Micro-dosing spending involves targeted, small-scale financial interventions aimed at immediate economic stimuli, optimizing resource allocation at the individual or community level. Macro-level fiscal policy encompasses broader government strategies including taxation, public spending, and budget management to influence national economic growth and stability. Explore how micro-dosing spending can complement macro-fiscal approaches to enhance overall economic resilience.
Why it is important
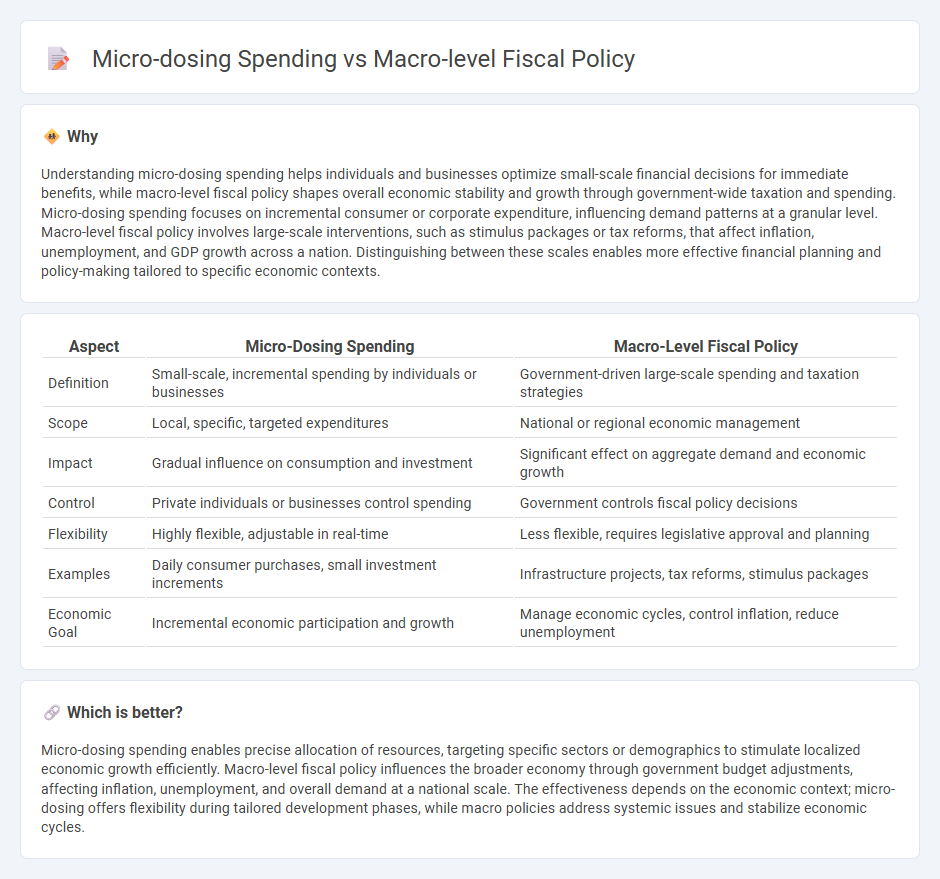
Understanding micro-dosing spending helps individuals and businesses optimize small-scale financial decisions for immediate benefits, while macro-level fiscal policy shapes overall economic stability and growth through government-wide taxation and spending. Micro-dosing spending focuses on incremental consumer or corporate expenditure, influencing demand patterns at a granular level. Macro-level fiscal policy involves large-scale interventions, such as stimulus packages or tax reforms, that affect inflation, unemployment, and GDP growth across a nation. Distinguishing between these scales enables more effective financial planning and policy-making tailored to specific economic contexts.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Micro-Dosing Spending | Macro-Level Fiscal Policy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Small-scale, incremental spending by individuals or businesses | Government-driven large-scale spending and taxation strategies |
| Scope | Local, specific, targeted expenditures | National or regional economic management |
| Impact | Gradual influence on consumption and investment | Significant effect on aggregate demand and economic growth |
| Control | Private individuals or businesses control spending | Government controls fiscal policy decisions |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, adjustable in real-time | Less flexible, requires legislative approval and planning |
| Examples | Daily consumer purchases, small investment increments | Infrastructure projects, tax reforms, stimulus packages |
| Economic Goal | Incremental economic participation and growth | Manage economic cycles, control inflation, reduce unemployment |
Which is better?
Micro-dosing spending enables precise allocation of resources, targeting specific sectors or demographics to stimulate localized economic growth efficiently. Macro-level fiscal policy influences the broader economy through government budget adjustments, affecting inflation, unemployment, and overall demand at a national scale. The effectiveness depends on the economic context; micro-dosing offers flexibility during tailored development phases, while macro policies address systemic issues and stabilize economic cycles.
Connection
Micro-dosing spending influences individual consumer behavior patterns, affecting aggregate demand and economic growth metrics. Macro-level fiscal policy leverages this aggregated data to fine-tune public expenditure and taxation strategies, aiming to stabilize inflation and stimulate employment. By aligning micro-level spending trends with broader economic objectives, policymakers optimize resource allocation and promote sustainable economic development.
Key Terms
Government Expenditure
Government expenditure at the macro-level involves large-scale fiscal policies aimed at stabilizing the economy, influencing aggregate demand, and promoting growth through public investments and social programs. In contrast, micro-dosing spending refers to targeted, small-scale fiscal actions designed to address specific sectoral needs or local economic challenges, optimizing resource allocation for maximum efficiency. Explore detailed analyses to understand the impact of these fiscal strategies on economic development.
Aggregate Demand
Macro-level fiscal policy influences aggregate demand through government spending and taxation, altering overall economic activity. Micro-dosing spending targets specific sectors or populations to stimulate demand incrementally and efficiently within a broader fiscal framework. Explore further to understand how these approaches uniquely impact economic growth and stability.
Marginal Propensity to Consume
Macro-level fiscal policy influences aggregate demand through government spending and taxation, impacting economic growth and stability. Micro-dosing spending targets individual or household consumption patterns to optimize Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC), increasing immediate consumption for faster economic stimulus. Explore deeper insights on how tailored fiscal approaches can enhance consumption efficiency and economic recovery.
Source and External Links
Expansionary and Contractionary Fiscal Policy - Macro-level fiscal policy involves government tax and spending decisions aimed at influencing aggregate demand to stabilize or stimulate the economy, using expansionary policy to increase demand in recessions and contractionary policy to reduce demand when overheating occurs.
What is fiscal policy? AP/IB/College - Fiscal policy at the macro level is the use of government spending and taxation to achieve goals like full employment, price stability, and economic growth, with tools including tax changes and government expenditure adjustments impacting overall economic output.
Fiscal Policy: Taking and Giving Away - Macro-level fiscal policy consists of modifying government spending and tax policies to directly affect aggregate demand, thereby influencing gross domestic product and resource allocation for economic stability and growth.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com