Account aggregation consolidates financial data from multiple bank accounts into a single platform, enabling users to monitor their finances comprehensively. Open banking provides secure access to a customer's banking information through APIs, allowing third-party developers to build innovative and personalized financial services. Explore how these technologies transform banking by enhancing data accessibility and customer experience.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between account aggregation and open banking is crucial for secure financial data management and enhanced user control. Account aggregation consolidates multiple bank accounts into a single view, while open banking enables third-party apps to access financial data via APIs securely. Knowing these distinctions helps consumers make informed choices about data privacy and service accessibility. This knowledge supports better financial decision-making and fosters trust in digital banking solutions.
Comparison Table
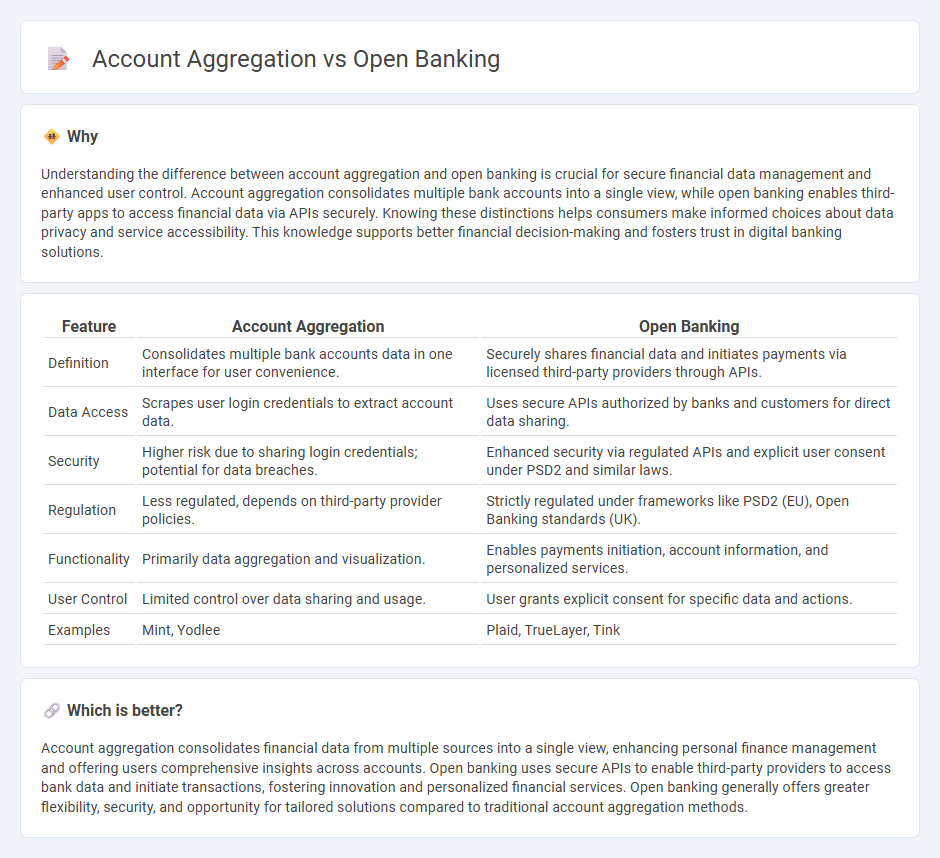
| Feature | Account Aggregation | Open Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consolidates multiple bank accounts data in one interface for user convenience. | Securely shares financial data and initiates payments via licensed third-party providers through APIs. |
| Data Access | Scrapes user login credentials to extract account data. | Uses secure APIs authorized by banks and customers for direct data sharing. |
| Security | Higher risk due to sharing login credentials; potential for data breaches. | Enhanced security via regulated APIs and explicit user consent under PSD2 and similar laws. |
| Regulation | Less regulated, depends on third-party provider policies. | Strictly regulated under frameworks like PSD2 (EU), Open Banking standards (UK). |
| Functionality | Primarily data aggregation and visualization. | Enables payments initiation, account information, and personalized services. |
| User Control | Limited control over data sharing and usage. | User grants explicit consent for specific data and actions. |
| Examples | Mint, Yodlee | Plaid, TrueLayer, Tink |
Which is better?
Account aggregation consolidates financial data from multiple sources into a single view, enhancing personal finance management and offering users comprehensive insights across accounts. Open banking uses secure APIs to enable third-party providers to access bank data and initiate transactions, fostering innovation and personalized financial services. Open banking generally offers greater flexibility, security, and opportunity for tailored solutions compared to traditional account aggregation methods.
Connection
Account aggregation and open banking are interconnected through the use of APIs that allow third-party providers to access multiple financial accounts securely. Open banking frameworks enable consumers to consolidate financial data from various banks into a single platform via account aggregation services. This integration enhances financial transparency, personalized services, and streamlined money management for users.
Key Terms
API (Application Programming Interface)
Open banking leverages APIs to enable third-party providers to securely access bank customers' financial data and initiate payments, promoting transparency and innovation in financial services. Account aggregation uses APIs to collect and consolidate users' financial information from multiple banks into a single platform for comprehensive account management. Discover how the evolution of APIs is transforming open banking and account aggregation for enhanced financial control.
Data Sharing Consent
Open banking requires explicit consumer consent for each data sharing transaction, ensuring transparency and control over personal financial information. Account aggregation consolidates data from multiple accounts but may operate under broader consent agreements, sometimes limiting user oversight on individual data accesses. Explore how these consent models impact security and user rights in financial data sharing to understand their differences better.
Payment Initiation
Open banking enables secure Payment Initiation Services (PIS) by allowing third-party providers to initiate payments directly from a user's bank account, enhancing transaction speed and security. Account aggregation primarily consolidates financial information from multiple accounts for user convenience but lacks direct payment initiation capabilities. Discover how Payment Initiation is transforming financial services through open banking innovations.
Source and External Links
Open banking - Open banking enables customers to securely share their financial information electronically with other banks or authorized financial organizations to enhance data sharing and services.
What is open banking? A guide to the future of finance - Plaid - Open banking is a system allowing consumers to securely share their banking and financial data with third-party providers via standardized APIs, improving transparency, service access, and innovation.
What is open banking? Your essential guide - Mastercard - Open banking allows secure sharing of financial account data with third parties to create innovative financial experiences, giving consumers control and expanding access to services.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com