Digital identity verification ensures secure user authentication by confirming personal information through biometric data or government-issued IDs, reducing fraud in banking transactions. OAuth authorization allows users to grant third-party applications limited access to their banking data without sharing credentials, enhancing privacy and convenience. Discover how these technologies revolutionize security and user experience in modern banking.
Why it is important
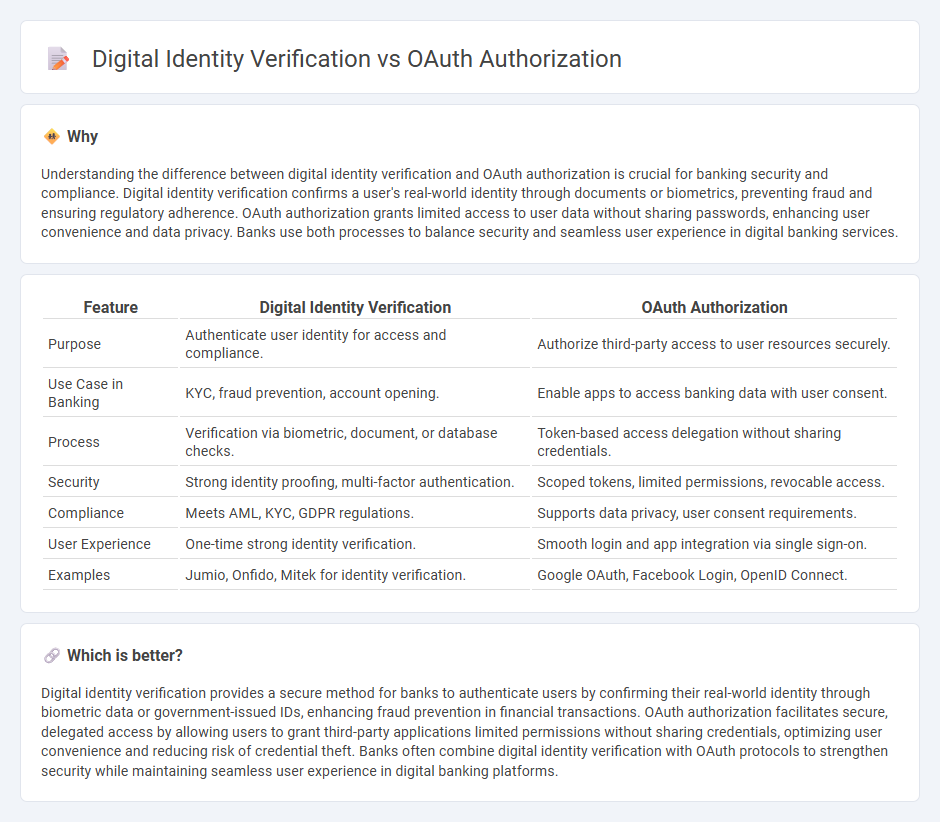
Understanding the difference between digital identity verification and OAuth authorization is crucial for banking security and compliance. Digital identity verification confirms a user's real-world identity through documents or biometrics, preventing fraud and ensuring regulatory adherence. OAuth authorization grants limited access to user data without sharing passwords, enhancing user convenience and data privacy. Banks use both processes to balance security and seamless user experience in digital banking services.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Digital Identity Verification | OAuth Authorization |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Authenticate user identity for access and compliance. | Authorize third-party access to user resources securely. |
| Use Case in Banking | KYC, fraud prevention, account opening. | Enable apps to access banking data with user consent. |
| Process | Verification via biometric, document, or database checks. | Token-based access delegation without sharing credentials. |
| Security | Strong identity proofing, multi-factor authentication. | Scoped tokens, limited permissions, revocable access. |
| Compliance | Meets AML, KYC, GDPR regulations. | Supports data privacy, user consent requirements. |
| User Experience | One-time strong identity verification. | Smooth login and app integration via single sign-on. |
| Examples | Jumio, Onfido, Mitek for identity verification. | Google OAuth, Facebook Login, OpenID Connect. |
Which is better?
Digital identity verification provides a secure method for banks to authenticate users by confirming their real-world identity through biometric data or government-issued IDs, enhancing fraud prevention in financial transactions. OAuth authorization facilitates secure, delegated access by allowing users to grant third-party applications limited permissions without sharing credentials, optimizing user convenience and reducing risk of credential theft. Banks often combine digital identity verification with OAuth protocols to strengthen security while maintaining seamless user experience in digital banking platforms.
Connection
Digital identity verification enables secure recognition of users by validating credentials, while OAuth authorization provides controlled access to resources without sharing passwords. Together, they enhance banking security by ensuring only verified identities can grant or obtain permissions to sensitive financial data. This integration reduces fraud risks and streamlines user authentication processes in digital banking platforms.
Key Terms
Access Token
OAuth authorization relies on access tokens as temporary credentials granting specific permissions to third-party applications without exposing user passwords. Digital identity verification ensures accurate user authentication by validating personal information or biometric data before token issuance. Discover how these mechanisms interplay to secure modern authentication systems and streamline user access.
KYC (Know Your Customer)
OAuth authorization streamlines secure user authentication by enabling third-party applications to access user data without exposing credentials, enhancing privacy but not inherently verifying identity. Digital identity verification in KYC involves comprehensive processes such as document validation, biometric checks, and cross-referencing official databases to confirm an individual's true identity and prevent fraud. Explore how integrating OAuth with advanced digital identity verification can strengthen KYC compliance and improve customer onboarding experiences.
Authentication
OAuth authorization enables secure resource access by allowing third-party applications to obtain limited user permissions without sharing credentials, emphasizing delegated access control. Digital identity verification focuses on authenticating an individual's identity through methods like biometrics, multi-factor authentication (MFA), or government-issued ID validation to ensure legitimacy. Explore further how these authentication approaches impact security frameworks and user experience.
Source and External Links
RFC 6749 - The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework - Datatracker - OAuth 2.0 enables third-party applications to obtain limited access to an HTTP service by redirecting the resource owner through authorization endpoints to grant access tokens without sharing credentials directly.
OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework - Auth0 - OAuth 2.0 is a protocol that lets users grant third-party apps access to their protected resources via access tokens that represent scopes and permissions, without exposing their credentials or identity.
What Is OAuth (Open Authorization) and How Does It Work? - IBM - OAuth involves an authorization server granting access tokens to clients after the resource owner consents, allowing the client to access protected resources on a resource server under scopes defining permissions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com