Micro-mobility solutions, including e-bikes and scooters, significantly reduce urban congestion and carbon emissions by offering efficient, short-distance transportation options. Scooter sharing platforms enable users to access electric scooters on-demand, promoting convenience and sustainability in city travel. Explore how micro-mobility and scooter sharing are reshaping urban economies and transforming green transportation trends.
Why it is important
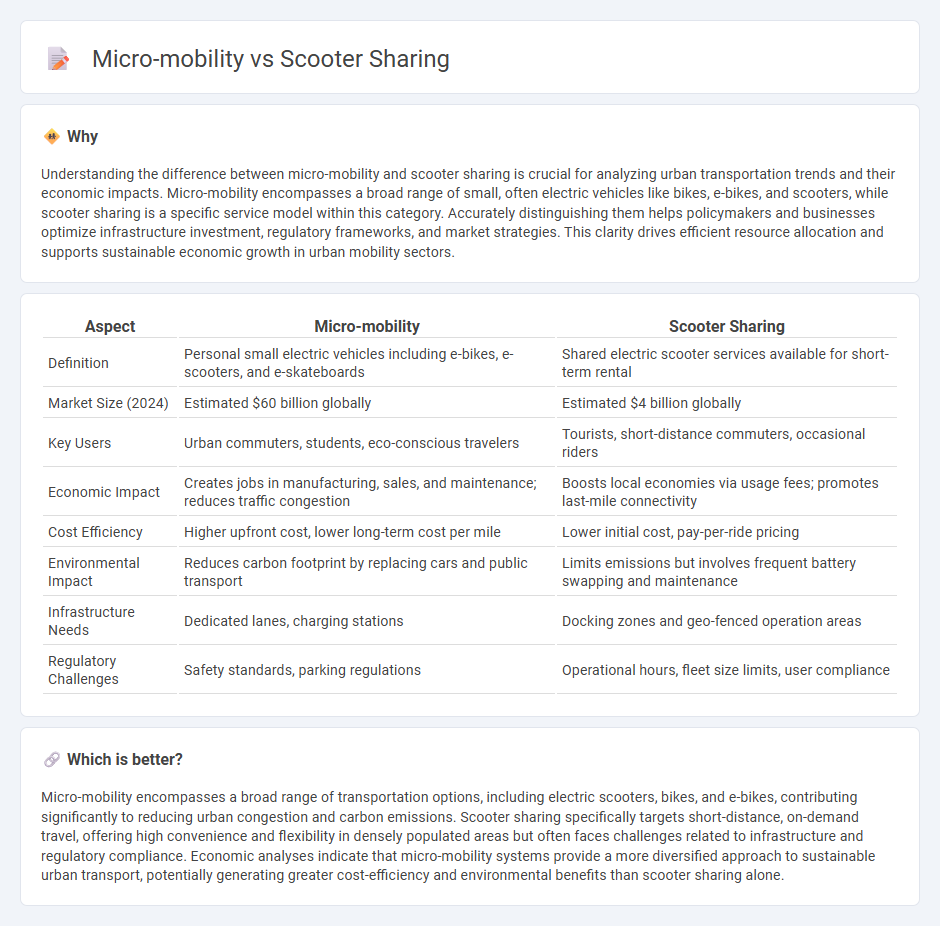
Understanding the difference between micro-mobility and scooter sharing is crucial for analyzing urban transportation trends and their economic impacts. Micro-mobility encompasses a broad range of small, often electric vehicles like bikes, e-bikes, and scooters, while scooter sharing is a specific service model within this category. Accurately distinguishing them helps policymakers and businesses optimize infrastructure investment, regulatory frameworks, and market strategies. This clarity drives efficient resource allocation and supports sustainable economic growth in urban mobility sectors.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Micro-mobility | Scooter Sharing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Personal small electric vehicles including e-bikes, e-scooters, and e-skateboards | Shared electric scooter services available for short-term rental |
| Market Size (2024) | Estimated $60 billion globally | Estimated $4 billion globally |
| Key Users | Urban commuters, students, eco-conscious travelers | Tourists, short-distance commuters, occasional riders |
| Economic Impact | Creates jobs in manufacturing, sales, and maintenance; reduces traffic congestion | Boosts local economies via usage fees; promotes last-mile connectivity |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher upfront cost, lower long-term cost per mile | Lower initial cost, pay-per-ride pricing |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces carbon footprint by replacing cars and public transport | Limits emissions but involves frequent battery swapping and maintenance |
| Infrastructure Needs | Dedicated lanes, charging stations | Docking zones and geo-fenced operation areas |
| Regulatory Challenges | Safety standards, parking regulations | Operational hours, fleet size limits, user compliance |
Which is better?
Micro-mobility encompasses a broad range of transportation options, including electric scooters, bikes, and e-bikes, contributing significantly to reducing urban congestion and carbon emissions. Scooter sharing specifically targets short-distance, on-demand travel, offering high convenience and flexibility in densely populated areas but often faces challenges related to infrastructure and regulatory compliance. Economic analyses indicate that micro-mobility systems provide a more diversified approach to sustainable urban transport, potentially generating greater cost-efficiency and environmental benefits than scooter sharing alone.
Connection
Micro-mobility and scooter sharing are interconnected by promoting sustainable urban transportation through compact, electric vehicles designed for short-distance travel. Scooter sharing platforms enhance accessibility, reduce traffic congestion, and lower emissions by providing affordable, convenient alternatives to traditional car use. This synergy drives economic growth by creating new market opportunities and supporting smart city infrastructure development.
Key Terms
Asset Utilization
Scooter sharing platforms maximize asset utilization by enabling multiple users to access a single scooter throughout the day, reducing idle time and increasing operational efficiency. Micro-mobility systems, which include bikes, e-scooters, and other compact vehicles, optimize asset use through flexible deployment in high-demand urban areas, enhancing last-mile connectivity. Explore further insights on how asset utilization drives innovation in micro-mobility solutions.
Cost Structure
Scooter sharing platforms typically incur costs related to vehicle maintenance, battery replacement, and operational expenses like redistribution and customer support. Micro-mobility services extend beyond scooters to include e-bikes and shared bicycles, diversifying cost structures with factors such as docking infrastructure and varied maintenance needs. Explore comprehensive analyses to understand how these cost differences impact scalability and profitability.
Market Penetration
Scooter sharing represents a significant segment of the micro-mobility market, with global market penetration reaching over 45% in urban areas as of 2023, driven by increasing environmental concerns and urban congestion. Micro-mobility also encompasses e-bikes and other small electric vehicles, which collectively are projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20% through 2030. Explore the latest trends and detailed analysis to understand how scooter sharing is shaping the future of urban transportation.
Source and External Links
Scooter-sharing system - Wikipedia - A scooter-sharing system offers electric motorized scooters for short-term rentals, typically dockless, providing fast and convenient last-mile urban transport with jobs for charging and maintenance as part of the ecosystem.
JET - scooter sharing on the App Store - Apple - JET is a mobile app-based electric scooter rental service operating in several cities, allowing easy rental by scanning a QR code without deposit, supporting up to five scooters per account.
WHOOSH | Electric Scooter and Bike Sharing - Parking - WHOOSH provides a scooter-sharing app where users register, locate, reserve, and unlock scooters via QR code and park them in designated areas, operating in multiple Latin American cities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com