Reshoring and offshoring represent opposing strategies in global business operations, where reshoring involves bringing manufacturing and services back to the company's home country, while offshoring refers to relocating these processes to foreign nations to leverage cost advantages. Economic factors such as labor costs, supply chain reliability, and geopolitical stability heavily influence the decision-making process between these two approaches. Explore the economic implications and strategic benefits of reshoring versus offshoring to understand their impact on global commerce.
Why it is important
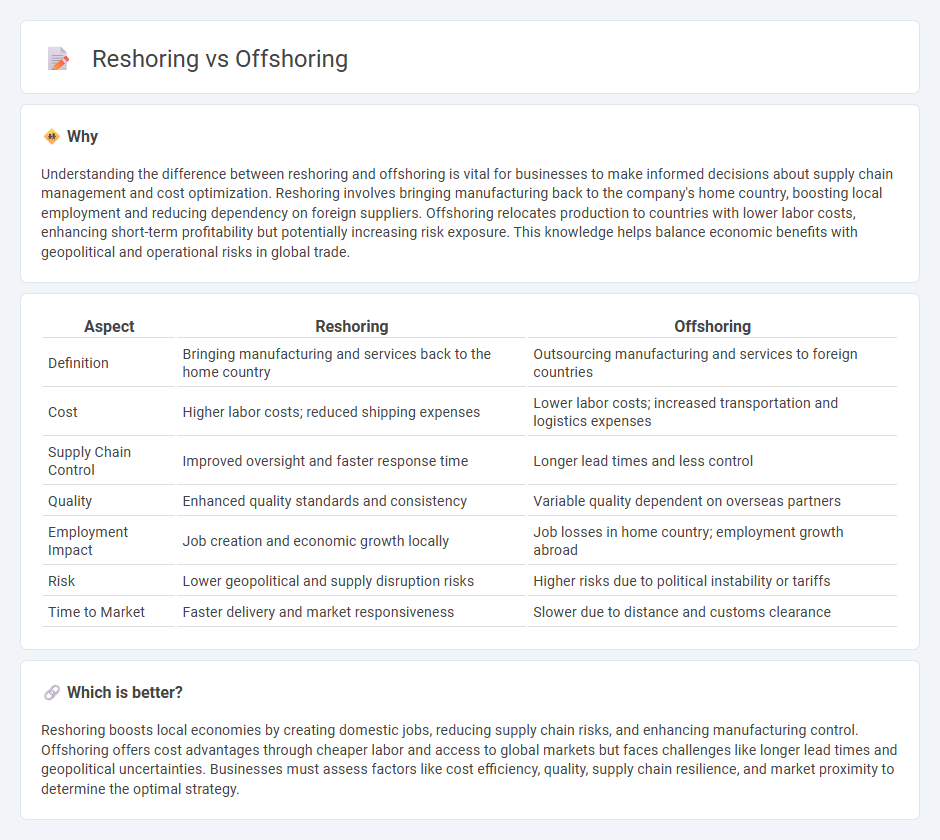
Understanding the difference between reshoring and offshoring is vital for businesses to make informed decisions about supply chain management and cost optimization. Reshoring involves bringing manufacturing back to the company's home country, boosting local employment and reducing dependency on foreign suppliers. Offshoring relocates production to countries with lower labor costs, enhancing short-term profitability but potentially increasing risk exposure. This knowledge helps balance economic benefits with geopolitical and operational risks in global trade.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Reshoring | Offshoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bringing manufacturing and services back to the home country | Outsourcing manufacturing and services to foreign countries |
| Cost | Higher labor costs; reduced shipping expenses | Lower labor costs; increased transportation and logistics expenses |
| Supply Chain Control | Improved oversight and faster response time | Longer lead times and less control |
| Quality | Enhanced quality standards and consistency | Variable quality dependent on overseas partners |
| Employment Impact | Job creation and economic growth locally | Job losses in home country; employment growth abroad |
| Risk | Lower geopolitical and supply disruption risks | Higher risks due to political instability or tariffs |
| Time to Market | Faster delivery and market responsiveness | Slower due to distance and customs clearance |
Which is better?
Reshoring boosts local economies by creating domestic jobs, reducing supply chain risks, and enhancing manufacturing control. Offshoring offers cost advantages through cheaper labor and access to global markets but faces challenges like longer lead times and geopolitical uncertainties. Businesses must assess factors like cost efficiency, quality, supply chain resilience, and market proximity to determine the optimal strategy.
Connection
Reshoring and offshoring represent inverse strategies in global supply chain management, where companies relocate production either back to their home country or to foreign nations to optimize costs and efficiency. The interplay between reshoring and offshoring is influenced by factors such as labor costs, trade policies, political stability, and supply chain resilience. Shifts in this dynamic affect global economic patterns, impacting employment rates, manufacturing output, and international trade balances.
Key Terms
Labor Costs
Labor costs significantly influence the decision between offshoring and reshoring, with offshoring often pursued to capitalize on cheaper wages in countries such as China, India, or Mexico. Reshoring is gaining traction as companies aim to reduce hidden expenses and risks related to long supply chains, favoring regions with higher labor costs but improved quality control and faster response times. Explore detailed labor cost comparisons and strategic implications to understand how these factors shape global manufacturing choices.
Supply Chain
Offshoring in supply chain management involves relocating production or services to foreign countries to leverage cost advantages, while reshoring refers to bringing manufacturing or operations back to the company's home country to enhance control and reduce risks. Companies increasingly weigh factors such as lead times, transportation costs, geopolitical stability, and supply chain resilience when choosing between offshoring and reshoring strategies. Explore detailed insights into optimizing supply chains through offshoring and reshoring decisions to improve efficiency and agility.
Domestic Manufacturing
Offshoring diverts production to lower-cost countries, often resulting in longer supply chains and increased exposure to geopolitical risks, while reshoring emphasizes revitalizing domestic manufacturing to enhance quality control, reduce lead times, and foster local job growth. Recent trends indicate that companies reshoring production back to the U.S. benefit from improved supply chain resilience and government incentives supporting domestic industry. Explore how reshoring initiatives can transform your manufacturing strategy and strengthen local economies.
Source and External Links
Offshoring - Wikipedia - Offshoring is the relocation of a business process from one country to another, often involving manufacturing or support functions, not necessarily outsourcing, and motivated by lower costs, access to skilled labor, or faster time to market.
Offshoring: Definition, Overview, Pros and Cons - Velocity Global - Offshoring involves moving business operations or services to another country to leverage lower labor costs, specialized skills, or global expansion benefits, often resulting in increased efficiencies and profitability.
What Is Offshoring? With Definition, Benefits and Tips | Indeed.com - Offshoring occurs when a company relocates a business function to a country with lower operational costs, distinct from outsourcing, and aims mainly at reducing expenses while maintaining business control over the process.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com