Excess savings occur when households or businesses accumulate more funds than are immediately invested, often leading to increased financial reserves and liquidity. Capital flight refers to the rapid outflow of assets or capital from a country, triggered by economic instability, unfavorable policies, or political risk, which can undermine national economic growth. Explore how these contrasting financial behaviors impact economic stability and investment strategies worldwide.
Why it is important
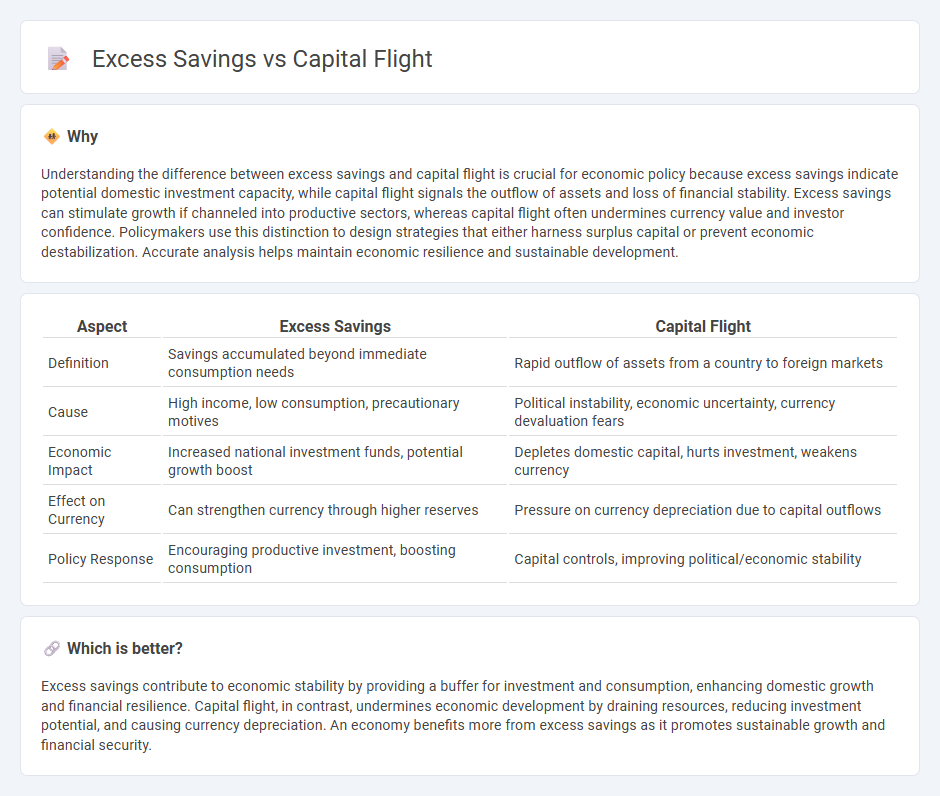
Understanding the difference between excess savings and capital flight is crucial for economic policy because excess savings indicate potential domestic investment capacity, while capital flight signals the outflow of assets and loss of financial stability. Excess savings can stimulate growth if channeled into productive sectors, whereas capital flight often undermines currency value and investor confidence. Policymakers use this distinction to design strategies that either harness surplus capital or prevent economic destabilization. Accurate analysis helps maintain economic resilience and sustainable development.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Excess Savings | Capital Flight |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Savings accumulated beyond immediate consumption needs | Rapid outflow of assets from a country to foreign markets |
| Cause | High income, low consumption, precautionary motives | Political instability, economic uncertainty, currency devaluation fears |
| Economic Impact | Increased national investment funds, potential growth boost | Depletes domestic capital, hurts investment, weakens currency |
| Effect on Currency | Can strengthen currency through higher reserves | Pressure on currency depreciation due to capital outflows |
| Policy Response | Encouraging productive investment, boosting consumption | Capital controls, improving political/economic stability |
Which is better?
Excess savings contribute to economic stability by providing a buffer for investment and consumption, enhancing domestic growth and financial resilience. Capital flight, in contrast, undermines economic development by draining resources, reducing investment potential, and causing currency depreciation. An economy benefits more from excess savings as it promotes sustainable growth and financial security.
Connection
Excess savings in an economy can lead to capital flight when investors seek higher returns or safer assets abroad, causing a significant outflow of funds. This phenomenon reduces domestic investment and weakens currency stability, impacting economic growth. Persistent capital flight exacerbates financial vulnerabilities by draining reserves and limiting resources for productive uses.
Key Terms
Outflows
Capital flight refers to large-scale exodus of financial assets and capital from a country due to economic instability, political uncertainty, or unfavorable government policies, leading to significant outflows. Excess savings occur when domestic savings exceed investment opportunities within the country, prompting surplus funds to flow abroad, often seeking higher returns or safer assets. Explore how these outflows impact national economies and global financial markets for deeper insights.
Investment
Capital flight drains domestic resources, reducing funds available for investment and hindering economic growth. Excess savings, when not effectively channeled into productive investments, lead to underutilized capital and slow development. Explore strategies to balance capital flows and savings to maximize investment impact.
Interest rates
Capital flight occurs when investors withdraw assets from a country to seek higher interest rates abroad, negatively impacting domestic investment and currency stability. Excess savings refer to the surplus funds within an economy that outpace available investment opportunities, often leading to lower interest rates as capital supply exceeds demand. Understanding the interplay between capital flight and excess savings helps clarify interest rate fluctuations; explore more to grasp their full economic impact.
Source and External Links
Capital Flight - Definitions, Impact, Causes, Prevention - Capital flight is the large, rapid outflow of assets or capital from a country, often triggered by economic or political instability, leading to negative consequences like reduced tax revenue, weakened currency, and loss of purchasing power for citizens.
Capital Flight: Estimates, Issues, and Explanations - The term typically refers to short-term speculative outflows of "hot money" in response to crises, anticipated currency devaluation, or unfavorable policy changes, which can reduce a country's growth potential and investment income from abroad.
Capital flight - Capital flight involves the rapid movement of money or assets out of a country due to economic or political shocks, often causing sharp currency depreciation and a significant loss of wealth and confidence in the domestic economy.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com