De-dollarization involves reducing reliance on the US dollar in international trade, aiming to mitigate risks associated with dollar fluctuations and US economic policies. A multipolar currency system promotes the use of multiple global currencies, such as the euro, yuan, and yen, to enhance financial stability and diversify economic influence. Explore in-depth analyses on how these strategies reshape global economic dynamics.
Why it is important
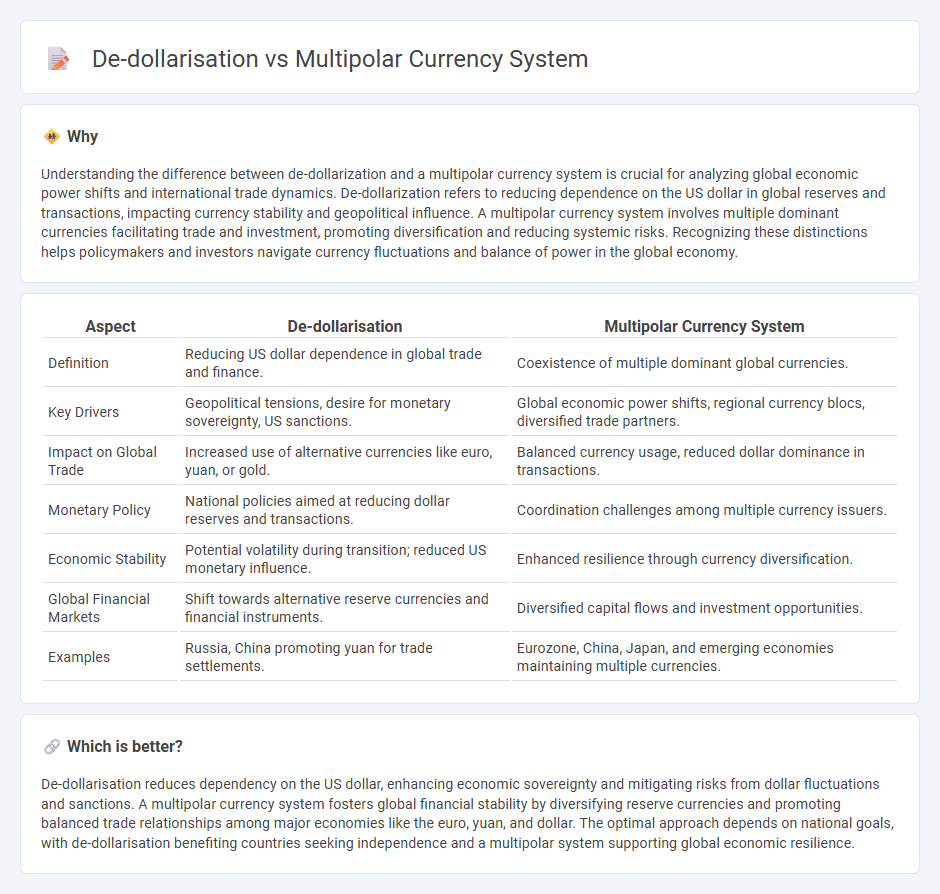
Understanding the difference between de-dollarization and a multipolar currency system is crucial for analyzing global economic power shifts and international trade dynamics. De-dollarization refers to reducing dependence on the US dollar in global reserves and transactions, impacting currency stability and geopolitical influence. A multipolar currency system involves multiple dominant currencies facilitating trade and investment, promoting diversification and reducing systemic risks. Recognizing these distinctions helps policymakers and investors navigate currency fluctuations and balance of power in the global economy.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | De-dollarisation | Multipolar Currency System |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reducing US dollar dependence in global trade and finance. | Coexistence of multiple dominant global currencies. |
| Key Drivers | Geopolitical tensions, desire for monetary sovereignty, US sanctions. | Global economic power shifts, regional currency blocs, diversified trade partners. |
| Impact on Global Trade | Increased use of alternative currencies like euro, yuan, or gold. | Balanced currency usage, reduced dollar dominance in transactions. |
| Monetary Policy | National policies aimed at reducing dollar reserves and transactions. | Coordination challenges among multiple currency issuers. |
| Economic Stability | Potential volatility during transition; reduced US monetary influence. | Enhanced resilience through currency diversification. |
| Global Financial Markets | Shift towards alternative reserve currencies and financial instruments. | Diversified capital flows and investment opportunities. |
| Examples | Russia, China promoting yuan for trade settlements. | Eurozone, China, Japan, and emerging economies maintaining multiple currencies. |
Which is better?
De-dollarisation reduces dependency on the US dollar, enhancing economic sovereignty and mitigating risks from dollar fluctuations and sanctions. A multipolar currency system fosters global financial stability by diversifying reserve currencies and promoting balanced trade relationships among major economies like the euro, yuan, and dollar. The optimal approach depends on national goals, with de-dollarisation benefiting countries seeking independence and a multipolar system supporting global economic resilience.
Connection
De-dollarisation reduces reliance on the US dollar by encouraging countries to use alternative currencies, fostering a multipolar currency system where multiple currencies hold significant global economic influence. This shift promotes diversification in international trade and finance, mitigating risks associated with dollar dominance and US monetary policy fluctuations. The emergence of regional currencies and digital assets further accelerates the transition toward a multipolar currency environment, reshaping global economic power dynamics.
Key Terms
Reserve Currency
A multipolar currency system involves multiple currencies, such as the Chinese yuan, euro, and yen, sharing reserve currency status alongside the US dollar, reducing reliance on a single dominant currency. De-dollarisation highlights efforts by countries to diversify foreign exchange reserves and international trade settlements away from the US dollar to limit exposure to American financial policies and sanctions. Explore deeper insights on how changing reserve currency dynamics are reshaping global economic power.
Exchange Rate Regime
A multipolar currency system features several dominant currencies influencing global exchange rates, providing diverse monetary alternatives and reducing dependency on a single currency, unlike de-dollarisation which specifically targets diminishing the U.S. dollar's hegemony. Exchange rate regimes in multipolar systems often involve managed floats or currency baskets to stabilize trade, whereas de-dollarisation may prompt countries to adopt local currencies or regional currencies with fixed or flexible rates to insulate from dollar volatility. Explore the nuances of how these frameworks impact global financial stability and economic sovereignty.
Currency Diversification
A multipolar currency system promotes currency diversification by allowing multiple currencies to coexist as global reserves, reducing reliance on the US dollar and mitigating exchange rate risks. De-dollarisation accelerates this trend by encouraging countries and corporations to shift their reserves and transactions away from the dollar towards alternative currencies like the euro, yuan, or gold-backed digital currencies. Explore how strategic currency diversification shapes the evolving global financial landscape.
Source and External Links
Multipolar Dollar - Institute of Political Economy - A multipolar currency system reduces reliance on a single reserve currency like the US dollar, promoting economic stability, enhancing global trade efficiency, and increasing geopolitical independence by limiting one nation's dominance in financial flows.
The New Multi-polar International Monetary System - This system reflects a shift from a unipolar US-dollar dominated order to one where multiple currencies from emerging powers like BRIC countries share reserve currency status, though requiring strong global cooperation to manage risks like exchange rate volatility.
Two Views of the International Monetary System - A multipolar international monetary system is possible but depends on coordinated and stable policies among central banks and governments, with institutions like the IMF playing a key role in providing coordination and liquidity assurance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com