Shein's rapid growth has revolutionized the global economy by leveraging a highly efficient supply chain and data-driven fast fashion model, outperforming traditional dropshipping methods in speed and scalability. While dropshipping relies on third-party suppliers and often faces inventory and shipping challenges, Shein's vertically integrated approach controls production, quality, and distribution, drastically reducing lead times and costs. Explore how these contrasting models impact market dynamics and consumer behavior in the evolving e-commerce landscape.
Why it is important
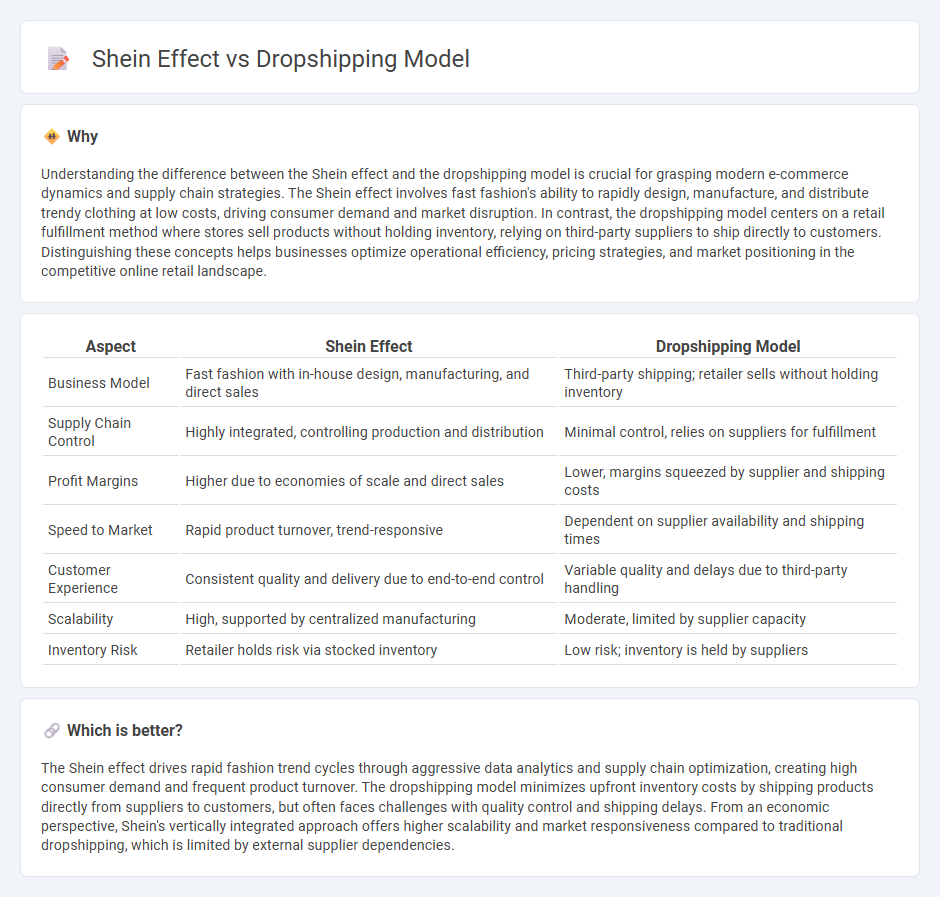
Understanding the difference between the Shein effect and the dropshipping model is crucial for grasping modern e-commerce dynamics and supply chain strategies. The Shein effect involves fast fashion's ability to rapidly design, manufacture, and distribute trendy clothing at low costs, driving consumer demand and market disruption. In contrast, the dropshipping model centers on a retail fulfillment method where stores sell products without holding inventory, relying on third-party suppliers to ship directly to customers. Distinguishing these concepts helps businesses optimize operational efficiency, pricing strategies, and market positioning in the competitive online retail landscape.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Shein Effect | Dropshipping Model |
|---|---|---|
| Business Model | Fast fashion with in-house design, manufacturing, and direct sales | Third-party shipping; retailer sells without holding inventory |
| Supply Chain Control | Highly integrated, controlling production and distribution | Minimal control, relies on suppliers for fulfillment |
| Profit Margins | Higher due to economies of scale and direct sales | Lower, margins squeezed by supplier and shipping costs |
| Speed to Market | Rapid product turnover, trend-responsive | Dependent on supplier availability and shipping times |
| Customer Experience | Consistent quality and delivery due to end-to-end control | Variable quality and delays due to third-party handling |
| Scalability | High, supported by centralized manufacturing | Moderate, limited by supplier capacity |
| Inventory Risk | Retailer holds risk via stocked inventory | Low risk; inventory is held by suppliers |
Which is better?
The Shein effect drives rapid fashion trend cycles through aggressive data analytics and supply chain optimization, creating high consumer demand and frequent product turnover. The dropshipping model minimizes upfront inventory costs by shipping products directly from suppliers to customers, but often faces challenges with quality control and shipping delays. From an economic perspective, Shein's vertically integrated approach offers higher scalability and market responsiveness compared to traditional dropshipping, which is limited by external supplier dependencies.
Connection
The Shein effect drives rapid inventory turnover and low-cost fashion, heavily relying on the dropshipping model to minimize upfront investment and streamline global supply chains. Dropshipping enables Shein to offer vast product varieties without maintaining extensive physical stock, reducing overhead and enhancing responsiveness to market trends. This synergy accelerates e-commerce growth and disrupts traditional retail economies by leveraging agile, demand-driven logistics.
Key Terms
Supply Chain Integration
The dropshipping model relies on third-party suppliers to ship products directly to customers, minimizing inventory costs but often resulting in longer delivery times and less control over product quality. In contrast, the Shein effect exemplifies end-to-end supply chain integration, enabling ultra-fast fashion cycles through real-time data analytics, in-house manufacturing, and sophisticated logistics. Explore deeper insights into how these distinct supply chain strategies shape modern e-commerce success.
Inventory Management
The dropshipping model minimizes inventory risks by allowing retailers to sell products without holding stock, relying on suppliers to fulfill orders directly to customers. In contrast, the Shein effect leverages rapid inventory turnover and data-driven demand forecasting to maintain a dynamic and responsive stock, enabling faster adaptation to fashion trends. Explore how these differing inventory management strategies impact scalability and profitability in e-commerce.
Direct-to-Consumer (DTC)
The dropshipping model enables retailers to sell products directly from suppliers without holding inventory, reducing upfront costs but often compromising on shipping times and quality control. The Shein effect revolutionizes Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) by combining fast fashion with aggressive digital marketing and efficient global supply chain management, offering trendy products at ultra-competitive prices. Explore how DTC strategies are evolving with these models to capitalize on consumer demand and supply chain innovations.
Source and External Links
What is dropshipping & does it work in 2025? - Dropshipping is a business model where you sell products without holding inventory, and your supplier ships directly to customers, taking care of fulfillment.
Dropshipping Business Model: All You Need to Know - In dropshipping, an eCommerce business takes orders from customers but relies on a supplier to deliver products directly, allowing focus mainly on marketing rather than inventory management.
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? (2025) - Dropshipping involves partnering with suppliers who store, package, and ship products, enabling you to sell items via your online store without keeping inventory yourself.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com