Data lake auditing leverages centralized storage to aggregate vast volumes of financial data, enabling comprehensive historical analysis and anomaly detection across diverse accounting records. Automated transaction monitoring employs real-time analytics and machine learning algorithms to identify irregularities and compliance issues instantly within ongoing transactions. Explore the advancements and applications of these technologies in modern accounting practices to enhance accuracy and fraud prevention.
Why it is important
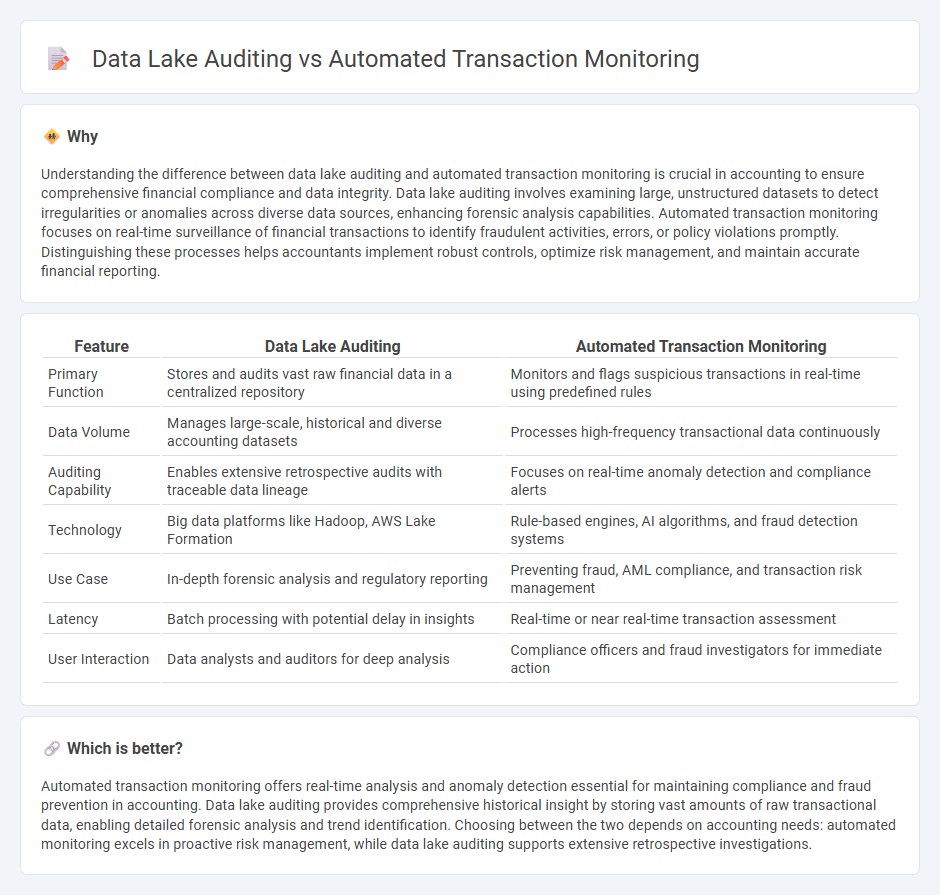
Understanding the difference between data lake auditing and automated transaction monitoring is crucial in accounting to ensure comprehensive financial compliance and data integrity. Data lake auditing involves examining large, unstructured datasets to detect irregularities or anomalies across diverse data sources, enhancing forensic analysis capabilities. Automated transaction monitoring focuses on real-time surveillance of financial transactions to identify fraudulent activities, errors, or policy violations promptly. Distinguishing these processes helps accountants implement robust controls, optimize risk management, and maintain accurate financial reporting.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Data Lake Auditing | Automated Transaction Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Stores and audits vast raw financial data in a centralized repository | Monitors and flags suspicious transactions in real-time using predefined rules |
| Data Volume | Manages large-scale, historical and diverse accounting datasets | Processes high-frequency transactional data continuously |
| Auditing Capability | Enables extensive retrospective audits with traceable data lineage | Focuses on real-time anomaly detection and compliance alerts |
| Technology | Big data platforms like Hadoop, AWS Lake Formation | Rule-based engines, AI algorithms, and fraud detection systems |
| Use Case | In-depth forensic analysis and regulatory reporting | Preventing fraud, AML compliance, and transaction risk management |
| Latency | Batch processing with potential delay in insights | Real-time or near real-time transaction assessment |
| User Interaction | Data analysts and auditors for deep analysis | Compliance officers and fraud investigators for immediate action |
Which is better?
Automated transaction monitoring offers real-time analysis and anomaly detection essential for maintaining compliance and fraud prevention in accounting. Data lake auditing provides comprehensive historical insight by storing vast amounts of raw transactional data, enabling detailed forensic analysis and trend identification. Choosing between the two depends on accounting needs: automated monitoring excels in proactive risk management, while data lake auditing supports extensive retrospective investigations.
Connection
Data lake auditing enhances the accuracy and completeness of financial records by storing and analyzing vast amounts of unstructured and structured accounting data in a centralized repository. Automated transaction monitoring leverages data lake insights to detect anomalies, fraud, and compliance issues in real time, improving the reliability and transparency of accounting processes. Integration of both technologies streamlines audit trails and regulatory reporting, ensuring robust internal controls within the accounting ecosystem.
Key Terms
Real-time Alerts
Automated transaction monitoring systems leverage advanced algorithms and machine learning to provide real-time alerts, enabling immediate detection of suspicious activities and enhancing financial fraud prevention. Data lake auditing, while comprehensive in aggregating large volumes of information, often lacks the instant alert capabilities necessary for swift responses to potential threats. Explore the latest solutions to understand how integrating real-time alerts can optimize your transaction monitoring strategy.
Data Ingestion
Automated transaction monitoring leverages real-time data ingestion to detect suspicious activities by continuously analyzing transactional data streams, enhancing fraud detection accuracy and compliance. Data lake auditing involves ingesting vast volumes of diverse data from multiple sources, enabling comprehensive historical analysis and regulatory review to maintain data integrity and traceability. Explore detailed insights on optimizing data ingestion techniques for both automated transaction monitoring and data lake auditing to strengthen your data security framework.
Anomaly Detection
Automated transaction monitoring systems leverage real-time algorithms to identify patterns indicating fraudulent activities, while data lake auditing aggregates large volumes of historical data for in-depth anomaly detection using advanced analytics. Transaction monitoring emphasizes speed and immediate alerts, whereas data lake auditing provides comprehensive insights through machine learning models trained on diverse datasets across different timelines. Explore the latest techniques in anomaly detection to enhance your fraud prevention strategy.
Source and External Links
How Does Automated Transaction Monitoring Work? - Automated transaction monitoring uses AI and machine learning to analyze transaction data in real-time, detecting suspicious patterns and scoring risks to help comply with AML regulations and generate alerts for investigation.
Automated Transaction Monitoring: A New Era - These systems employ rule-based and behavior-based algorithms with machine learning that continuously evolve to identify deviations and financial crimes efficiently, balancing sensitivity with reducing false positives for regulatory compliance.
Automated Transaction Monitoring for AML Compliance - Alessa - Automated transaction monitoring integrates with existing systems to flag suspicious transactions like large transfers or unusual patterns, assisting institutions in meeting AML compliance through advanced analytics and rule-based engines tailored to specific risk scenarios.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com