Income streaming in banking refers to the diversified sources of revenue including fees, commissions, and investment income, while net interest income represents the difference between interest earned on assets and interest paid on liabilities. Banks focus on optimizing both income streams to enhance profitability and maintain financial stability. Explore the dynamics of income streaming versus net interest income to understand their impact on banking performance.
Why it is important
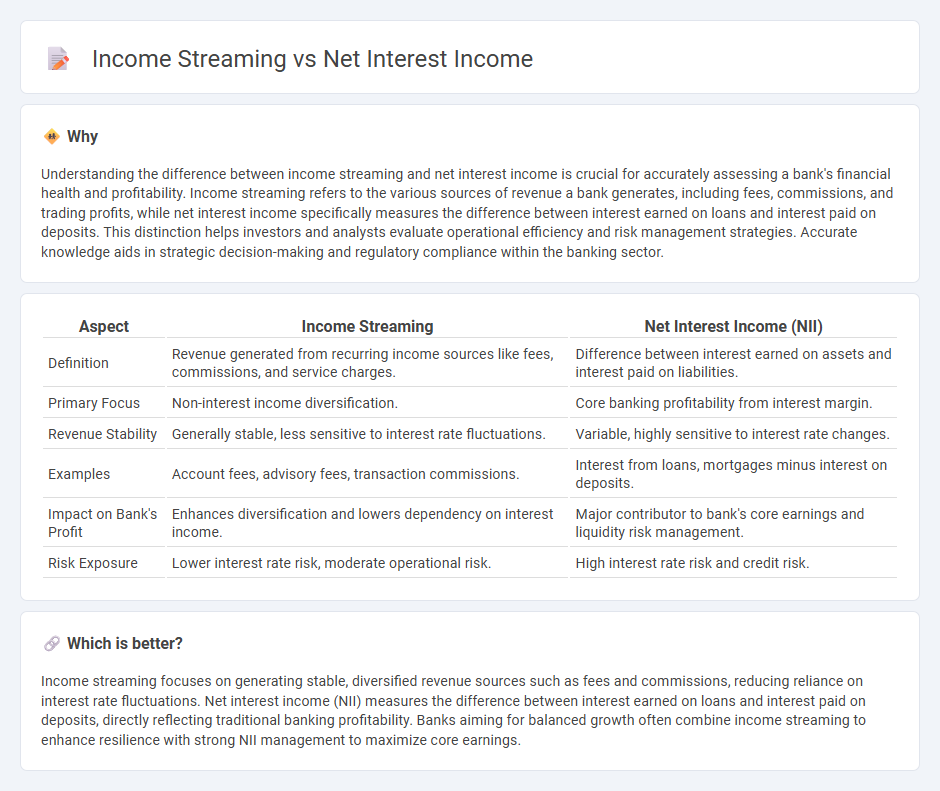
Understanding the difference between income streaming and net interest income is crucial for accurately assessing a bank's financial health and profitability. Income streaming refers to the various sources of revenue a bank generates, including fees, commissions, and trading profits, while net interest income specifically measures the difference between interest earned on loans and interest paid on deposits. This distinction helps investors and analysts evaluate operational efficiency and risk management strategies. Accurate knowledge aids in strategic decision-making and regulatory compliance within the banking sector.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Income Streaming | Net Interest Income (NII) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Revenue generated from recurring income sources like fees, commissions, and service charges. | Difference between interest earned on assets and interest paid on liabilities. |
| Primary Focus | Non-interest income diversification. | Core banking profitability from interest margin. |
| Revenue Stability | Generally stable, less sensitive to interest rate fluctuations. | Variable, highly sensitive to interest rate changes. |
| Examples | Account fees, advisory fees, transaction commissions. | Interest from loans, mortgages minus interest on deposits. |
| Impact on Bank's Profit | Enhances diversification and lowers dependency on interest income. | Major contributor to bank's core earnings and liquidity risk management. |
| Risk Exposure | Lower interest rate risk, moderate operational risk. | High interest rate risk and credit risk. |
Which is better?
Income streaming focuses on generating stable, diversified revenue sources such as fees and commissions, reducing reliance on interest rate fluctuations. Net interest income (NII) measures the difference between interest earned on loans and interest paid on deposits, directly reflecting traditional banking profitability. Banks aiming for balanced growth often combine income streaming to enhance resilience with strong NII management to maximize core earnings.
Connection
Income streaming in banking refers to the continuous generation of revenue through various financial products and services. Net interest income (NII) is a major component of this income, derived from the difference between interest earned on loans and interest paid on deposits. Efficient income streaming strategies directly impact NII by optimizing loan portfolios and deposit costs to maximize profitability.
Key Terms
Interest Margin
Net interest income represents the difference between interest earned on assets and interest paid on liabilities, serving as a key profitability metric for financial institutions. Interest margin, often expressed as net interest margin (NIM), measures this income relative to earning assets, providing insight into the efficiency of interest-generating operations compared to overall income streams such as fees and trading revenue. Explore detailed analyses of interest margin trends and their impact on diversified income streams to enhance understanding of financial performance.
Non-Interest Income
Non-interest income, distinct from net interest income, encompasses revenue generated from fees, service charges, and trading activities rather than interest earned on loans or securities. This income stream significantly enhances financial institutions' profitability by diversifying revenue sources beyond traditional interest margins. Explore the strategic advantages and implications of non-interest income in modern banking to understand its growing importance.
Diversification
Net interest income represents the difference between interest earned on assets like loans and interest paid on liabilities such as deposits, serving as a primary revenue source for banks. Income streaming involves diversifying revenue by incorporating non-interest income streams like fees, trading gains, and service charges to reduce reliance on net interest income. Explore how diversifying income streams enhances financial stability and growth potential in banking.
Source and External Links
Net Interest Income (NII) | Formula + Calculator - This webpage explains that Net Interest Income (NII) is a profit metric calculated as the difference between a bank's total interest income and its interest expense, serving as a key indicator of profitability in the financial sector.
What is NII and why is it important? - This article highlights NII as a crucial metric for banks, indicating the financial health derived from lending and borrowing operations by subtracting interest expenses from interest income.
Net Interest Income - Overview, Types, Calculation - This resource defines Net Interest Income as the difference between interest revenues and expenses, emphasizing its role in financial institutions' profitability, particularly in managing assets and liabilities effectively.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com