Quiet vacationing fosters mental rejuvenation by promoting mindfulness and reducing sensory overload, contrasting sharply with disengagement, which may lead to feelings of isolation and decreased productivity. Understanding the economic impact of these leisure styles reveals how consumer behavior shifts during periods of intentional rest versus complete withdrawal. Explore further to uncover the nuanced effects of vacationing habits on economic trends and workforce efficiency.
Why it is important
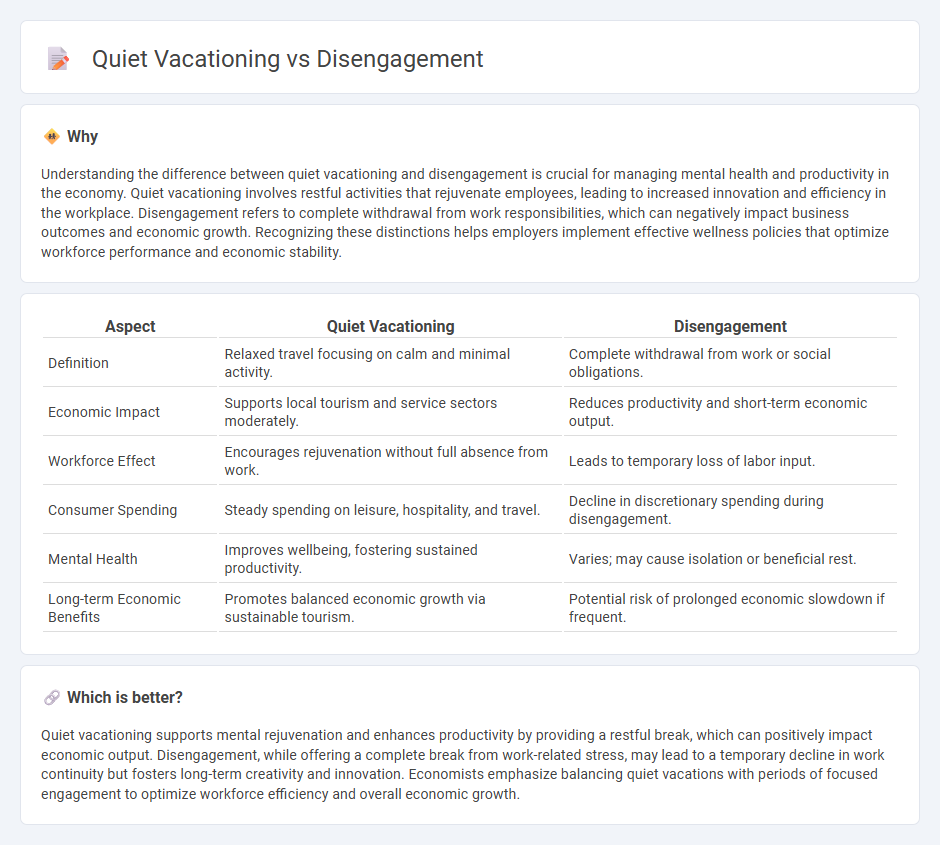
Understanding the difference between quiet vacationing and disengagement is crucial for managing mental health and productivity in the economy. Quiet vacationing involves restful activities that rejuvenate employees, leading to increased innovation and efficiency in the workplace. Disengagement refers to complete withdrawal from work responsibilities, which can negatively impact business outcomes and economic growth. Recognizing these distinctions helps employers implement effective wellness policies that optimize workforce performance and economic stability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quiet Vacationing | Disengagement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Relaxed travel focusing on calm and minimal activity. | Complete withdrawal from work or social obligations. |
| Economic Impact | Supports local tourism and service sectors moderately. | Reduces productivity and short-term economic output. |
| Workforce Effect | Encourages rejuvenation without full absence from work. | Leads to temporary loss of labor input. |
| Consumer Spending | Steady spending on leisure, hospitality, and travel. | Decline in discretionary spending during disengagement. |
| Mental Health | Improves wellbeing, fostering sustained productivity. | Varies; may cause isolation or beneficial rest. |
| Long-term Economic Benefits | Promotes balanced economic growth via sustainable tourism. | Potential risk of prolonged economic slowdown if frequent. |
Which is better?
Quiet vacationing supports mental rejuvenation and enhances productivity by providing a restful break, which can positively impact economic output. Disengagement, while offering a complete break from work-related stress, may lead to a temporary decline in work continuity but fosters long-term creativity and innovation. Economists emphasize balancing quiet vacations with periods of focused engagement to optimize workforce efficiency and overall economic growth.
Connection
Quiet vacationing promotes mental disengagement from work-related stress, enhancing overall economic productivity by reducing burnout and improving employee well-being. This form of relaxation supports cognitive recovery, leading to increased focus and innovation upon return to the workplace. Businesses and economies benefit as employees who disengage effectively during vacations tend to exhibit higher performance and reduced absenteeism.
Key Terms
Productivity
Disengagement involves completely detaching from work tasks to restore mental energy, leading to enhanced focus and productivity upon return. Quiet vacationing emphasizes low-key activities that reduce stress without full disconnection, promoting sustained creativity and efficient workflow. Discover more about optimizing productivity through strategic breaks and vacations.
Employee engagement
Disengagement in the workplace leads to decreased productivity and higher turnover rates, as employees feel disconnected from their roles and organizational goals. Quiet vacationing, characterized by employees taking meaningful breaks without digital distractions, significantly boosts mental well-being and restores focus, enhancing overall employee engagement upon return. Explore effective strategies to balance engagement and recuperation for sustained workplace performance.
Organizational culture
Disengagement in organizational culture refers to employees withdrawing emotionally or cognitively from their work, leading to decreased productivity and morale. Quiet vacationing symbolizes a subtle, non-intrusive break where employees recharge without overtly disconnecting, preserving organizational harmony. Explore techniques to balance engagement and quiet breaks within company culture for optimal performance.
Source and External Links
Emotional Disengagement - Marshall Digital Scholar - Emotional disengagement is a psychological pattern where a person suppresses or denies negative emotions, leading to difficulty in relating emotionally with others and impacting intimate relationships and family dynamics.
DISENGAGEMENT definition | Cambridge English Dictionary - Disengagement generally refers to the act or fact of stopping involvement in something, such as social activities, political engagement, or military operations.
Disengagement - Wikipedia - Disengagement can denote various concepts including apathy, social withdrawal, moral disengagement, military disengagement, and more, showing its broad applicability across disciplines and contexts.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com