Central bank digital currency (CBDC) represents a digital form of a nation's official currency issued directly by the central bank, designed to enhance payment efficiency and financial inclusion. Settlement accounts, managed by commercial banks within central bank frameworks, serve as the primary channels for interbank transactions and liquidity management. Explore the distinctions and implications of CBDCs versus settlement accounts to understand their impact on modern banking systems.
Why it is important
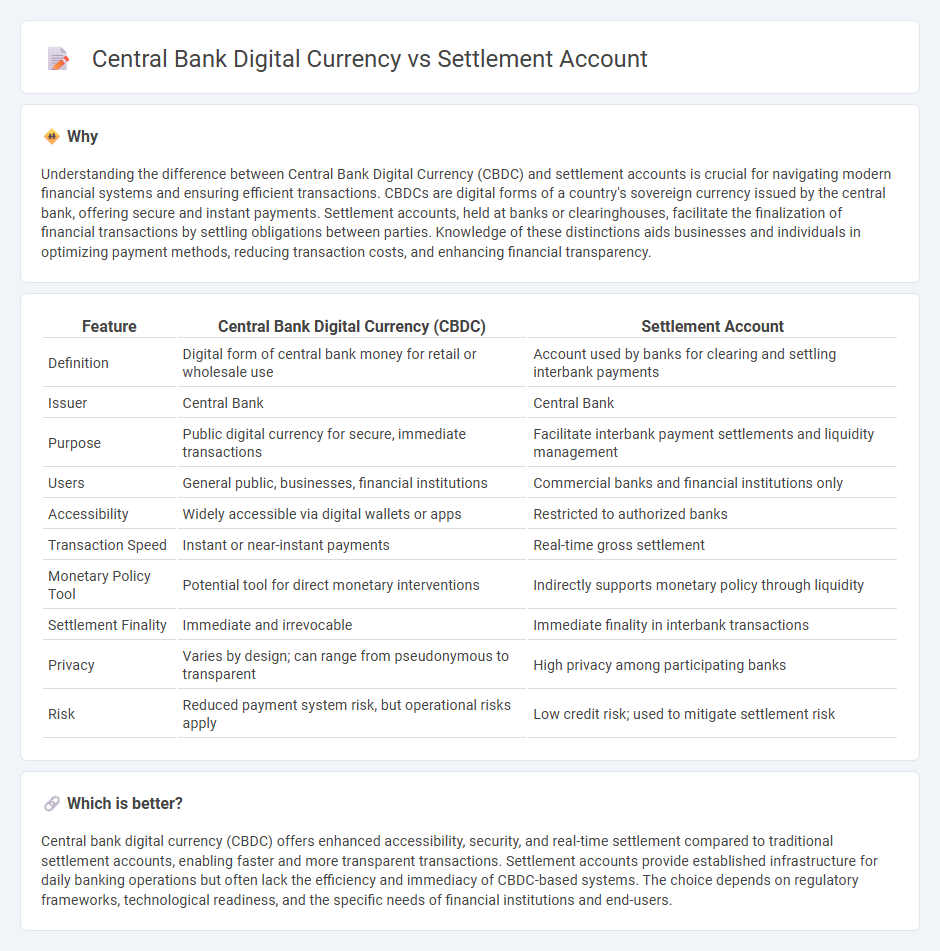
Understanding the difference between Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) and settlement accounts is crucial for navigating modern financial systems and ensuring efficient transactions. CBDCs are digital forms of a country's sovereign currency issued by the central bank, offering secure and instant payments. Settlement accounts, held at banks or clearinghouses, facilitate the finalization of financial transactions by settling obligations between parties. Knowledge of these distinctions aids businesses and individuals in optimizing payment methods, reducing transaction costs, and enhancing financial transparency.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) | Settlement Account |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital form of central bank money for retail or wholesale use | Account used by banks for clearing and settling interbank payments |
| Issuer | Central Bank | Central Bank |
| Purpose | Public digital currency for secure, immediate transactions | Facilitate interbank payment settlements and liquidity management |
| Users | General public, businesses, financial institutions | Commercial banks and financial institutions only |
| Accessibility | Widely accessible via digital wallets or apps | Restricted to authorized banks |
| Transaction Speed | Instant or near-instant payments | Real-time gross settlement |
| Monetary Policy Tool | Potential tool for direct monetary interventions | Indirectly supports monetary policy through liquidity |
| Settlement Finality | Immediate and irrevocable | Immediate finality in interbank transactions |
| Privacy | Varies by design; can range from pseudonymous to transparent | High privacy among participating banks |
| Risk | Reduced payment system risk, but operational risks apply | Low credit risk; used to mitigate settlement risk |
Which is better?
Central bank digital currency (CBDC) offers enhanced accessibility, security, and real-time settlement compared to traditional settlement accounts, enabling faster and more transparent transactions. Settlement accounts provide established infrastructure for daily banking operations but often lack the efficiency and immediacy of CBDC-based systems. The choice depends on regulatory frameworks, technological readiness, and the specific needs of financial institutions and end-users.
Connection
Central bank digital currency (CBDC) facilitates seamless transactions by directly linking to settlement accounts held by financial institutions at the central bank, enhancing payment efficiency and security. Settlement accounts serve as the foundational infrastructure enabling real-time gross settlement of CBDC transactions, reducing counterparty risk and liquidity constraints. This integration supports faster cross-border payments and improves monetary policy implementation through enhanced transaction transparency and control.
Key Terms
Liquidity
Settlement accounts provide liquidity by enabling immediate transfer of funds between financial institutions, ensuring smooth transaction clearance and financial stability. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) enhance liquidity by offering a secure, programmable digital asset directly issued by the central bank, reducing settlement times and counterparty risks. Explore how integrating CBDCs with traditional settlement systems can transform liquidity management in finance.
Interbank Transfers
Settlement accounts facilitate real-time interbank transfers by allowing banks to manage liquidity and clear payments efficiently within established payment systems. Central bank digital currency (CBDC) offers a digital alternative that could streamline settlement processes, reduce counterparty risk, and enhance transaction speed by enabling direct transfers on a secure blockchain or distributed ledger technology. Explore the evolving role of CBDCs and settlement accounts in transforming interbank transfer mechanisms.
Digital Ledger
Settlement accounts are traditional banking tools used for recording and managing transactions between parties, while Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) utilize digital ledgers to provide a secure, transparent, and efficient means of payment directly issued by the central bank. The digital ledger technology underlying CBDCs ensures immutability and real-time settlement, reducing counterparty risk and operational costs compared to conventional settlement accounts. Explore the evolving role of digital ledgers in transforming financial infrastructures and payment systems.
Source and External Links
The role of your settlement fund in brokerage trades - Vanguard - A settlement account or fund is where money for purchases is taken from and proceeds from sales are received in brokerage trades, ensuring funds are available to complete transactions on settlement dates.
settlement account - FCA Handbook - A settlement account is an account held with a central bank, securities depository, or settlement agent used to settle transactions between participants or members of a commercial settlement system.
Account Settlement: Definition, Types, and Applications - Tickeron - Account settlement refers to the process of paying outstanding balances to bring accounts to zero or completing offset processes between parties, which is key in financial transactions and trading contexts.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com