Friendshoring prioritizes relocating supply chains to allied nations to enhance economic security and reduce geopolitical risks, while localization focuses on producing goods within domestic borders to boost local employment and control. Both strategies aim to strengthen economic resilience amid global uncertainties but differ in scale and partnership scope. Explore the nuances between friendshoring and localization to understand their impacts on modern economic policies.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between friendshoring and localization is crucial for businesses to optimize supply chain resilience and reduce geopolitical risks. Friendshoring involves relocating operations to allied countries, enhancing political trust and security, while localization focuses on producing goods close to the end market to minimize transportation costs and delays. This knowledge helps companies strategically balance cost efficiency, risk management, and market responsiveness. Accurate application can improve economic stability and competitiveness in global trade.
Comparison Table
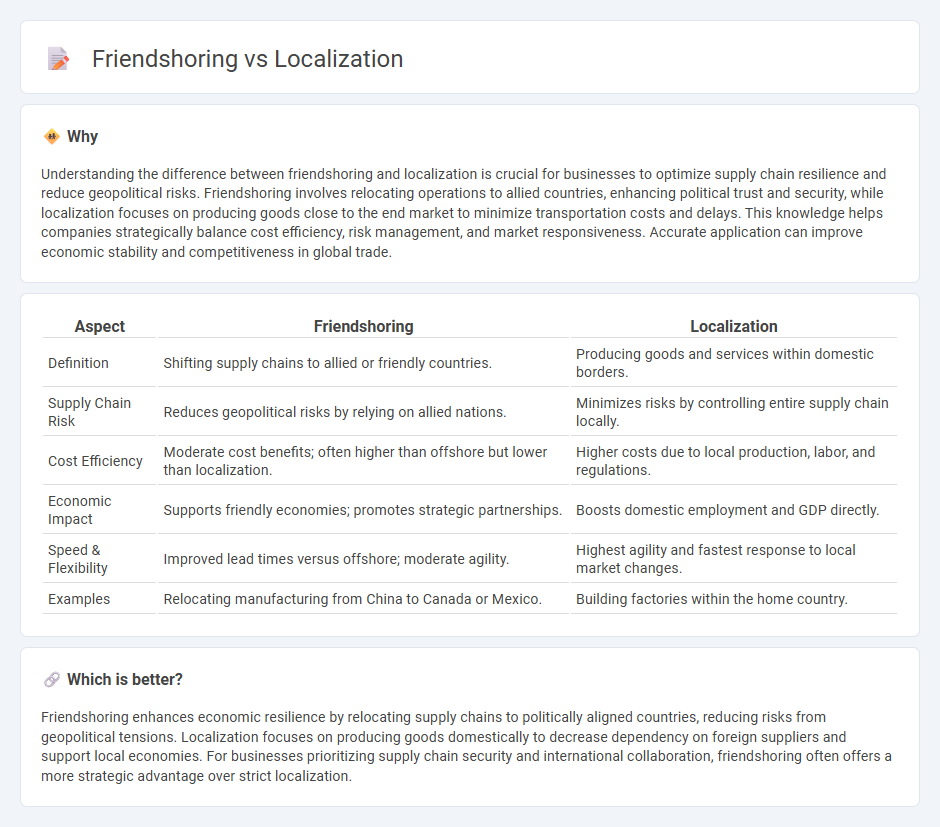
| Aspect | Friendshoring | Localization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shifting supply chains to allied or friendly countries. | Producing goods and services within domestic borders. |
| Supply Chain Risk | Reduces geopolitical risks by relying on allied nations. | Minimizes risks by controlling entire supply chain locally. |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate cost benefits; often higher than offshore but lower than localization. | Higher costs due to local production, labor, and regulations. |
| Economic Impact | Supports friendly economies; promotes strategic partnerships. | Boosts domestic employment and GDP directly. |
| Speed & Flexibility | Improved lead times versus offshore; moderate agility. | Highest agility and fastest response to local market changes. |
| Examples | Relocating manufacturing from China to Canada or Mexico. | Building factories within the home country. |
Which is better?
Friendshoring enhances economic resilience by relocating supply chains to politically aligned countries, reducing risks from geopolitical tensions. Localization focuses on producing goods domestically to decrease dependency on foreign suppliers and support local economies. For businesses prioritizing supply chain security and international collaboration, friendshoring often offers a more strategic advantage over strict localization.
Connection
Friendshoring and localization both enhance supply chain resilience by prioritizing geographically and politically stable partners, reducing dependency on distant or risky locations. Friendshoring focuses on shifting production to allied countries to secure economic and strategic interests, while localization emphasizes producing goods close to the end consumer to minimize transportation costs and mitigate disruptions. Together, these strategies optimize operational efficiency and strengthen economic security in the global marketplace.
Key Terms
Supply Chains
Localization emphasizes sourcing and producing goods within the same country to reduce transportation costs and increase supply chain resilience. Friendshoring involves relocating supply chains to politically and economically aligned countries, enhancing security and stability while maintaining cost efficiency. Explore how these strategies impact global supply chain management and risk mitigation.
Trade Policy
Localization emphasizes producing goods within domestic borders to reduce reliance on international supply chains, boosting national economic resilience and job creation. Friendshoring, on the other hand, involves relocating production to politically allied countries to enhance supply chain security and minimize geopolitical risks in trade policy. Explore the strategic trade implications of localization versus friendshoring to fully understand their impact on global commerce.
Geopolitical Alliances
Localization prioritizes sourcing and production within a company's home country to reduce dependence on global supply chains, enhancing national security and economic resilience. Friendshoring involves relocating supply chains to allied countries with strong geopolitical ties, minimizing risks associated with hostile international relationships and fostering strategic economic partnerships. Discover how evolving geopolitical alliances shape the future of global trade through localization and friendshoring strategies.
Source and External Links
LOCALIZATION definition | Cambridge English Dictionary - Localization is the process of organizing a business or industry so that its main activities happen in local areas rather than nationally or internationally; it also refers to adapting content or services to local markets.
Localization (l10n): What It Is, and How to Build a Strategy? - Phrase - Localization is the adaptation of a product to meet the cultural, linguistic, legal, and other requirements of a target market, involving strategic analysis, choices, and execution.
What is localization? | Definition from TechTarget - Localization is the process of adapting and customizing a product to meet the needs of a specific market including language, culture, local standards, and legal requirements, distinct from but related to translation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com