Just-in-time hiring enables companies to rapidly adjust their workforce based on immediate demand, enhancing operational flexibility and reducing labor costs. In contrast, a contingent workforce consists of temporary or freelance workers employed to fulfill specific project needs or seasonal peaks without long-term commitments. Explore the advantages and challenges of each approach to optimize workforce strategy in today's dynamic economy.
Why it is important
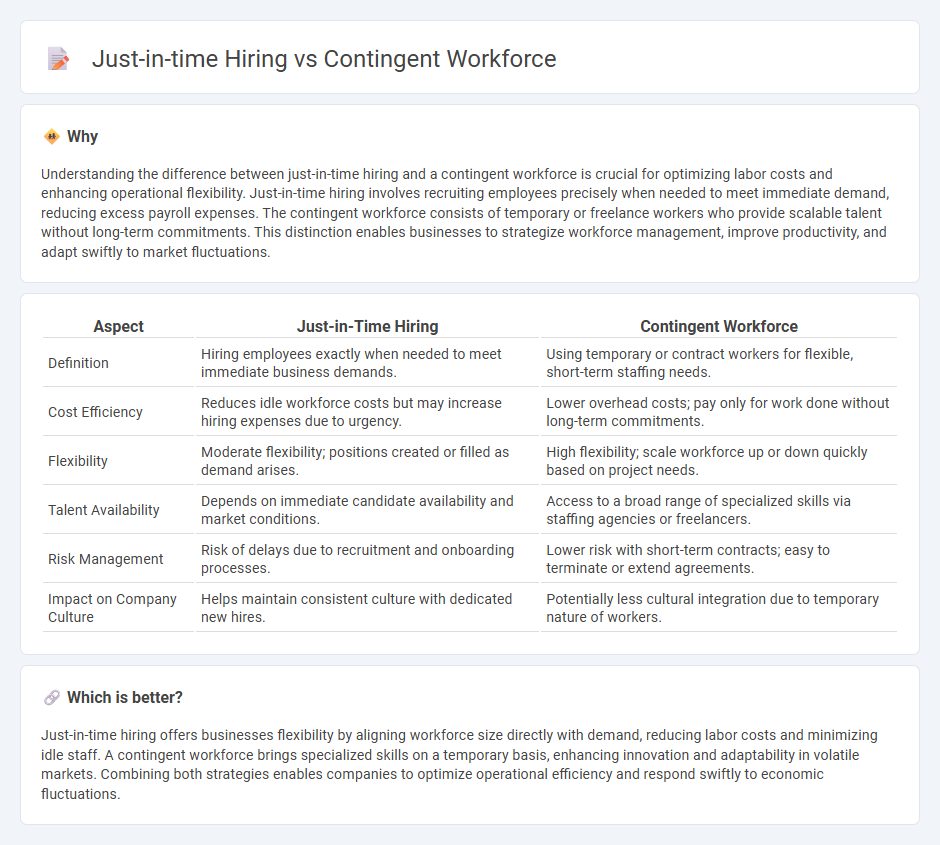
Understanding the difference between just-in-time hiring and a contingent workforce is crucial for optimizing labor costs and enhancing operational flexibility. Just-in-time hiring involves recruiting employees precisely when needed to meet immediate demand, reducing excess payroll expenses. The contingent workforce consists of temporary or freelance workers who provide scalable talent without long-term commitments. This distinction enables businesses to strategize workforce management, improve productivity, and adapt swiftly to market fluctuations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Just-in-Time Hiring | Contingent Workforce |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hiring employees exactly when needed to meet immediate business demands. | Using temporary or contract workers for flexible, short-term staffing needs. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces idle workforce costs but may increase hiring expenses due to urgency. | Lower overhead costs; pay only for work done without long-term commitments. |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility; positions created or filled as demand arises. | High flexibility; scale workforce up or down quickly based on project needs. |
| Talent Availability | Depends on immediate candidate availability and market conditions. | Access to a broad range of specialized skills via staffing agencies or freelancers. |
| Risk Management | Risk of delays due to recruitment and onboarding processes. | Lower risk with short-term contracts; easy to terminate or extend agreements. |
| Impact on Company Culture | Helps maintain consistent culture with dedicated new hires. | Potentially less cultural integration due to temporary nature of workers. |
Which is better?
Just-in-time hiring offers businesses flexibility by aligning workforce size directly with demand, reducing labor costs and minimizing idle staff. A contingent workforce brings specialized skills on a temporary basis, enhancing innovation and adaptability in volatile markets. Combining both strategies enables companies to optimize operational efficiency and respond swiftly to economic fluctuations.
Connection
Just-in-time hiring enhances economic agility by aligning workforce size with fluctuating demand, minimizing labor costs and improving operational efficiency. The contingent workforce plays a crucial role by providing flexible, on-demand talent that supports this adaptive employment strategy. Together, they optimize resource allocation and responsiveness in dynamic market conditions.
Key Terms
Flexibility
Contingent workforce models offer organizations flexibility by enabling rapid scaling of labor based on project demand without long-term commitments, reducing fixed costs and operational risks. Just-in-time hiring emphasizes timely recruitment to fill immediate needs, optimizing workforce agility and minimizing idle capacity. Explore detailed strategies to leverage flexibility through contingent and just-in-time hiring approaches.
Cost-efficiency
Contingent workforce models reduce labor costs by leveraging temporary or freelance talent without long-term commitments, optimizing expense based on project needs. Just-in-time hiring minimizes payroll overhead by aligning recruitment precisely with real-time demand, preventing overstaffing and reducing idle labor costs. Explore how businesses balance these strategies to maximize cost-efficiency in dynamic markets.
Labor scalability
Contingent workforce offers flexible labor scalability by allowing businesses to quickly adjust staffing levels based on project demands without long-term commitments. Just-in-time hiring focuses on precise timing to acquire talent exactly when needed, minimizing idle labor costs and increasing operational efficiency. Discover how these workforce strategies optimize labor scalability and impact overall business agility.
Source and External Links
What is a Contingent Workforce? - Definition from TechTarget.com - A contingent workforce consists of freelancers, independent contractors, and consultants hired on-demand, not as full-time employees, offering companies flexibility and agility in staffing.
What Is a Contingent Workforce? - Oracle - Contingent workers include contractors, consultants, freelancers, and temps hired under contract for specific projects or to fill temporary roles, providing organizations with specialized skills and flexibility to address short-term needs.
Contingent work - Wikipedia - Contingent work refers to non-permanent employment with limited job security, often part-time or project-based, and includes gig workers, independent contractors, temps, and others in alternative work arrangements.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com