Invisible payments utilize seamless technology to process transactions without traditional card swipes or cash exchanges, enhancing customer convenience and speeding up the checkout experience. Point of sale (POS) payments involve physical or digital terminals where customers intentionally authorize transactions using cards, mobile wallets, or cash, providing transparency and control over the payment process. Explore deeper insights into how invisible and POS payments are transforming the future of banking transactions.
Why it is important
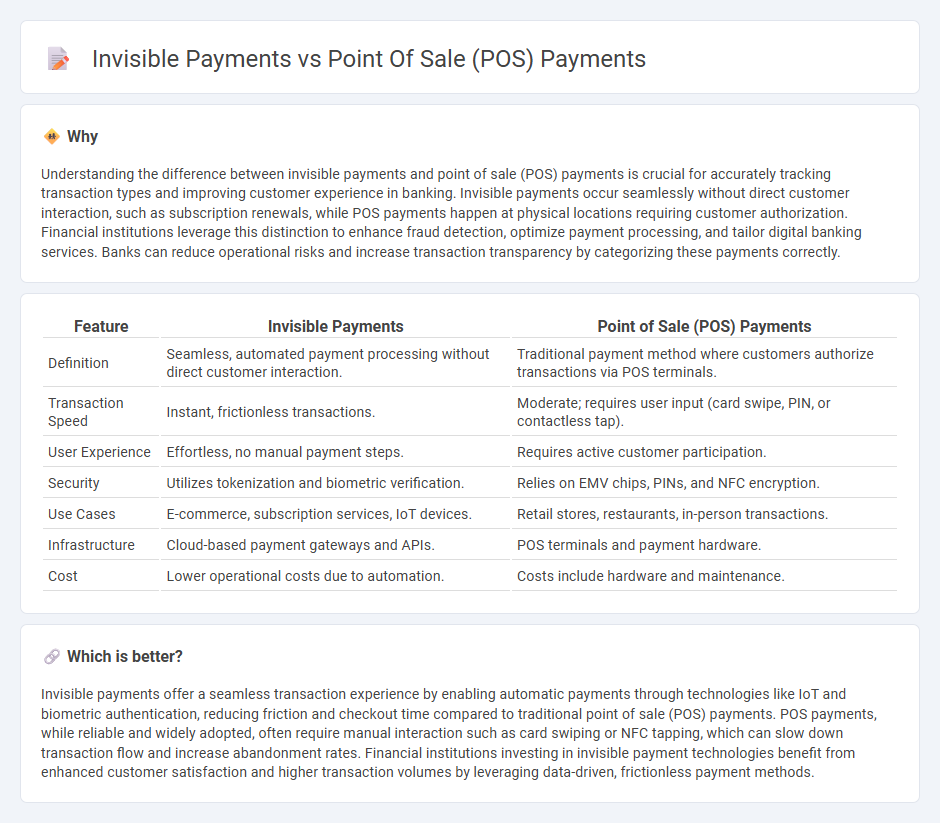
Understanding the difference between invisible payments and point of sale (POS) payments is crucial for accurately tracking transaction types and improving customer experience in banking. Invisible payments occur seamlessly without direct customer interaction, such as subscription renewals, while POS payments happen at physical locations requiring customer authorization. Financial institutions leverage this distinction to enhance fraud detection, optimize payment processing, and tailor digital banking services. Banks can reduce operational risks and increase transaction transparency by categorizing these payments correctly.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Invisible Payments | Point of Sale (POS) Payments |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Seamless, automated payment processing without direct customer interaction. | Traditional payment method where customers authorize transactions via POS terminals. |
| Transaction Speed | Instant, frictionless transactions. | Moderate; requires user input (card swipe, PIN, or contactless tap). |
| User Experience | Effortless, no manual payment steps. | Requires active customer participation. |
| Security | Utilizes tokenization and biometric verification. | Relies on EMV chips, PINs, and NFC encryption. |
| Use Cases | E-commerce, subscription services, IoT devices. | Retail stores, restaurants, in-person transactions. |
| Infrastructure | Cloud-based payment gateways and APIs. | POS terminals and payment hardware. |
| Cost | Lower operational costs due to automation. | Costs include hardware and maintenance. |
Which is better?
Invisible payments offer a seamless transaction experience by enabling automatic payments through technologies like IoT and biometric authentication, reducing friction and checkout time compared to traditional point of sale (POS) payments. POS payments, while reliable and widely adopted, often require manual interaction such as card swiping or NFC tapping, which can slow down transaction flow and increase abandonment rates. Financial institutions investing in invisible payment technologies benefit from enhanced customer satisfaction and higher transaction volumes by leveraging data-driven, frictionless payment methods.
Connection
Invisible payments leverage contactless technologies such as Near Field Communication (NFC) and tokenization directly integrated into point of sale (POS) systems to enable seamless, secure transactions without physical interaction. POS payments serve as the primary hardware interface where invisible payments occur, facilitating instant authentication and authorization through digital wallets or embedded device credentials. This integration enhances transaction speed, reduces fraud risks, and improves customer experience by minimizing checkout time and eliminating the need for cash or physical cards.
Key Terms
Authentication
Point of sale (POS) payments require visible user interaction and authentication methods such as PIN entry or biometric verification to complete transactions securely. Invisible payments leverage background authentication technologies like tokenization, device fingerprinting, and behavioral biometrics to authorize payments without disrupting the user experience. Explore the evolving authentication techniques shaping the future of seamless and secure payment systems.
Customer Experience
Point of sale (POS) payments involve direct customer interaction through devices like card readers or mobile payment terminals, facilitating a tangible and secure transaction process that often includes receipt issuance and immediate confirmation. Invisible payments operate seamlessly in the background using technologies such as RFID, NFC, or biometric authentication, minimizing friction and enhancing convenience by eliminating the need for active customer input during checkout. Explore the advantages and challenges of both payment methods to understand their impact on customer experience in retail environments.
Source and External Links
POS vs. Online Payments - What's the Difference? - Payfactory - Point of sale (POS) payments are electronic transactions made in physical locations like retail or restaurants, using POS terminals with capabilities including chip reading and contactless payments, forming a key part of omnichannel shopping experiences.
What Is a POS Transaction? A Short Guide for B2B Sellers - Versapay - POS transactions involve capturing payment data via a POS device and processing it through credit card networks and banks to authorize and settle payments, often automatically via payment gateways.
Point of sale (POS) systems for small businesses explained | Stripe - POS systems combine hardware and software to accept payments, process transactions, communicate with banks and processors, and often manage inventory and sales data, with cloud-based and on-premises options available.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com