Resilient supply chains prioritize flexibility, risk management, and adaptability to disruptions, contrasting with centralized supply chains that focus on efficiency and cost reduction through consolidated operations. The rising frequency of global crises has underscored the vulnerabilities inherent in highly centralized systems, prompting businesses to adopt decentralized and diversified supply networks. Explore the benefits and challenges of resilient versus centralized supply chains to understand their impact on economic stability.
Why it is important
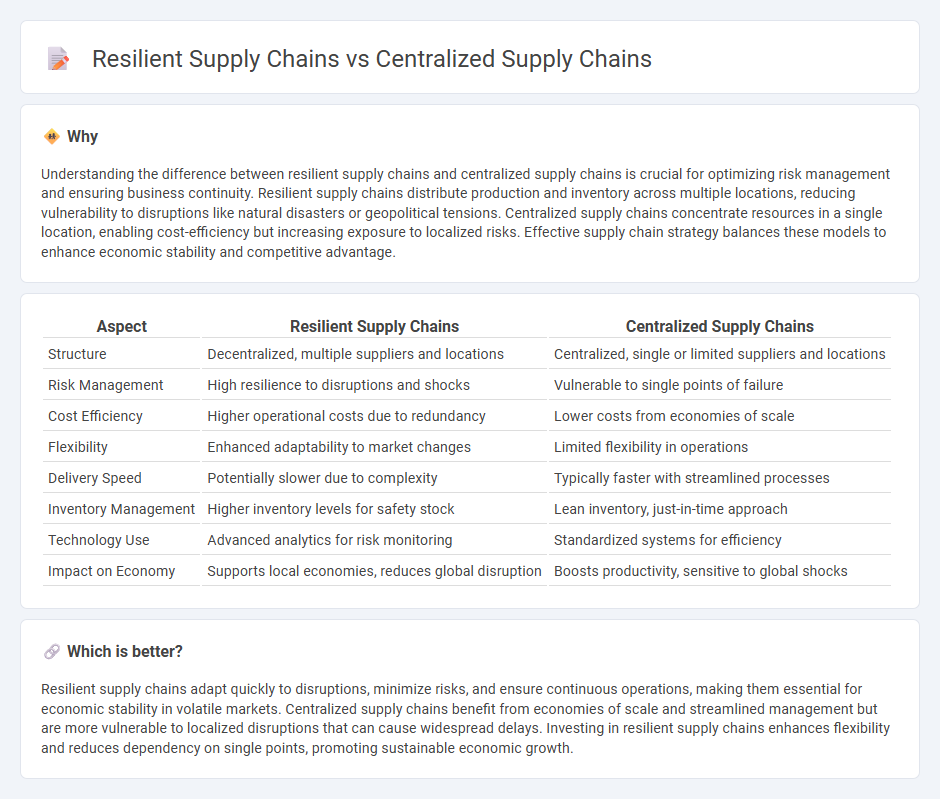
Understanding the difference between resilient supply chains and centralized supply chains is crucial for optimizing risk management and ensuring business continuity. Resilient supply chains distribute production and inventory across multiple locations, reducing vulnerability to disruptions like natural disasters or geopolitical tensions. Centralized supply chains concentrate resources in a single location, enabling cost-efficiency but increasing exposure to localized risks. Effective supply chain strategy balances these models to enhance economic stability and competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Resilient Supply Chains | Centralized Supply Chains |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Decentralized, multiple suppliers and locations | Centralized, single or limited suppliers and locations |
| Risk Management | High resilience to disruptions and shocks | Vulnerable to single points of failure |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher operational costs due to redundancy | Lower costs from economies of scale |
| Flexibility | Enhanced adaptability to market changes | Limited flexibility in operations |
| Delivery Speed | Potentially slower due to complexity | Typically faster with streamlined processes |
| Inventory Management | Higher inventory levels for safety stock | Lean inventory, just-in-time approach |
| Technology Use | Advanced analytics for risk monitoring | Standardized systems for efficiency |
| Impact on Economy | Supports local economies, reduces global disruption | Boosts productivity, sensitive to global shocks |
Which is better?
Resilient supply chains adapt quickly to disruptions, minimize risks, and ensure continuous operations, making them essential for economic stability in volatile markets. Centralized supply chains benefit from economies of scale and streamlined management but are more vulnerable to localized disruptions that can cause widespread delays. Investing in resilient supply chains enhances flexibility and reduces dependency on single points, promoting sustainable economic growth.
Connection
Resilient supply chains rely on centralized supply chain structures to enhance control and visibility over inventory, enabling quicker responses to disruptions and reducing lead times. Centralized supply chains consolidate resources and decision-making processes, which improves coordination and risk management in volatile economic conditions. This connection strengthens overall supply chain adaptability, ensuring steady product availability and minimizing financial losses during market fluctuations.
Key Terms
Efficiency
Centralized supply chains prioritize efficiency by consolidating operations and resources in a single location, reducing costs and streamlining processes. Resilient supply chains, while potentially less cost-efficient, emphasize robustness against disruptions through diversification and flexibility in sourcing and distribution. Explore how balancing efficiency and resilience can optimize your supply chain strategy.
Flexibility
Centralized supply chains concentrate inventory and production in a single or few locations to optimize cost efficiency but often lack flexibility to adapt to disruptions. Resilient supply chains emphasize decentralized networks and agile processes that enable quick response and recovery from unforeseen events, enhancing flexibility. Explore more to understand how balancing centralization and resilience can optimize supply chain performance.
Risk Mitigation
Centralized supply chains concentrate inventory and operations in a single location, often reducing costs but increasing vulnerability to disruptions such as natural disasters or geopolitical events. Resilient supply chains, by contrast, diversify suppliers and distribute inventory across multiple sites to mitigate risks and maintain continuity in volatile conditions. Explore strategies to balance efficiency and resilience for effective risk management in supply chain design.
Source and External Links
Centralized vs. Decentralized Supply Chains | Wayfindr - Discusses the pros and cons of centralized supply chains, including their limited agility and susceptibility to supply chain disasters.
Centralised vs. decentralised supply chains -- the pros and cons - Explores the traditional centralized supply chain model with a central headquarters and warehouse, highlighting its management structure.
Centralized vs. Decentralized Supply Chain Structure - Highlights the benefits of centralized supply chains, such as economies of scale and consistent quality control, while contrasting with decentralized structures.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com