Open banking revolutionizes financial services by enabling third-party providers to access banking data securely through APIs, fostering innovation and personalized offerings. Mobile banking offers convenient financial management via smartphone apps, allowing users to perform transactions, check balances, and pay bills anytime, anywhere. Explore the differences and benefits of open banking versus mobile banking to optimize your financial experience.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between open banking and mobile banking is crucial for leveraging secure, innovative financial services and enhancing user control over data. Open banking allows third-party developers to build applications and services around financial institutions by securely sharing data through APIs. Mobile banking primarily refers to accessing traditional banking services via smartphone apps for convenience and real-time transactions. Recognizing these distinctions helps consumers make informed decisions about privacy, security, and the range of financial functionalities available.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Open Banking | Mobile Banking |
|---|---|---|
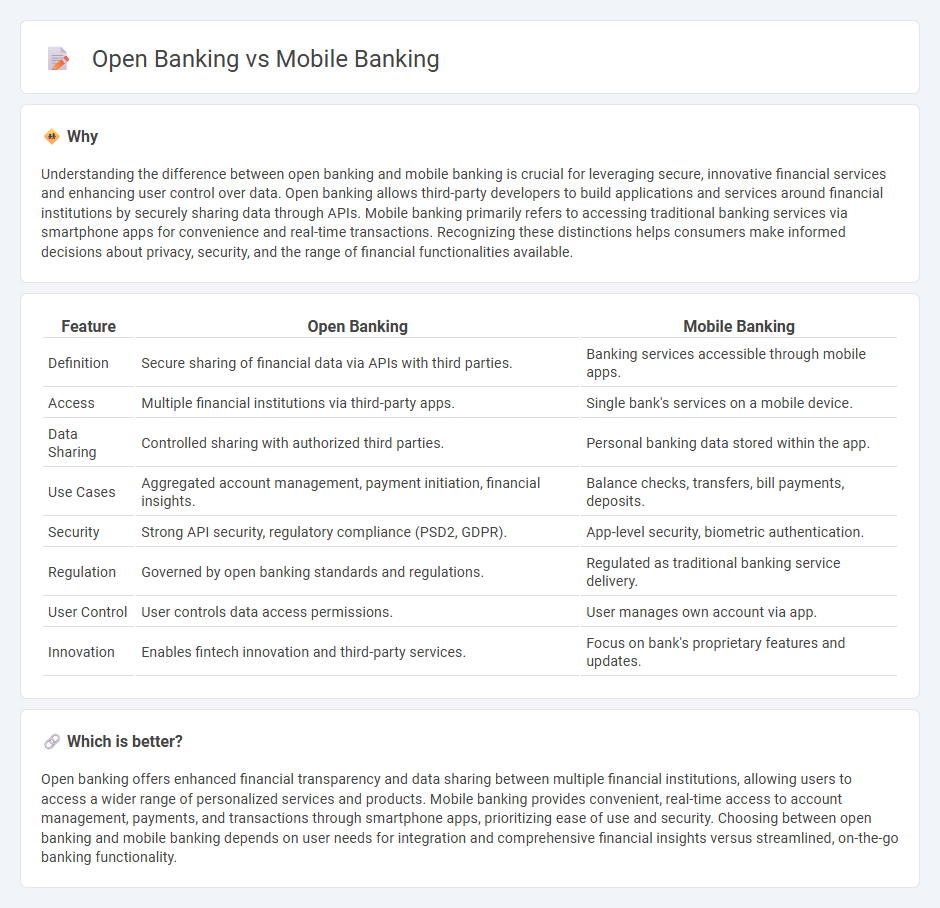
| Definition | Secure sharing of financial data via APIs with third parties. | Banking services accessible through mobile apps. |
| Access | Multiple financial institutions via third-party apps. | Single bank's services on a mobile device. |
| Data Sharing | Controlled sharing with authorized third parties. | Personal banking data stored within the app. |
| Use Cases | Aggregated account management, payment initiation, financial insights. | Balance checks, transfers, bill payments, deposits. |
| Security | Strong API security, regulatory compliance (PSD2, GDPR). | App-level security, biometric authentication. |
| Regulation | Governed by open banking standards and regulations. | Regulated as traditional banking service delivery. |
| User Control | User controls data access permissions. | User manages own account via app. |
| Innovation | Enables fintech innovation and third-party services. | Focus on bank's proprietary features and updates. |
Which is better?
Open banking offers enhanced financial transparency and data sharing between multiple financial institutions, allowing users to access a wider range of personalized services and products. Mobile banking provides convenient, real-time access to account management, payments, and transactions through smartphone apps, prioritizing ease of use and security. Choosing between open banking and mobile banking depends on user needs for integration and comprehensive financial insights versus streamlined, on-the-go banking functionality.
Connection
Open banking enhances mobile banking by enabling secure data sharing between financial institutions and third-party providers through APIs, expanding the range of mobile services available to users. This connection allows mobile banking apps to offer personalized financial insights, seamless payment options, and integrated account management from multiple banks within a single platform. The synergy between open banking and mobile banking drives innovation, improves user experience, and promotes financial inclusivity.
Key Terms
API (Application Programming Interface)
Mobile banking relies on proprietary APIs controlled by individual banks to provide secure access to account information and basic transaction services within their apps. Open banking leverages standardized, publicly accessible APIs to enable third-party developers to create innovative financial services, fostering competition and enhancing customer choice. Explore how API strategies shape the future of digital finance by learning more about mobile and open banking ecosystems.
User Authentication
Mobile banking primarily relies on traditional authentication methods such as passwords, PINs, and biometric verification like fingerprint or facial recognition to ensure secure access. Open banking enhances user authentication by incorporating advanced APIs that enable seamless, real-time identity verification and multi-factor authentication across different financial institutions. Discover how these evolving authentication techniques improve security and user experience in financial services.
Data Privacy
Mobile banking encrypts users' financial data and stores it within bank-managed servers, ensuring direct control over sensitive information. Open banking uses APIs to share customer data securely with third-party providers, governed by strict regulations like PSD2 to enhance data privacy and consent. Explore how evolving data privacy standards shape the future of both mobile and open banking services.
Source and External Links
PNC Mobile Banking - Offers features like mobile check deposit, bill pay, money transfers via Zelle(r), card management, and real-time card locking through the PNC Mobile App and Mobile Web.
Mobile banking - Wikipedia - Enables users to conduct a range of financial transactions and access account information, payments, investments, and support services via mobile devices.
Bank of America Mobile Banking - Provides secure account management, alerts, card activation, Zelle(r) transfers, bill payments, and access to checking, savings, credit, loan, and investment accounts in the U.S..
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com