Sustainable finance focuses on investment strategies that prioritize environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to promote long-term socio-economic benefits, contrasting with traditional finance, which primarily targets short-term financial returns. By integrating sustainability metrics, sustainable finance supports projects that reduce carbon emissions, enhance social equity, and foster responsible corporate behavior. Explore how sustainable finance is transforming the banking sector and reshaping investment priorities.
Why it is important
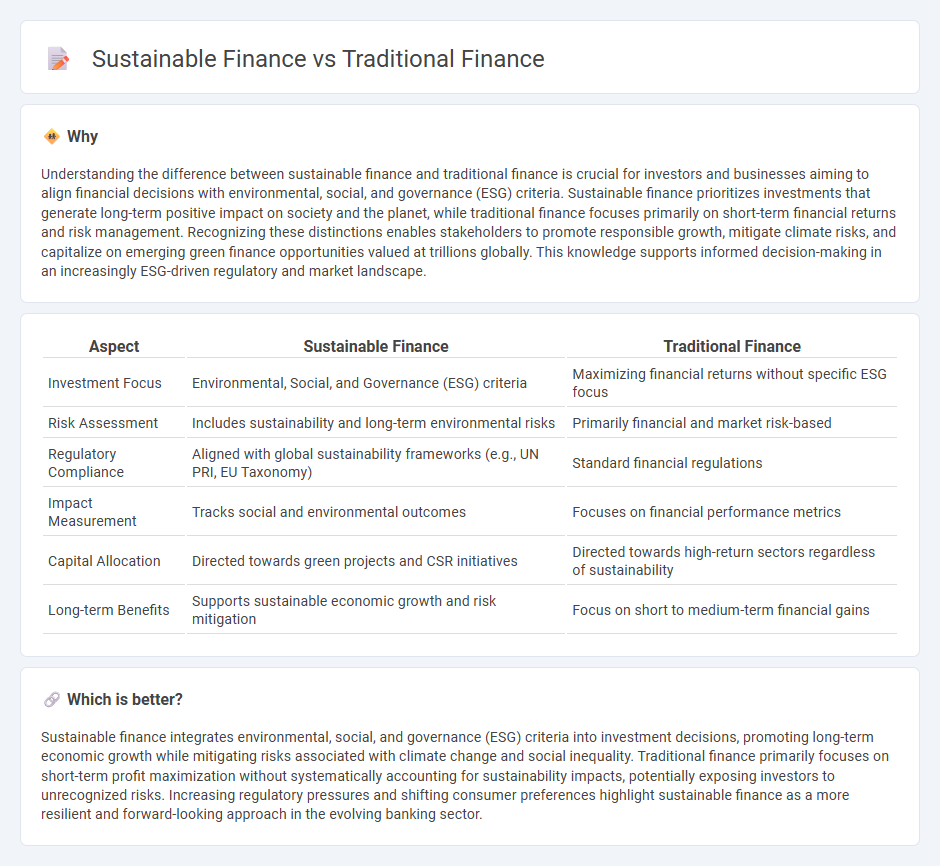
Understanding the difference between sustainable finance and traditional finance is crucial for investors and businesses aiming to align financial decisions with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria. Sustainable finance prioritizes investments that generate long-term positive impact on society and the planet, while traditional finance focuses primarily on short-term financial returns and risk management. Recognizing these distinctions enables stakeholders to promote responsible growth, mitigate climate risks, and capitalize on emerging green finance opportunities valued at trillions globally. This knowledge supports informed decision-making in an increasingly ESG-driven regulatory and market landscape.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Sustainable Finance | Traditional Finance |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Focus | Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria | Maximizing financial returns without specific ESG focus |
| Risk Assessment | Includes sustainability and long-term environmental risks | Primarily financial and market risk-based |
| Regulatory Compliance | Aligned with global sustainability frameworks (e.g., UN PRI, EU Taxonomy) | Standard financial regulations |
| Impact Measurement | Tracks social and environmental outcomes | Focuses on financial performance metrics |
| Capital Allocation | Directed towards green projects and CSR initiatives | Directed towards high-return sectors regardless of sustainability |
| Long-term Benefits | Supports sustainable economic growth and risk mitigation | Focus on short to medium-term financial gains |
Which is better?
Sustainable finance integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into investment decisions, promoting long-term economic growth while mitigating risks associated with climate change and social inequality. Traditional finance primarily focuses on short-term profit maximization without systematically accounting for sustainability impacts, potentially exposing investors to unrecognized risks. Increasing regulatory pressures and shifting consumer preferences highlight sustainable finance as a more resilient and forward-looking approach in the evolving banking sector.
Connection
Sustainable finance integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into traditional banking practices to enhance long-term financial stability and risk management. Traditional finance institutions are increasingly adopting green bonds, ESG investing, and impact financing to align with global sustainability goals while maintaining profitability. This convergence drives innovation in credit assessment and portfolio management, fostering a resilient and responsible financial ecosystem.
Key Terms
Risk Management
Traditional finance primarily emphasizes financial risks such as credit, market, and liquidity risks to protect investors and institutions. Sustainable finance integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into risk management, addressing long-term impacts like climate change and social inequality that can affect financial performance. Explore how sustainable finance redefines risk frameworks to support resilient and ethical investment practices.
ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance)
Traditional finance primarily emphasizes financial returns and risk management, often overlooking environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. Sustainable finance integrates ESG criteria to promote long-term value creation, addressing climate change, social equity, and corporate governance standards. Explore the growing impact of ESG-driven investments and their role in reshaping financial markets.
Return on Investment (ROI)
Traditional finance prioritizes maximizing Return on Investment (ROI) through short-term financial gains and risk-adjusted returns, often relying on conventional assets and market performance. Sustainable finance integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into investment decisions, aiming for both competitive ROI and long-term positive impact on society and the planet. Explore how integrating sustainability reshapes ROI metrics and investment strategies.
Source and External Links
What is meant by 'traditional finance'? - Pegasus Funding - Traditional finance refers to established funding methods used by businesses through lenders such as banks, credit unions, and conventional financial products including loans, overdrafts, mortgages, credit lines, invoice factoring, and trade finance.
TradFi Meaning - Ledger - TradFi, or traditional finance, is the conventional centralized financial system managed by institutions like banks and stock markets, operating under government regulation and contrasting with decentralized finance (DeFi).
TradFi ( Traditional Finance ) - Liminal Custody - Traditional finance (TradFi) encompasses long-established centralized financial systems and services such as banking, insurance, and stock exchanges, characterized by regulatory oversight, consumer protections, and slower innovation compared to DeFi.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com