Reshoring involves relocating manufacturing and business processes back to the company's home country to reduce costs and enhance control, while foreign direct investment (FDI) entails investing in production or business operations in a foreign country to access new markets and resources. Key factors influencing reshoring decisions include labor costs, supply chain resilience, and government incentives, whereas FDI is driven by market potential, trade agreements, and comparative advantage. Explore the economic impacts and strategic considerations behind choosing reshoring versus foreign direct investment.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between reshoring and foreign direct investment (FDI) is crucial for economic strategy as reshoring involves bringing manufacturing back to the home country, boosting domestic job creation and supply chain resilience. FDI refers to investing capital in foreign enterprises, which can enhance global market access and technology transfer but may not directly stimulate local job growth. Policymakers and businesses must distinguish these to optimize economic growth, trade policies, and employment impacts. Reshoring often strengthens national economic security, whereas FDI promotes international economic integration.
Comparison Table
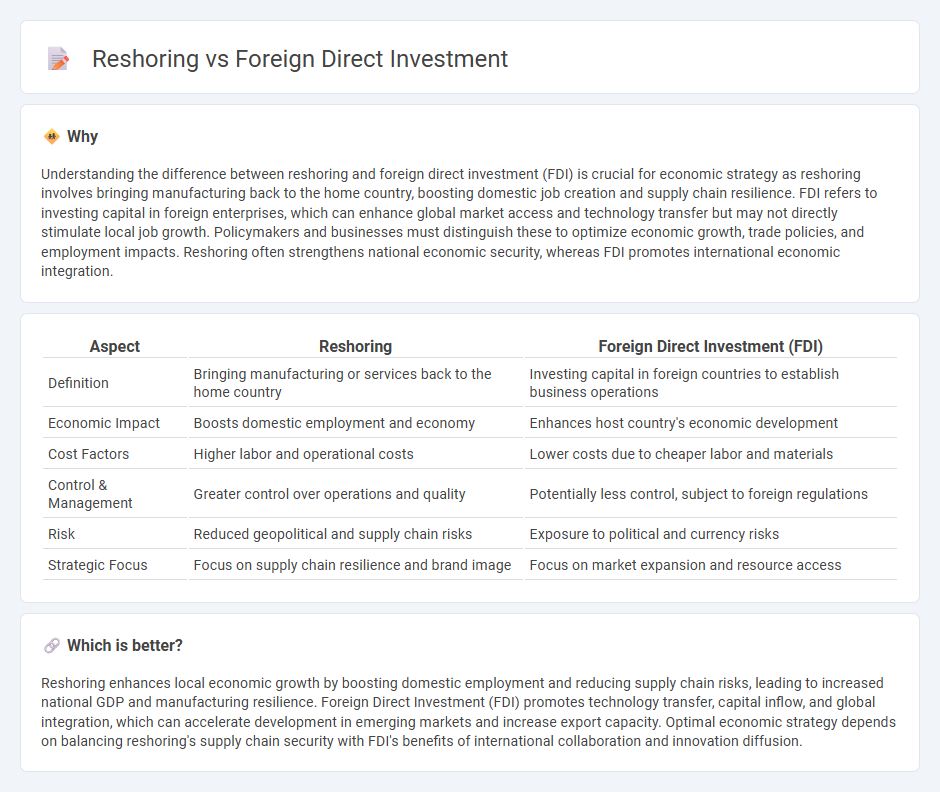
| Aspect | Reshoring | Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bringing manufacturing or services back to the home country | Investing capital in foreign countries to establish business operations |
| Economic Impact | Boosts domestic employment and economy | Enhances host country's economic development |
| Cost Factors | Higher labor and operational costs | Lower costs due to cheaper labor and materials |
| Control & Management | Greater control over operations and quality | Potentially less control, subject to foreign regulations |
| Risk | Reduced geopolitical and supply chain risks | Exposure to political and currency risks |
| Strategic Focus | Focus on supply chain resilience and brand image | Focus on market expansion and resource access |
Which is better?
Reshoring enhances local economic growth by boosting domestic employment and reducing supply chain risks, leading to increased national GDP and manufacturing resilience. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) promotes technology transfer, capital inflow, and global integration, which can accelerate development in emerging markets and increase export capacity. Optimal economic strategy depends on balancing reshoring's supply chain security with FDI's benefits of international collaboration and innovation diffusion.
Connection
Reshoring stimulates foreign direct investment (FDI) by encouraging multinational companies to reinvest capital domestically, boosting local manufacturing and job creation. Increased reshoring initiatives often attract FDI due to improved supply chain resilience and proximity to key markets. This dynamic fosters economic growth by integrating domestic production with global investment flows, enhancing competitiveness and innovation.
Key Terms
Capital Flows
Foreign direct investment (FDI) drives capital flows across borders by enabling companies to establish or expand operations in foreign markets, fostering economic integration and access to new resources. Reshoring redirects capital flow back to a company's home country as firms relocate production to reduce risks and costs linked to global supply chains, impacting domestic investment levels and labor markets. Explore how these contrasting capital flow trends influence global economic strategies and investment decisions.
Supply Chain
Foreign direct investment (FDI) often extends global supply chains by establishing production or operations in foreign countries to capitalize on lower costs and market access, while reshoring strategically brings manufacturing back to domestic locations to enhance supply chain resilience and reduce transportation risks. Companies reshoring aim to shorten supply chains, improve inventory control, and mitigate disruptions caused by geopolitical issues or pandemics, contrasting with FDI's focus on expansion and cost efficiency. Explore detailed case studies and trend analyses to understand how supply chain priorities influence decisions between FDI and reshoring.
Domestic Production
Foreign direct investment (FDI) involves multinational companies investing in production facilities abroad to access new markets and reduce costs, often leading to offshoring of domestic production. Reshoring, in contrast, brings manufacturing activities back to the home country, aiming to revitalize domestic production capacity, enhance supply chain resilience, and create local jobs. Explore the impact of these strategies on domestic production and economic growth to understand the best approach for your business.
Source and External Links
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) - Overview, Benefits & Disadvantages - Foreign direct investment (FDI) is an investment from a party in one country into a business or corporation in another country, with the intention of establishing a lasting interest and control, typically signified by owning at least 10% of the voting power in the foreign company.
Glossary:Foreign direct investment (FDI) - FDI is an international investment where a resident entity in one economy seeks to obtain a lasting interest in an enterprise resident in another economy, implying a long-term relationship and significant influence on management, usually defined by owning 10% or more of ordinary shares or voting rights.
Foreign direct investment, net inflows (BoP, current US$) - Global FDI data show net inflows and positions, reflecting cross-border investments that contribute to the balance of payments and are tracked by major international organizations such as the IMF and UNCTAD.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com