De-dollarization represents a strategic shift as countries seek to reduce reliance on the US dollar, aiming to diversify reserve currencies and mitigate risks from dollar-centric economic policies. Dollar hegemony continues to dominate global trade and finance, reinforcing the dollar's status as the primary currency for international transactions and reserve holdings. Explore deeper insights into how these contrasting dynamics shape the future of the global economy.
Why it is important
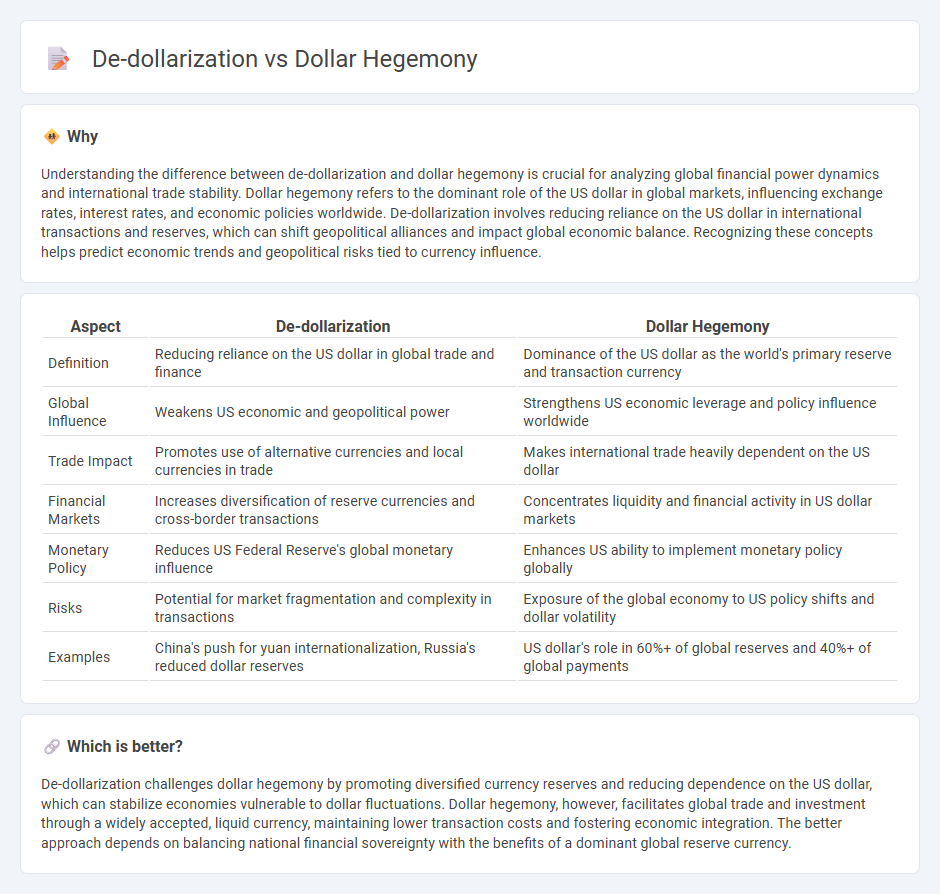
Understanding the difference between de-dollarization and dollar hegemony is crucial for analyzing global financial power dynamics and international trade stability. Dollar hegemony refers to the dominant role of the US dollar in global markets, influencing exchange rates, interest rates, and economic policies worldwide. De-dollarization involves reducing reliance on the US dollar in international transactions and reserves, which can shift geopolitical alliances and impact global economic balance. Recognizing these concepts helps predict economic trends and geopolitical risks tied to currency influence.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | De-dollarization | Dollar Hegemony |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reducing reliance on the US dollar in global trade and finance | Dominance of the US dollar as the world's primary reserve and transaction currency |
| Global Influence | Weakens US economic and geopolitical power | Strengthens US economic leverage and policy influence worldwide |
| Trade Impact | Promotes use of alternative currencies and local currencies in trade | Makes international trade heavily dependent on the US dollar |
| Financial Markets | Increases diversification of reserve currencies and cross-border transactions | Concentrates liquidity and financial activity in US dollar markets |
| Monetary Policy | Reduces US Federal Reserve's global monetary influence | Enhances US ability to implement monetary policy globally |
| Risks | Potential for market fragmentation and complexity in transactions | Exposure of the global economy to US policy shifts and dollar volatility |
| Examples | China's push for yuan internationalization, Russia's reduced dollar reserves | US dollar's role in 60%+ of global reserves and 40%+ of global payments |
Which is better?
De-dollarization challenges dollar hegemony by promoting diversified currency reserves and reducing dependence on the US dollar, which can stabilize economies vulnerable to dollar fluctuations. Dollar hegemony, however, facilitates global trade and investment through a widely accepted, liquid currency, maintaining lower transaction costs and fostering economic integration. The better approach depends on balancing national financial sovereignty with the benefits of a dominant global reserve currency.
Connection
De-dollarization involves countries reducing their reliance on the US dollar for international trade and reserves, directly challenging dollar hegemony, which is the dominance of the US dollar in global finance. This shift impacts global economic leverage by diversifying currency usage and reducing the dollar's influence on global markets. Persistent efforts in de-dollarization reflect strategic moves to minimize economic vulnerability linked to the dollar's central role in trade and finance.
Key Terms
Reserve Currency
Dollar hegemony remains dominant as the U.S. dollar accounts for over 59% of global foreign exchange reserves, underscoring its critical role in international finance. De-dollarization efforts are gaining momentum, with countries diversifying reserves into yuan, euro, and gold to reduce dependency on the dollar amidst geopolitical tensions and economic sanctions. Explore how shifting reserve currency dynamics could reshape global economic power and trade flows.
Petrodollar
The dollar hegemony is reinforced by the petrodollar system, where oil trade is predominantly conducted in U.S. dollars, maintaining global demand for the currency. De-dollarization efforts by countries like China and Russia aim to reduce reliance on the U.S. dollar in energy transactions, challenging the petrodollar's dominance. Explore the evolving dynamics of petrodollar influence and its impact on global economic power.
Currency Swap
Currency swaps play a crucial role in the dynamics between dollar hegemony and de-dollarization, enabling countries to bypass the US dollar in bilateral trade and finance. Nations like China and Russia have expanded their currency swap agreements to reduce dependence on the dollar, thereby challenging its global dominance. Explore how evolving currency swap frameworks impact the future of the international monetary system.
Source and External Links
The Future of Dollar Hegemony - The U.S. dollar dominates global finance as the primary reserve currency, enabling the U.S. to borrow cheaply, impose sanctions, and benefit from a strong currency, though challenges to its dominance are increasing.
Theorizing dollar hegemony, Part 1: the political economic ... - Dollar hegemony is rooted in U.S. economic, military, and political power and has evolved through two eras: Bretton Woods (1946-1971) focused on trade dominance, and the neoliberal era (1980-present) centered on financial dominance within global capitalism.
Dollar Hegemony: America's Unnamed Empire - Dollar hegemony depends on America's global political and military strength, including alliances like with Saudi Arabia, and can collapse through loss of political power or financial mismanagement such as excessive debt.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com