Zero-day work contracts, characterized by their lack of guaranteed working hours, offer flexibility for employers while increasing income instability for workers compared to permanent contracts. Permanent contracts provide employees with job security, consistent wages, and social benefits, supporting economic stability for households. Explore the key economic impacts and worker rights implications of zero-day versus permanent work contracts to understand their broader societal effects.
Why it is important
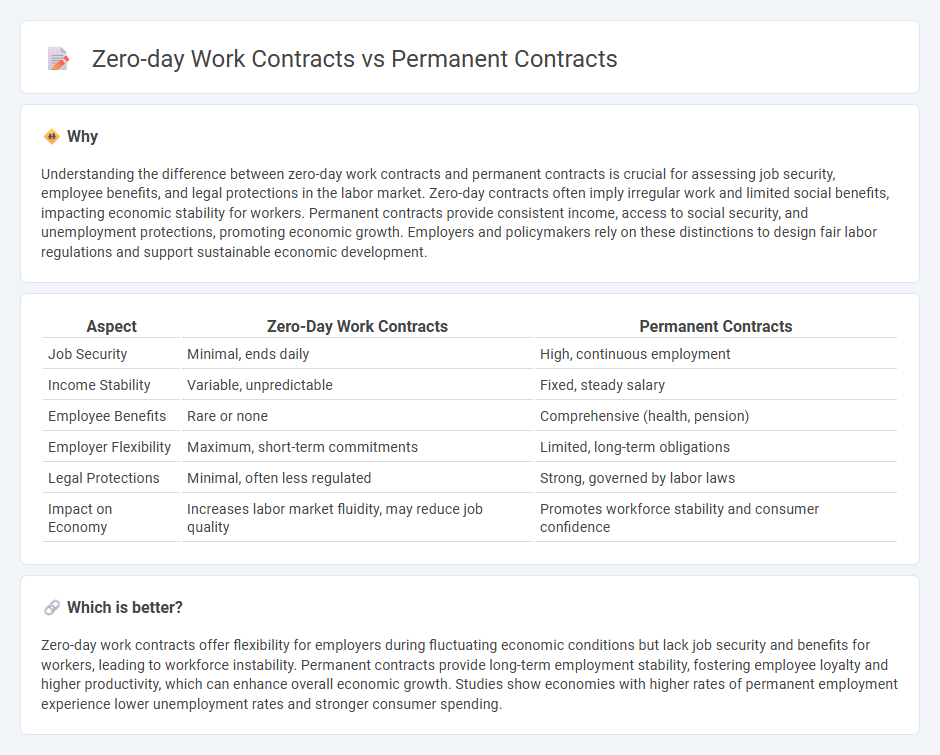
Understanding the difference between zero-day work contracts and permanent contracts is crucial for assessing job security, employee benefits, and legal protections in the labor market. Zero-day contracts often imply irregular work and limited social benefits, impacting economic stability for workers. Permanent contracts provide consistent income, access to social security, and unemployment protections, promoting economic growth. Employers and policymakers rely on these distinctions to design fair labor regulations and support sustainable economic development.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Zero-Day Work Contracts | Permanent Contracts |
|---|---|---|
| Job Security | Minimal, ends daily | High, continuous employment |
| Income Stability | Variable, unpredictable | Fixed, steady salary |
| Employee Benefits | Rare or none | Comprehensive (health, pension) |
| Employer Flexibility | Maximum, short-term commitments | Limited, long-term obligations |
| Legal Protections | Minimal, often less regulated | Strong, governed by labor laws |
| Impact on Economy | Increases labor market fluidity, may reduce job quality | Promotes workforce stability and consumer confidence |
Which is better?
Zero-day work contracts offer flexibility for employers during fluctuating economic conditions but lack job security and benefits for workers, leading to workforce instability. Permanent contracts provide long-term employment stability, fostering employee loyalty and higher productivity, which can enhance overall economic growth. Studies show economies with higher rates of permanent employment experience lower unemployment rates and stronger consumer spending.
Connection
Zero-day work contracts, often characterized by daily or short-term employment agreements, influence the stability and predictability of labor markets traditionally dominated by permanent contracts. The shift toward zero-day contracts affects economic productivity and employee job security, leading to changes in consumer spending and social welfare demands. Understanding the balance between zero-day work contracts and permanent contracts is crucial for policymakers aiming to foster sustainable economic growth and labor market flexibility.
Key Terms
Job Security
Permanent contracts offer employees consistent job security with predictable income, benefits, and legal protections that ensure stability over time. Zero-day work contracts, often gig-based or freelance, provide flexibility but lack guaranteed income and benefits, resulting in higher employment risk. Explore more about how contract types impact long-term career stability and worker protections.
Employee Rights
Permanent contracts provide employees with enhanced job security, comprehensive benefits, and clear pathways for career progression, ensuring protection under labor laws and access to social security. Zero-day work contracts, often characterized by episodic engagement without guaranteed hours or continuity, limit employee rights and obscure eligibility for benefits, often leaving workers vulnerable to exploitation. Explore the detailed differences in employee rights protection to understand the full impact of these contract types.
Flexibility
Permanent contracts offer job security with fixed terms and benefits, limiting flexibility for both employers and employees due to long-term commitment requirements. Zero-day work contracts provide maximum flexibility, enabling workers to engage in tasks without predetermined hours or duration, appealing to those seeking adaptable schedules. Explore more to understand how each contract type impacts workforce dynamics and personal work-life balance.
Source and External Links
Permanent Contract - Links International - A permanent contract, also called an indefinite or open-ended contract, is an employment agreement with no specified end date, offering job security and access to employee benefits as long as the employee complies with terms and conditions.
Understanding the Permanent Contract for Employers - A permanent contract legally binds employer and employee with no end date specified, outlining job responsibilities, salary, benefits, and termination terms, representing a long-term investment in the workforce.
What Is Permanent Contracts? - Sloneek(r) - Permanent contracts must include details like remuneration, working hours, benefits, statutory leave, and notice periods, protecting the rights and responsibilities of both parties in an ongoing employment relationship.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com