Circular economy emphasizes resource efficiency by minimizing waste through recycling and reuse, fostering sustainable production and consumption cycles. Bioeconomy focuses on utilizing renewable biological resources to produce food, energy, and industrial goods, promoting environmental sustainability and economic growth. Explore the key differences and benefits of circular economy versus bioeconomy to understand their impact on future economic development.
Why it is important
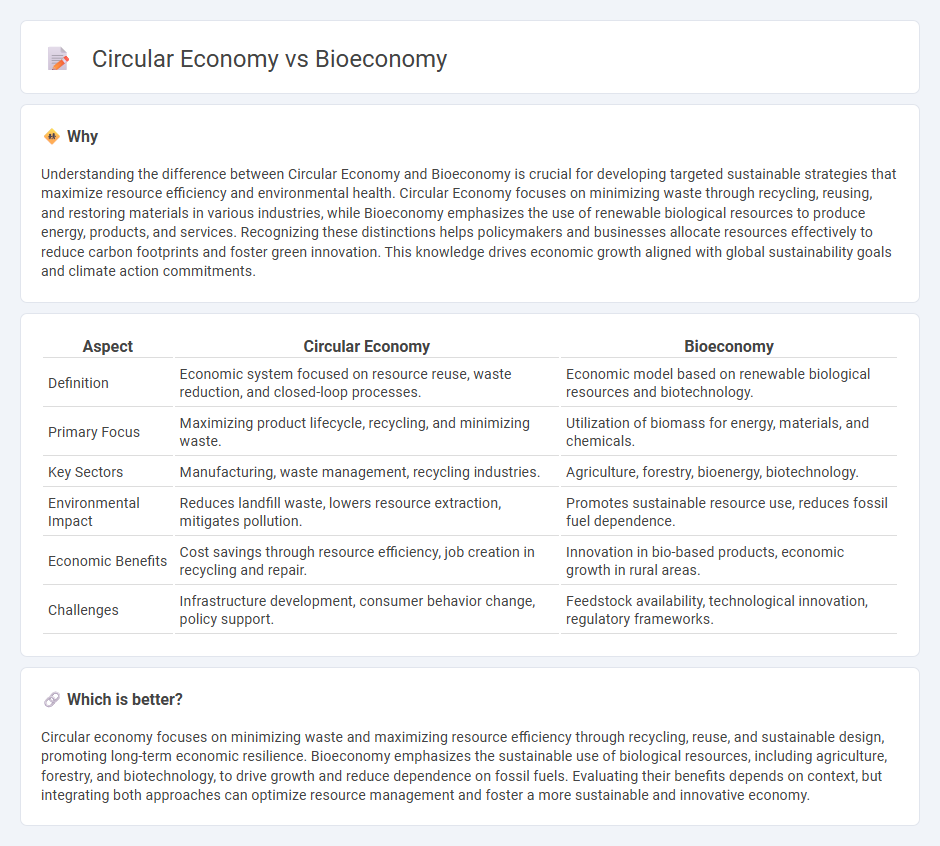
Understanding the difference between Circular Economy and Bioeconomy is crucial for developing targeted sustainable strategies that maximize resource efficiency and environmental health. Circular Economy focuses on minimizing waste through recycling, reusing, and restoring materials in various industries, while Bioeconomy emphasizes the use of renewable biological resources to produce energy, products, and services. Recognizing these distinctions helps policymakers and businesses allocate resources effectively to reduce carbon footprints and foster green innovation. This knowledge drives economic growth aligned with global sustainability goals and climate action commitments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Circular Economy | Bioeconomy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Economic system focused on resource reuse, waste reduction, and closed-loop processes. | Economic model based on renewable biological resources and biotechnology. |
| Primary Focus | Maximizing product lifecycle, recycling, and minimizing waste. | Utilization of biomass for energy, materials, and chemicals. |
| Key Sectors | Manufacturing, waste management, recycling industries. | Agriculture, forestry, bioenergy, biotechnology. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces landfill waste, lowers resource extraction, mitigates pollution. | Promotes sustainable resource use, reduces fossil fuel dependence. |
| Economic Benefits | Cost savings through resource efficiency, job creation in recycling and repair. | Innovation in bio-based products, economic growth in rural areas. |
| Challenges | Infrastructure development, consumer behavior change, policy support. | Feedstock availability, technological innovation, regulatory frameworks. |
Which is better?
Circular economy focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency through recycling, reuse, and sustainable design, promoting long-term economic resilience. Bioeconomy emphasizes the sustainable use of biological resources, including agriculture, forestry, and biotechnology, to drive growth and reduce dependence on fossil fuels. Evaluating their benefits depends on context, but integrating both approaches can optimize resource management and foster a more sustainable and innovative economy.
Connection
Circular economy and bioeconomy intersect through their shared emphasis on sustainable resource management and waste reduction. Circular economy promotes the continuous reuse and recycling of materials, while bioeconomy relies on renewable biological resources to create sustainable goods and energy. Both frameworks drive innovation in sustainable production systems that minimize environmental impact and support long-term economic growth.
Key Terms
Biomass
Bioeconomy leverages renewable biomass to produce sustainable bio-based products, energy, and materials, prioritizing biological resources and their efficient use. Circular economy emphasizes minimizing waste and resource inputs by recycling, reusing, and regenerating materials, including biomass, to create a closed-loop system. Explore the differences and synergies between biomass applications in bioeconomy and circular economy for sustainable development.
Resource Efficiency
Bioeconomy leverages renewable biological resources to produce food, materials, and energy, emphasizing sustainable agriculture and biotechnology innovations to reduce environmental impact. Circular economy prioritizes waste minimization by designing out waste and promoting reuse, repair, and recycling to extend product lifecycles and optimize resource efficiency. Explore how integrating bioeconomy and circular economy principles can maximize resource efficiency and drive sustainable development.
Waste Valorization
Waste valorization is a critical component in both bioeconomy and circular economy frameworks, targeting the efficient transformation of organic and inorganic waste into valuable products such as biofuels, bioplastics, and fertilizers. The bioeconomy emphasizes sustainable biomass utilization and biotechnology innovations to convert biological waste into energy and materials, while the circular economy prioritizes resource recovery and waste minimization through closed-loop systems. Explore the latest advancements and strategies in waste valorization to understand how these economies drive sustainability and economic growth.
Source and External Links
What is the bioeconomy and how can it drive sustainable development? - The bioeconomy uses renewable biological resources and cutting-edge technologies like gene editing to produce food, energy, and goods while promoting sustainability and reducing environmental impact.
Bioeconomy - Wikipedia - The bioeconomy encompasses economic activities using biological resources such as plants, animals, and biomass for food, bio-based products, bioenergy, and services, with a strong focus on sustainability and circularity.
Bioeconomy Strategy - European Commission - The EU bioeconomy integrates biomass production and conversion into food, materials, and energy to meet climate and environmental goals through innovation and circular economy principles.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com