Sustainable banking integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into financial services to support long-term economic and social development. Green banking specifically focuses on financing projects that reduce environmental impact, such as renewable energy and energy efficiency initiatives. Explore the differences and benefits of sustainable versus green banking to make informed financial decisions.
Why it is important
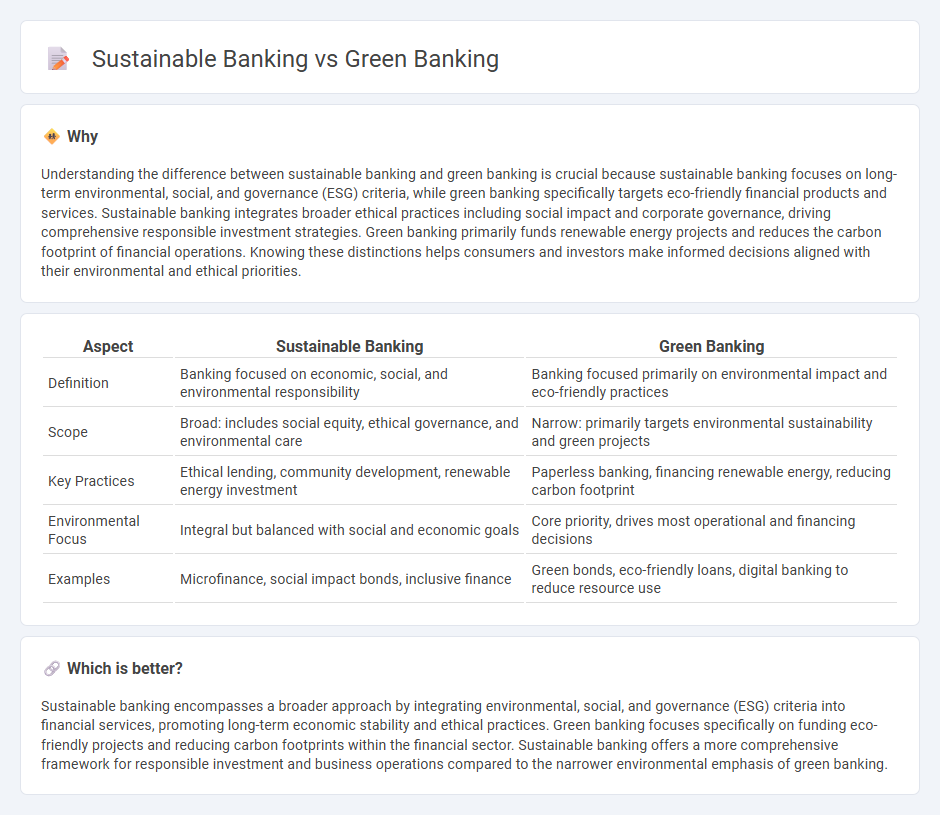
Understanding the difference between sustainable banking and green banking is crucial because sustainable banking focuses on long-term environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria, while green banking specifically targets eco-friendly financial products and services. Sustainable banking integrates broader ethical practices including social impact and corporate governance, driving comprehensive responsible investment strategies. Green banking primarily funds renewable energy projects and reduces the carbon footprint of financial operations. Knowing these distinctions helps consumers and investors make informed decisions aligned with their environmental and ethical priorities.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Sustainable Banking | Green Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Banking focused on economic, social, and environmental responsibility | Banking focused primarily on environmental impact and eco-friendly practices |
| Scope | Broad: includes social equity, ethical governance, and environmental care | Narrow: primarily targets environmental sustainability and green projects |
| Key Practices | Ethical lending, community development, renewable energy investment | Paperless banking, financing renewable energy, reducing carbon footprint |
| Environmental Focus | Integral but balanced with social and economic goals | Core priority, drives most operational and financing decisions |
| Examples | Microfinance, social impact bonds, inclusive finance | Green bonds, eco-friendly loans, digital banking to reduce resource use |
Which is better?
Sustainable banking encompasses a broader approach by integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into financial services, promoting long-term economic stability and ethical practices. Green banking focuses specifically on funding eco-friendly projects and reducing carbon footprints within the financial sector. Sustainable banking offers a more comprehensive framework for responsible investment and business operations compared to the narrower environmental emphasis of green banking.
Connection
Sustainable banking and green banking are interconnected through their shared focus on promoting environmentally responsible financial practices. Both prioritize investments in renewable energy, energy efficiency projects, and environmentally friendly technologies to reduce carbon footprints and support climate change mitigation. By integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into lending and investment decisions, these banking models drive the transition toward a low-carbon economy.
Key Terms
Environmental Risk Assessment
Green banking primarily emphasizes financing projects that promote environmental sustainability, such as renewable energy and pollution reduction initiatives, ensuring minimal ecological impact. Sustainable banking extends beyond environmental concerns, incorporating social and governance factors while systematically evaluating environmental risk through detailed environmental risk assessments to mitigate potential negative effects on ecosystems. Explore how integrating comprehensive environmental risk assessment enhances the effectiveness of green and sustainable banking practices.
Socially Responsible Investment
Green banking primarily targets environmental sustainability by financing eco-friendly projects, whereas sustainable banking encompasses a broader approach, integrating social, environmental, and economic factors into financial decisions. Socially Responsible Investment (SRI) within sustainable banking emphasizes transparency, ethical corporate practices, and positive social impact alongside financial returns. Explore the evolving role of SRI in reshaping banking strategies and fostering impactful community development.
Carbon Footprint Reduction
Green banking emphasizes eco-friendly financial products and services designed to minimize environmental impact, particularly through reducing carbon footprints via funding renewable energy projects. Sustainable banking extends beyond carbon reduction by integrating comprehensive environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into all banking operations and investment decisions. Explore the differences and benefits of green and sustainable banking approaches for effective carbon footprint reduction.
Source and External Links
Green Banking: What is an Eco-Friendly Bank? | GreenFi - Green banking is a financing trend where banks shift investments to sustainable technologies and eco-friendly initiatives, promoting clean energy and climate resilience by supporting projects like renewable energy and reforestation, and instituting eco-friendly lending policies such as loans for electric vehicles and solar systems.
What Is Green Banking: 4 Ways You Can Help Protect ... - Bankrate - Green banking refers to choosing financial institutions that prioritize investments in clean energy and sustainable initiatives, allowing consumers to align their finances with environmental values while supporting community conservation and transparency in financial practices.
Green bank - Wikipedia - Green banks are specialized financial institutions using credit enhancements, co-investments, and securitization to reduce financing risks and costs, stimulating private-sector investment in clean energy and accelerating the transition to a low-carbon economy.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com