Micro-dosing spending focuses on small, incremental investments that allow startups and small enterprises to validate ideas quickly and minimize financial risk. In contrast, industrial scaling involves substantial capital allocation for mass production and market expansion, leveraging economies of scale to reduce costs and maximize output. Explore deeper insights into how these spending strategies impact economic growth and business sustainability.
Why it is important
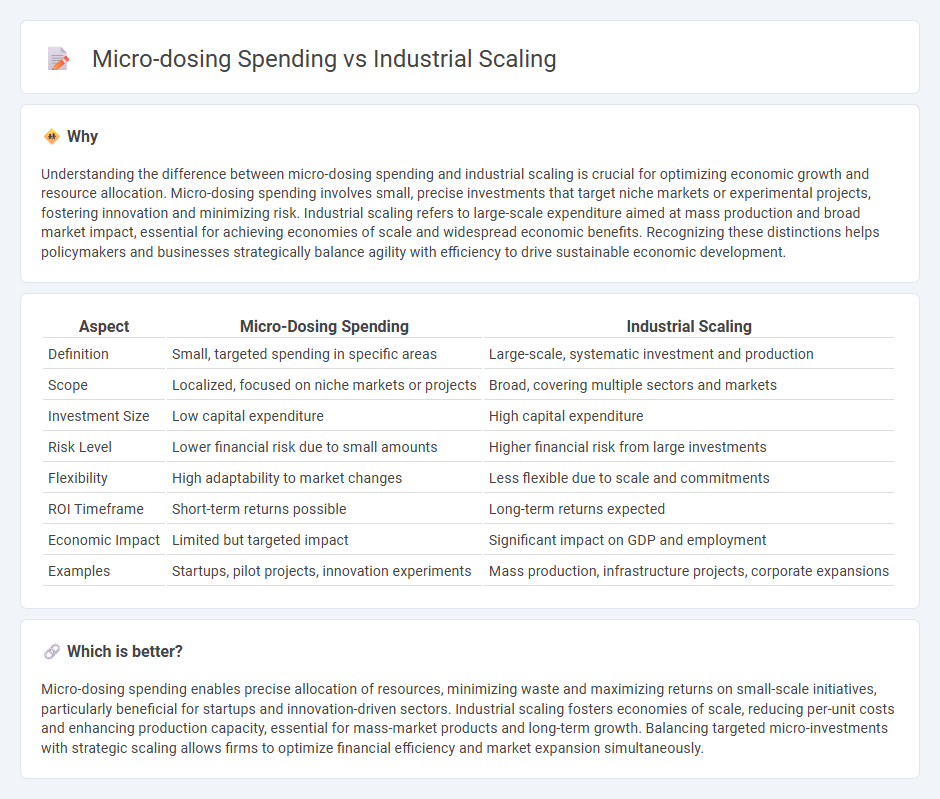
Understanding the difference between micro-dosing spending and industrial scaling is crucial for optimizing economic growth and resource allocation. Micro-dosing spending involves small, precise investments that target niche markets or experimental projects, fostering innovation and minimizing risk. Industrial scaling refers to large-scale expenditure aimed at mass production and broad market impact, essential for achieving economies of scale and widespread economic benefits. Recognizing these distinctions helps policymakers and businesses strategically balance agility with efficiency to drive sustainable economic development.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Micro-Dosing Spending | Industrial Scaling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Small, targeted spending in specific areas | Large-scale, systematic investment and production |
| Scope | Localized, focused on niche markets or projects | Broad, covering multiple sectors and markets |
| Investment Size | Low capital expenditure | High capital expenditure |
| Risk Level | Lower financial risk due to small amounts | Higher financial risk from large investments |
| Flexibility | High adaptability to market changes | Less flexible due to scale and commitments |
| ROI Timeframe | Short-term returns possible | Long-term returns expected |
| Economic Impact | Limited but targeted impact | Significant impact on GDP and employment |
| Examples | Startups, pilot projects, innovation experiments | Mass production, infrastructure projects, corporate expansions |
Which is better?
Micro-dosing spending enables precise allocation of resources, minimizing waste and maximizing returns on small-scale initiatives, particularly beneficial for startups and innovation-driven sectors. Industrial scaling fosters economies of scale, reducing per-unit costs and enhancing production capacity, essential for mass-market products and long-term growth. Balancing targeted micro-investments with strategic scaling allows firms to optimize financial efficiency and market expansion simultaneously.
Connection
Micro-dosing spending influences industrial scaling by enabling businesses to allocate resources incrementally based on real-time performance data, reducing financial risks while optimizing production capacities. This targeted expenditure approach supports gradual expansion, allowing industries to adjust scaling strategies dynamically in response to market demand and technological advancements. Efficient micro-dosing of capital fosters sustainable growth, enhancing operational agility and competitive advantage in fluctuating economic environments.
Key Terms
Economies of Scale
Industrial scaling leverages economies of scale to reduce per-unit costs significantly as production volume increases, optimizing resources and operational efficiency. In contrast, micro-dosing spending targets precise, small-scale investment to test market responses and minimize risks, often with higher per-unit costs but greater flexibility. Explore more to understand how balancing these approaches can maximize financial performance and operational agility.
Marginal Utility
Industrial scaling leverages economies of scale to optimize marginal utility by increasing production volume and reducing cost per unit, enhancing overall efficiency in resource allocation. Micro-dosing spending targets incremental benefits, aiming to maximize marginal utility through precise, smaller investments that yield targeted returns without significant capital outlay. Explore further to understand how marginal utility influences strategic decisions between these spending approaches.
Resource Allocation
Industrial scaling maximizes resource allocation by leveraging bulk purchasing, streamlined production processes, and economies of scale to reduce unit costs and increase profit margins. Micro-dosing spending targets precise, minimal resource use tailored to niche applications or sensitive processes, optimizing efficiency and reducing waste in high-value or experimental settings. Explore how strategic resource allocation differs between these approaches to enhance operational efficiency and cost management.
Source and External Links
7 tips for industrial scaling - beneficial for your colleagues as well - Industrial scaling refers to the comprehensive measures startups take to increase production capabilities, including technological solutions, process improvements, risk management, and refining business models to scale operations from pilot stages to global commercialization.
Industrial Weighing Scales - Industrial scales are precision instruments used to measure the weight of materials and products accurately in manufacturing, production, and logistics, designed for durability and versatility in diverse industries such as pharmaceuticals, automotive, and agriculture.
Industrial Floor Scales & Platform Scales - Scales Plus - Industrial floor scales, or platform scales, support heavy-capacity weighing tasks in industrial and agricultural environments, facilitating the weighing of large items like pallets and drums with robust construction suitable for harsh or hygienic settings.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com