and scalability. Friendshoring shifts supply chain operations to allied or politically stable nations, reducing risks related to trade conflicts, geopolitical instability, and supply chain disruptions. Explore how friendshoring can enhance supply chain resilience and operational efficiency in today's global market.
Geopolitical Risk
Outsourcing involves delegating business processes to third-party providers often in distant countries to reduce costs, while friendshoring emphasizes relocating operations to allied or politically stable nations to mitigate geopolitical risk. Geopolitical tensions, trade wars, and supply chain disruptions prompt companies to prioritize friendshoring, leveraging trusted partnerships to ensure continuity and security. Explore how these strategies can safeguard your operations amid global uncertainty.
Source and External Links
What Is Outsourcing? - Indeed.com - Outsourcing is the practice of hiring external companies or contractors to perform tasks or create goods for an organization, typically to reduce costs and leverage specialized skills not available in-house.
What is Outsourcing and How Does it Work? - TechTarget - Outsourcing involves a company contracting a third-party provider to handle specific operations, services, or tasks--ranging from IT and customer service to manufacturing and HR--either onsite or at external locations.
What is Outsourcing? Definition, Advantages, and Examples - Inbound Logistics - Outsourcing allows businesses to contract with third-party suppliers to manage certain functions, enabling cost savings, access to expertise, and a greater focus on core business activities, though it can also introduce challenges like communication issues.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com