Sustainable investing integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to support companies with positive societal impact, contrasting with negative screening, which excludes investments based on specific industries or practices like fossil fuels or tobacco. This approach drives capital toward ethical businesses while maintaining competitive financial returns. Discover how these strategies reshape the future of banking and responsible investment.
Why it is important
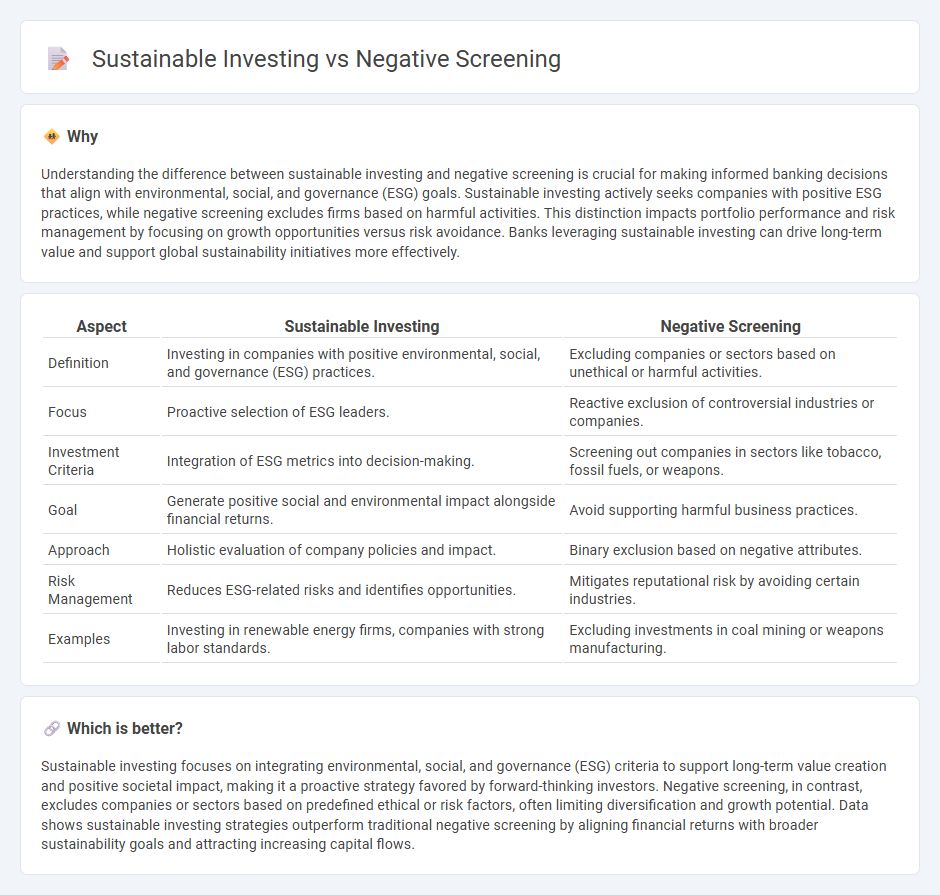
Understanding the difference between sustainable investing and negative screening is crucial for making informed banking decisions that align with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals. Sustainable investing actively seeks companies with positive ESG practices, while negative screening excludes firms based on harmful activities. This distinction impacts portfolio performance and risk management by focusing on growth opportunities versus risk avoidance. Banks leveraging sustainable investing can drive long-term value and support global sustainability initiatives more effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Sustainable Investing | Negative Screening |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investing in companies with positive environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices. | Excluding companies or sectors based on unethical or harmful activities. |
| Focus | Proactive selection of ESG leaders. | Reactive exclusion of controversial industries or companies. |
| Investment Criteria | Integration of ESG metrics into decision-making. | Screening out companies in sectors like tobacco, fossil fuels, or weapons. |
| Goal | Generate positive social and environmental impact alongside financial returns. | Avoid supporting harmful business practices. |
| Approach | Holistic evaluation of company policies and impact. | Binary exclusion based on negative attributes. |
| Risk Management | Reduces ESG-related risks and identifies opportunities. | Mitigates reputational risk by avoiding certain industries. |
| Examples | Investing in renewable energy firms, companies with strong labor standards. | Excluding investments in coal mining or weapons manufacturing. |
Which is better?
Sustainable investing focuses on integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to support long-term value creation and positive societal impact, making it a proactive strategy favored by forward-thinking investors. Negative screening, in contrast, excludes companies or sectors based on predefined ethical or risk factors, often limiting diversification and growth potential. Data shows sustainable investing strategies outperform traditional negative screening by aligning financial returns with broader sustainability goals and attracting increasing capital flows.
Connection
Sustainable investing integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to allocate capital towards responsible businesses, while negative screening excludes companies that engage in harmful activities like fossil fuels or tobacco. Both strategies align portfolios with ethical values by proactively avoiding investments that contradict sustainability goals. This connection enhances risk management and supports long-term financial performance by promoting corporate accountability and environmental stewardship.
Key Terms
Exclusion Criteria
Negative screening involves excluding companies or sectors based on specific exclusion criteria such as tobacco, fossil fuels, or weapons, aiming to avoid investments conflicting with ethical standards. Sustainable investing incorporates broader exclusion criteria but emphasizes ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) factors alongside positive impact and corporate responsibility. Explore detailed differences in exclusion practices and criteria for a deeper understanding of sustainable investment strategies.
ESG Integration
Negative screening excludes companies based on specific ESG criteria, such as fossil fuel involvement or poor labor practices, effectively filtering out high-risk or unethical investments. Sustainable investing integrates ESG factors directly into the decision-making process, balancing financial returns with positive environmental and social impact to create long-term value. Explore how ESG integration enhances investment strategies beyond traditional negative screening approaches.
Values Alignment
Negative screening filters out companies that do not meet specific ethical, environmental, or social criteria, ensuring investments avoid conflicting industries such as tobacco or fossil fuels. Sustainable investing incorporates positive criteria by selecting companies with strong environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance, promoting long-term value creation aligned with investors' values. Explore how these approaches can tailor your portfolio to better reflect your personal values and impact goals.
Source and External Links
Positive and Negative Investment Screening Explained - CNote - Negative screening is a method that excludes investments in companies whose activities contradict the investor's values, typically removing those with negative social or environmental impacts, such as companies involved in corruption, high greenhouse gas emissions, or poor diversity standards, making it widely inclusive and focused on "do no harm" impact investing.
Negative screening | EDHEC Impact Institute - Negative screening eliminates securities considered unethical or immoral--often sin stocks like alcohol, tobacco, gambling, and weapons--based on religious, philosophical, or internationally recognized norms such as UN Global Compact and human rights standards.
Positive and negative approaches - Candriam - Negative screening is an exclusionary approach used historically by religious and social investors, removing from portfolios companies involved in controversial industries like tobacco, alcohol, and firearms or those with poor human rights or environmental records, sometimes applying revenue thresholds rather than total exclusion.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com