Debt recycling is a financial strategy that involves converting non-deductible home loan debt into tax-deductible investment debt to optimize wealth building. Split loans divide a mortgage into separate portions with different interest rates or repayment terms, offering flexibility and risk management. Discover how each approach can impact your loan structure and financial goals.
Why it is important
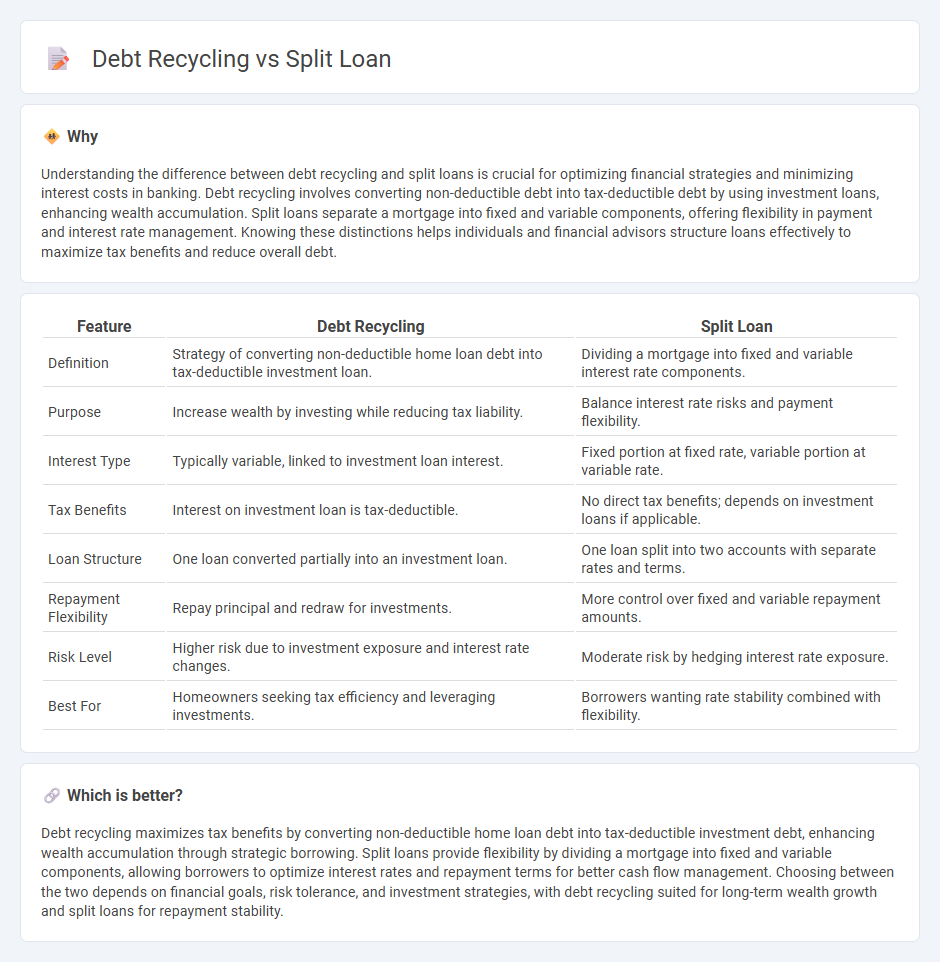
Understanding the difference between debt recycling and split loans is crucial for optimizing financial strategies and minimizing interest costs in banking. Debt recycling involves converting non-deductible debt into tax-deductible debt by using investment loans, enhancing wealth accumulation. Split loans separate a mortgage into fixed and variable components, offering flexibility in payment and interest rate management. Knowing these distinctions helps individuals and financial advisors structure loans effectively to maximize tax benefits and reduce overall debt.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Debt Recycling | Split Loan |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategy of converting non-deductible home loan debt into tax-deductible investment loan. | Dividing a mortgage into fixed and variable interest rate components. |
| Purpose | Increase wealth by investing while reducing tax liability. | Balance interest rate risks and payment flexibility. |
| Interest Type | Typically variable, linked to investment loan interest. | Fixed portion at fixed rate, variable portion at variable rate. |
| Tax Benefits | Interest on investment loan is tax-deductible. | No direct tax benefits; depends on investment loans if applicable. |
| Loan Structure | One loan converted partially into an investment loan. | One loan split into two accounts with separate rates and terms. |
| Repayment Flexibility | Repay principal and redraw for investments. | More control over fixed and variable repayment amounts. |
| Risk Level | Higher risk due to investment exposure and interest rate changes. | Moderate risk by hedging interest rate exposure. |
| Best For | Homeowners seeking tax efficiency and leveraging investments. | Borrowers wanting rate stability combined with flexibility. |
Which is better?
Debt recycling maximizes tax benefits by converting non-deductible home loan debt into tax-deductible investment debt, enhancing wealth accumulation through strategic borrowing. Split loans provide flexibility by dividing a mortgage into fixed and variable components, allowing borrowers to optimize interest rates and repayment terms for better cash flow management. Choosing between the two depends on financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment strategies, with debt recycling suited for long-term wealth growth and split loans for repayment stability.
Connection
Debt recycling and split loans are interconnected strategies used in banking to optimize financial management and mortgage efficiency. Debt recycling involves converting non-deductible debt into tax-deductible investment debt by leveraging equity, while split loans divide a mortgage into fixed and variable portions to balance repayment flexibility and interest rates. Together, they enable borrowers to strategically reduce interest costs, maximize tax benefits, and improve cash flow management within their loan structures.
Key Terms
Principal Splitting
Split loans allocate the loan amount between a fixed-rate portion and a variable-rate portion, enhancing interest rate flexibility and repayment strategies. Debt recycling involves converting non-deductible debt into tax-deductible investment debt by using equity from the home loan to invest, aiming to build wealth while managing interest costs efficiently. Discover how principal splitting can optimize repayments and tax benefits to enhance your financial planning.
Interest Deductibility
Split loans separate principal and interest payments, allowing interest deductibility on the investment portion. Debt recycling involves using borrowed funds to invest while converting non-deductible debt into tax-deductible debt through strategic refinancing. Explore in-depth comparisons to optimize interest deductibility and financial outcomes.
Investment Loan
Split loans divide the total borrowing into separate tranches with different interest rates, enabling borrowers to optimize between variable and fixed rates, often used in investment loans for better cash flow management. Debt recycling involves converting non-deductible home loan debt into tax-deductible investment loan debt by using available equity to invest, aiming to improve tax efficiency and build wealth. Discover more about how investment loans can be structured to maximize financial benefits and tax advantages.
Source and External Links
Split Home Loans - ANZ - A split home loan lets you divide your loan between a fixed and a variable rate, allowing you to benefit from the certainty of fixed repayments and the flexibility of variable rates tailored to your needs.
What Is A Split Home Loan? - NerdWallet Australia - A split home loan divides your mortgage into two parts, one fixed and one variable, combining security with flexibility, letting you choose the split ratio that suits your financial goals.
Split Home Loan - Option that is Flexible & Certain | Suncorp Bank - Splitting your loan allows you to allocate portions of your borrowings to fixed and variable rates as you choose, capturing benefits from both loan types like rate stability and payment flexibility.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com