De-dollarisation involves reducing reliance on the US dollar in international trade and finance to enhance monetary sovereignty and mitigate exposure to dollar fluctuations. Currency internationalization is a strategic process where a nation promotes its currency for global transactions, reserves, and investment purposes to increase economic influence. Explore how these dynamics are reshaping global economic power structures.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between de-dollarization and currency internationalization is crucial for analyzing global financial stability and economic sovereignty. De-dollarization involves reducing reliance on the US dollar in trade and reserves, impacting exchange rates and monetary policy autonomy. Currency internationalization refers to a country promoting its currency for global trade and investment, enhancing its financial influence and cross-border capital flows. Policymakers and investors must distinguish these concepts to assess geopolitical risks and strategize economic policies effectively.
Comparison Table
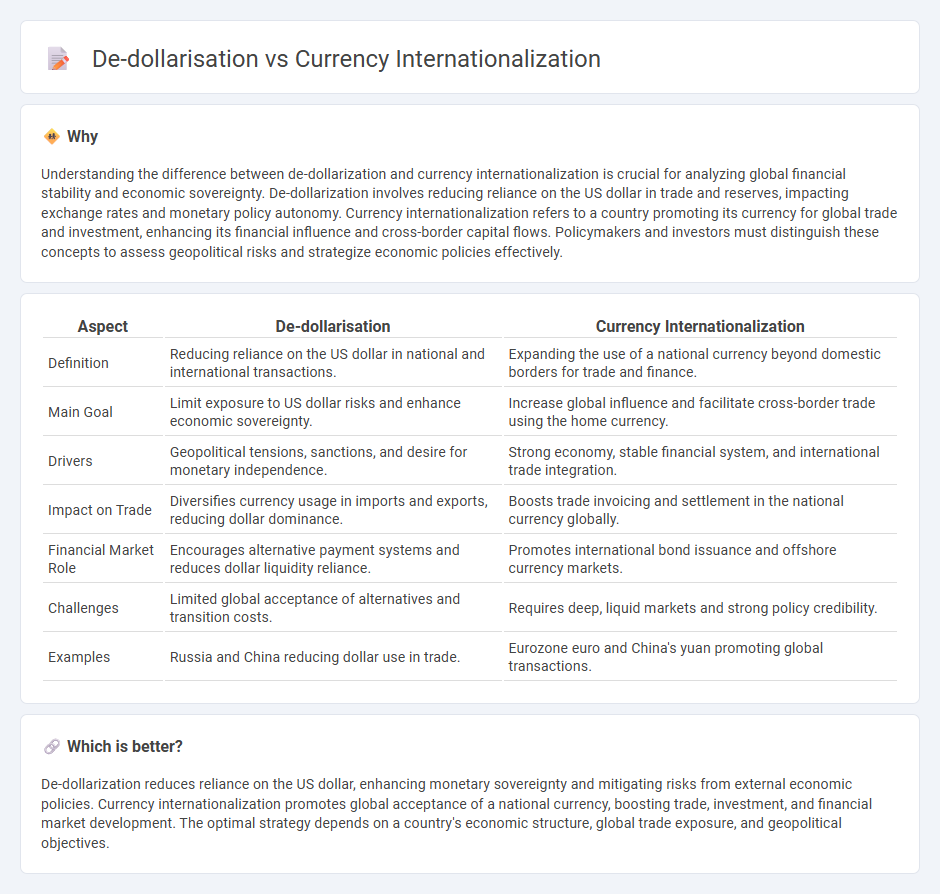
| Aspect | De-dollarisation | Currency Internationalization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reducing reliance on the US dollar in national and international transactions. | Expanding the use of a national currency beyond domestic borders for trade and finance. |
| Main Goal | Limit exposure to US dollar risks and enhance economic sovereignty. | Increase global influence and facilitate cross-border trade using the home currency. |
| Drivers | Geopolitical tensions, sanctions, and desire for monetary independence. | Strong economy, stable financial system, and international trade integration. |
| Impact on Trade | Diversifies currency usage in imports and exports, reducing dollar dominance. | Boosts trade invoicing and settlement in the national currency globally. |
| Financial Market Role | Encourages alternative payment systems and reduces dollar liquidity reliance. | Promotes international bond issuance and offshore currency markets. |
| Challenges | Limited global acceptance of alternatives and transition costs. | Requires deep, liquid markets and strong policy credibility. |
| Examples | Russia and China reducing dollar use in trade. | Eurozone euro and China's yuan promoting global transactions. |
Which is better?
De-dollarization reduces reliance on the US dollar, enhancing monetary sovereignty and mitigating risks from external economic policies. Currency internationalization promotes global acceptance of a national currency, boosting trade, investment, and financial market development. The optimal strategy depends on a country's economic structure, global trade exposure, and geopolitical objectives.
Connection
De-dollarization involves reducing reliance on the US dollar in international trade and finance, while currency internationalization refers to a nation's effort to promote its own currency for global use. Both processes are interconnected as currency internationalization is a strategic approach within de-dollarization, aiming to enhance monetary sovereignty and decrease exposure to dollar-related risks. Nations like China actively pursue currency internationalization of the yuan to support de-dollarization and diversify global reserve currencies.
Key Terms
Reserve Currency
Reserve currency status is crucial for global economic influence, with the US dollar dominating international trade, finance, and central bank reserves. Currency internationalization promotes the widespread use of alternative currencies like the euro and Chinese yuan to reduce reliance on the dollar and enhance financial stability. Explore how shifts in reserve currency preferences impact global markets and geopolitical power dynamics.
Exchange Rate Regime
Currency internationalization involves a country promoting its currency for global trade, finance, and reserves, often maintaining a flexible exchange rate regime to support international trust and liquidity. De-dollarization refers to reducing reliance on the US dollar, frequently by adopting alternative currencies or adjusting exchange rate policies to stabilize domestic financial systems and enhance monetary sovereignty. Explore the dynamics between exchange rate regimes and currency strategies to understand their impact on global economic stability.
Currency Swap Agreements
Currency internationalization involves promoting a nation's currency for global trade and investment to enhance economic influence, while de-dollarization aims to reduce reliance on the US dollar in international transactions. Currency Swap Agreements serve as crucial tools in both strategies, allowing countries to exchange their currencies directly, thereby facilitating smoother trade and financial stability without converting to the dollar. Explore how Currency Swap Agreements are reshaping global financial dynamics and fostering economic sovereignty.
Source and External Links
Local-currency debt and currency internationalization dynamics - Currency internationalization is a lengthy, progressive process driven by network effects, where a currency's use in one international function lowers transaction costs and encourages its adoption in others, often culminating in dominance by a currency like the US dollar.
Better Understanding the Renminbi's Internationalization - The internationalization of the renminbi involves developing cross-border payment networks with significant public sector involvement, marking a policy-driven approach to expanding the currency's acceptance globally amid efforts to create alternatives to the dollar-centric system.
Currency internationalisation: an overview - An international currency is one widely used and held beyond its home country, supporting trade and finance globally, with regional initiatives (like currency swap agreements and bond funds) promoting gradual currency internationalization through market integration and policy coordination.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com