Fraud orchestration systems integrate real-time data analysis and machine learning to detect sophisticated fraudulent activities across multiple channels, enhancing risk management in banking. Anti-money laundering (AML) focuses on identifying and preventing financial crimes related to money laundering and terrorist financing by monitoring transactions and customer behavior against regulatory compliance standards. Explore the differences and benefits of fraud orchestration versus AML solutions to strengthen your financial security strategy.
Why it is important
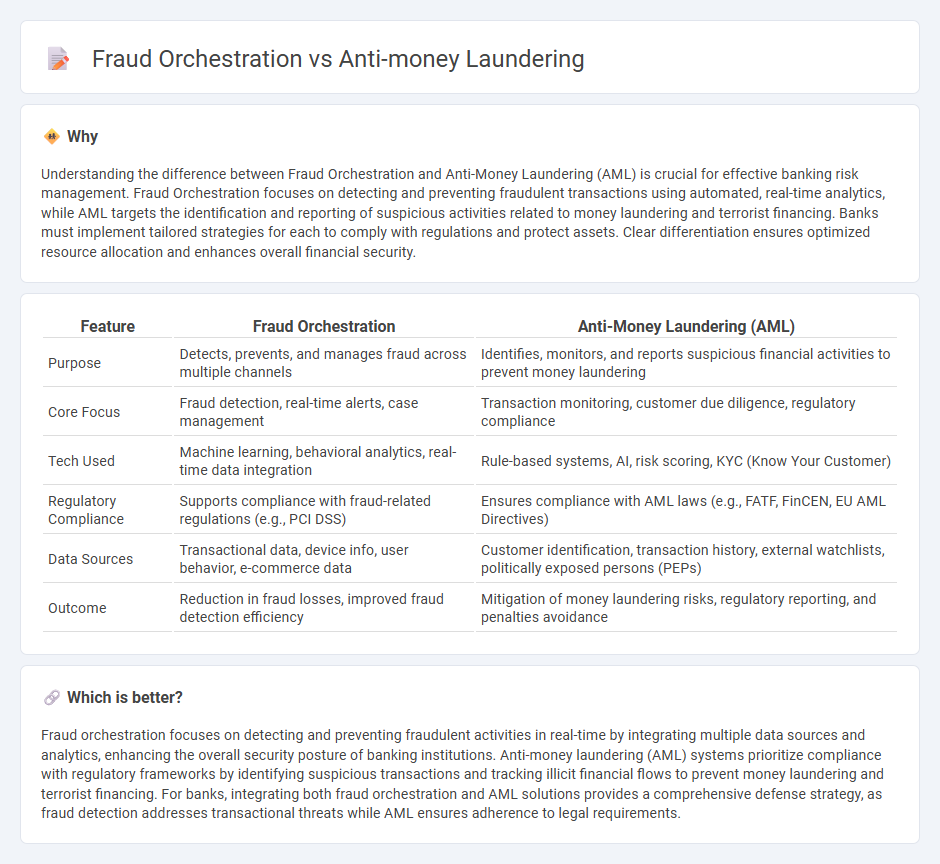
Understanding the difference between Fraud Orchestration and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) is crucial for effective banking risk management. Fraud Orchestration focuses on detecting and preventing fraudulent transactions using automated, real-time analytics, while AML targets the identification and reporting of suspicious activities related to money laundering and terrorist financing. Banks must implement tailored strategies for each to comply with regulations and protect assets. Clear differentiation ensures optimized resource allocation and enhances overall financial security.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Fraud Orchestration | Anti-Money Laundering (AML) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Detects, prevents, and manages fraud across multiple channels | Identifies, monitors, and reports suspicious financial activities to prevent money laundering |
| Core Focus | Fraud detection, real-time alerts, case management | Transaction monitoring, customer due diligence, regulatory compliance |
| Tech Used | Machine learning, behavioral analytics, real-time data integration | Rule-based systems, AI, risk scoring, KYC (Know Your Customer) |
| Regulatory Compliance | Supports compliance with fraud-related regulations (e.g., PCI DSS) | Ensures compliance with AML laws (e.g., FATF, FinCEN, EU AML Directives) |
| Data Sources | Transactional data, device info, user behavior, e-commerce data | Customer identification, transaction history, external watchlists, politically exposed persons (PEPs) |
| Outcome | Reduction in fraud losses, improved fraud detection efficiency | Mitigation of money laundering risks, regulatory reporting, and penalties avoidance |
Which is better?
Fraud orchestration focuses on detecting and preventing fraudulent activities in real-time by integrating multiple data sources and analytics, enhancing the overall security posture of banking institutions. Anti-money laundering (AML) systems prioritize compliance with regulatory frameworks by identifying suspicious transactions and tracking illicit financial flows to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing. For banks, integrating both fraud orchestration and AML solutions provides a comprehensive defense strategy, as fraud detection addresses transactional threats while AML ensures adherence to legal requirements.
Connection
Fraud orchestration integrates advanced analytics and machine learning to detect suspicious activities, enhancing anti-money laundering (AML) efforts by providing real-time risk assessment. AML frameworks leverage fraud orchestration platforms to streamline data from multiple sources, improving the accuracy of transaction monitoring and regulatory reporting. This synergy accelerates identification of illicit financial flows, reducing compliance costs and minimizing financial crime risks for banks.
Key Terms
**Anti-money laundering:**
Anti-money laundering (AML) involves a set of procedures and regulations designed to detect and prevent the illegal process of disguising the origins of money obtained through illicit activities. AML frameworks utilize advanced technologies such as transaction monitoring, customer due diligence, and suspicious activity reporting to identify and mitigate financial crimes. Explore the latest AML strategies and solutions to enhance your organization's compliance and security measures.
Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) plays a critical role in both anti-money laundering (AML) and fraud orchestration by verifying customer identities and assessing risk profiles to detect suspicious activities. AML frameworks focus on continuous transaction monitoring and enhanced due diligence for high-risk customers to prevent illicit fund flows, while fraud orchestration targets the detection of coordinated schemes designed to exploit CDD weaknesses. Explore effective strategies to strengthen CDD processes for robust defense against money laundering and fraud orchestration threats.
Suspicious Activity Report (SAR)
Anti-money laundering (AML) targets illicit financial transactions aiming to conceal the origins of illegally obtained funds, while fraud orchestration involves coordinated schemes to execute deceptive financial activities, often exploiting vulnerabilities in systems. Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) are critical tools for both AML and fraud orchestration detection, enabling regulatory bodies to monitor and investigate unusual or suspicious transactions that may indicate money laundering or fraud networks. Explore how SARs enhance detection capabilities and regulatory compliance in combating these financial crimes.
Source and External Links
Anti-money laundering - Wikipedia - Anti-money laundering (AML) refers to policies and practices ensuring that financial institutions prevent, detect, and report money laundering and related financial crimes, often coupled with combating terrorism financing (AML/CFT), and includes customer identification, risk-based controls, and suspicious activity reporting in a global regulatory framework.
History of Anti-Money Laundering Laws | FinCEN.gov - AML laws have evolved since 1970, strengthening customer identification, prohibiting business with foreign shell banks, expanding due diligence and information sharing, increasing penalties, and empowering regulators to address major money laundering concerns.
Anti-money laundering: What it is and why it matters - SAS - Modern AML programs use advanced technologies like AI and machine learning for suspicious activity monitoring, alert prioritization, automated reporting, client risk rating, and anomaly detection to combat increasingly sophisticated financial crimes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com