Behavioral biometrics analyze patterns in user behavior, such as typing rhythm and mouse movement, offering dynamic security measures for banking authentication. Static biometrics rely on physical traits like fingerprints or facial recognition, providing a fixed reference for identity verification. Explore how these biometric technologies enhance fraud prevention and secure access in modern banking systems.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between behavioral biometrics and static biometrics is crucial in banking for enhancing security protocols and preventing fraud. Behavioral biometrics analyze patterns like typing rhythm and mouse movements, while static biometrics rely on unchanging physical traits such as fingerprints and facial recognition. Financial institutions use behavioral biometrics to continuously authenticate users, reducing the risk of unauthorized access after login. Mastery of both types improves multi-factor authentication systems, leading to safer banking experiences.
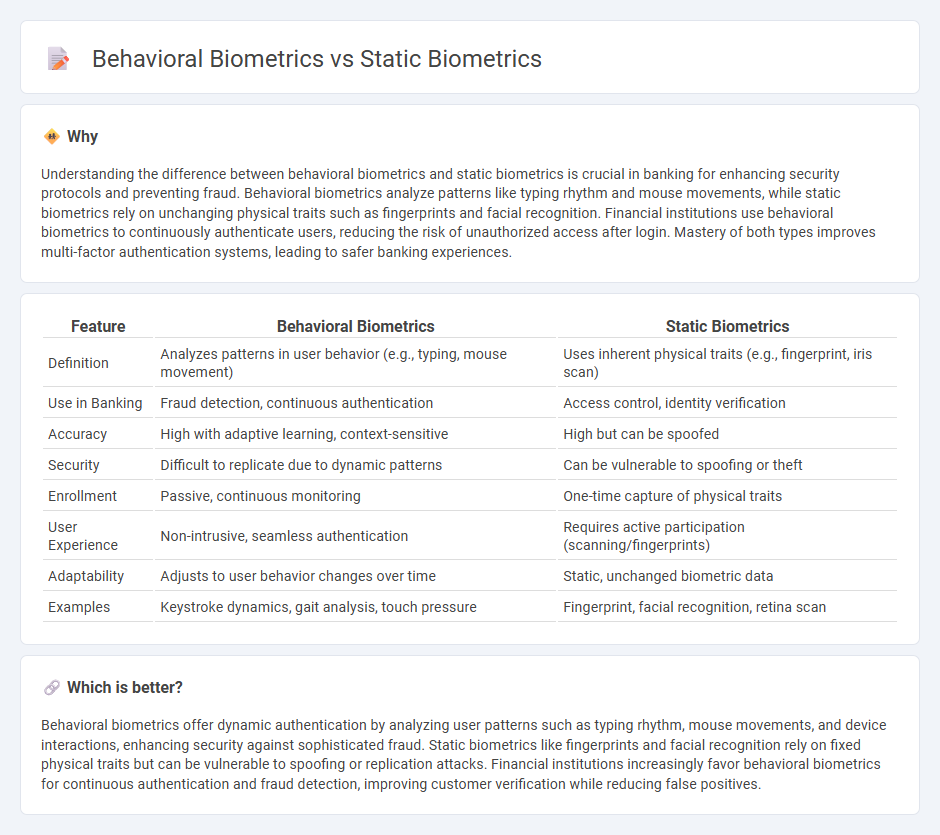
Comparison Table
| Feature | Behavioral Biometrics | Static Biometrics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analyzes patterns in user behavior (e.g., typing, mouse movement) | Uses inherent physical traits (e.g., fingerprint, iris scan) |
| Use in Banking | Fraud detection, continuous authentication | Access control, identity verification |
| Accuracy | High with adaptive learning, context-sensitive | High but can be spoofed |
| Security | Difficult to replicate due to dynamic patterns | Can be vulnerable to spoofing or theft |
| Enrollment | Passive, continuous monitoring | One-time capture of physical traits |
| User Experience | Non-intrusive, seamless authentication | Requires active participation (scanning/fingerprints) |
| Adaptability | Adjusts to user behavior changes over time | Static, unchanged biometric data |
| Examples | Keystroke dynamics, gait analysis, touch pressure | Fingerprint, facial recognition, retina scan |
Which is better?
Behavioral biometrics offer dynamic authentication by analyzing user patterns such as typing rhythm, mouse movements, and device interactions, enhancing security against sophisticated fraud. Static biometrics like fingerprints and facial recognition rely on fixed physical traits but can be vulnerable to spoofing or replication attacks. Financial institutions increasingly favor behavioral biometrics for continuous authentication and fraud detection, improving customer verification while reducing false positives.
Connection
Behavioral biometrics analyze patterns in user interactions such as typing rhythm and mouse movements, while static biometrics focus on immutable physical traits like fingerprints and facial recognition. Both biometric approaches integrate to enhance banking security by providing multi-layered authentication that detects fraud and prevents unauthorized access. Combining static biometric templates with real-time behavioral data creates a comprehensive identity verification system crucial for safeguarding digital banking transactions.
Key Terms
Fingerprint recognition
Fingerprint recognition, a form of static biometrics, relies on analyzing unique physical patterns such as ridges and minutiae points on a finger for identity verification. In contrast, behavioral biometrics assess dynamic patterns like typing rhythm or gait, which are less applicable to fingerprint technology. Explore deeper insights into the technological nuances and application contexts of fingerprint recognition versus behavioral biometrics.
Keystroke dynamics
Static biometrics rely on immutable physical characteristics such as fingerprints or facial features, while behavioral biometrics like keystroke dynamics analyze unique patterns in typing rhythm, speed, and pressure. Keystroke dynamics provide continuous authentication by monitoring typing patterns, enhancing security in environments where static biometrics may be insufficient or impractical. Discover how keystroke dynamics can transform authentication systems with adaptive, real-time behavioral analysis.
Voice authentication
Voice authentication leverages behavioral biometrics by analyzing unique vocal patterns such as pitch, tone, and speech rhythm, whereas static biometrics rely on fixed physical characteristics like fingerprints or facial features. Behavioral voice biometrics provide continuous verification, enhancing security in dynamic environments and reducing the risk of spoofing. Explore how voice authentication revolutionizes identity verification and improves user experience.
Source and External Links
What are biometrics? - Static biometrics use physical features like fingerprint scans or facial recognition to authenticate users by creating and comparing encrypted digital models of their physical traits, often including liveness detection to prevent spoofing attacks.
Behavioral vs. Static Biometrics: Dynamic Fraud Detection ... - Static biometrics rely on unique physical data points such as fingerprints or facial features for identification, but they raise concerns because the data is unchangeable, can be stolen or misused, and static biometrics have limitations such as demographic bias and vulnerability to fraud.
BioCatch Highlights Benefits of Behavioral Biometrics vs ... - Static biometric methods like fingerprint, voice, iris, and facial recognition provide stronger security than passwords but are still a single static factor that cannot be changed if compromised, limiting their long-term security compared to behavioral biometrics.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com