Resilient supply chains adapt swiftly to disruptions by diversifying sources, integrating advanced technologies, and maintaining strategic inventory buffers, minimizing operational downtime and financial losses. Fragile supply chains rely heavily on single suppliers and lack flexibility, increasing vulnerability to geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, and market fluctuations, which can severely disrupt production and distribution channels. Explore key strategies and real-world examples to understand how businesses build and benefit from resilient supply chains.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between resilient supply chains and fragile supply chains is crucial for minimizing disruptions, reducing costs, and ensuring continuous product availability in volatile markets. Resilient supply chains can quickly adapt to shocks such as natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, or pandemics, thereby safeguarding business operations and customer satisfaction. Fragile supply chains, conversely, are prone to breakdowns and delays, leading to revenue loss and damaged brand reputation. Companies with resilient supply chains outperform competitors by maintaining stability and agility in complex global economies.
Comparison Table
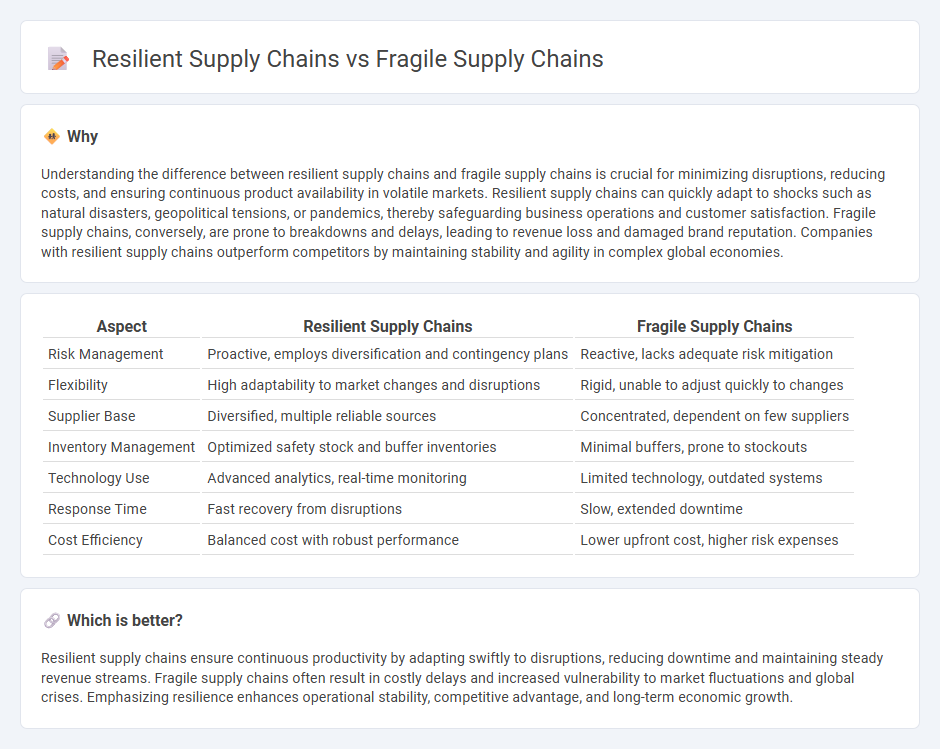
| Aspect | Resilient Supply Chains | Fragile Supply Chains |
|---|---|---|
| Risk Management | Proactive, employs diversification and contingency plans | Reactive, lacks adequate risk mitigation |
| Flexibility | High adaptability to market changes and disruptions | Rigid, unable to adjust quickly to changes |
| Supplier Base | Diversified, multiple reliable sources | Concentrated, dependent on few suppliers |
| Inventory Management | Optimized safety stock and buffer inventories | Minimal buffers, prone to stockouts |
| Technology Use | Advanced analytics, real-time monitoring | Limited technology, outdated systems |
| Response Time | Fast recovery from disruptions | Slow, extended downtime |
| Cost Efficiency | Balanced cost with robust performance | Lower upfront cost, higher risk expenses |
Which is better?
Resilient supply chains ensure continuous productivity by adapting swiftly to disruptions, reducing downtime and maintaining steady revenue streams. Fragile supply chains often result in costly delays and increased vulnerability to market fluctuations and global crises. Emphasizing resilience enhances operational stability, competitive advantage, and long-term economic growth.
Connection
Resilient supply chains incorporate flexibility, diversification, and real-time data analytics to quickly adapt to disruptions, whereas fragile supply chains rely on linear processes and single-source dependencies, increasing vulnerability to shocks. The interconnection lies in the transition potential; companies can transform fragile supply chains into resilient ones by investing in digital technologies, robust risk management, and localized sourcing strategies. This dynamic affects global trade stability and economic growth, emphasizing the need for resilience to mitigate supply chain interruptions and maintain market confidence.
Key Terms
Vulnerability
Fragile supply chains exhibit high vulnerability due to dependence on single suppliers, limited visibility, and inadequate risk management, leading to frequent disruptions from geopolitical events, natural disasters, and demand fluctuations. In contrast, resilient supply chains incorporate diversified sourcing, real-time data analytics, and contingency planning to mitigate risks and maintain operational continuity. Explore how advanced strategies can transform vulnerability into strength for supply chain resilience.
Diversification
Fragile supply chains often rely heavily on a limited number of suppliers or regions, making them vulnerable to disruptions such as natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, or pandemics. Resilient supply chains prioritize diversification by sourcing materials from multiple geographic locations and suppliers to reduce risk exposure and improve recovery speed after disruptions. Explore more to understand how strategic diversification enhances supply chain resilience and operational continuity.
Redundancy
Fragile supply chains suffer from a lack of redundancy, making them highly vulnerable to disruptions such as natural disasters, geopolitical issues, or sudden demand spikes. Resilient supply chains incorporate redundant elements like alternative suppliers, extra inventory, and backup logistics routes to ensure continuous operations despite uncertainties. Discover how building redundancy into your supply chain strategy can safeguard your business from unexpected shocks.
Source and External Links
Why global supply chains are so fragile - DCU Business School - Modern global supply chains are highly interconnected and vulnerable to natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, and infrastructure failures, making disruptions in one region cause widespread delays, shortages, and increased costs worldwide.
McKinsey Global Supply Chain Leader Survey 2024 - Supply chain disruptions remain frequent and widespread, with many organizations lacking sufficient risk management and board-level oversight, leaving them vulnerable to ongoing and future instability.
Pandemic revealed fragility of supply chain, and even now ... - The COVID-19 pandemic exposed how complexity and worker shortages in supply chains create bottlenecks, as seen in product shortages like toilet paper, exacerbated by logistic and labor constraints at every production and delivery stage.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com