Triple entry bookkeeping enhances traditional accounting by integrating cryptographic verification to create tamper-evident transaction records, improving transparency and auditability. Distributed ledger technology, such as blockchain, decentralizes data storage across multiple nodes, ensuring real-time synchronization and reducing the risk of fraud or data manipulation. Explore how these innovations revolutionize financial record-keeping and secure transaction validation.
Why it is important
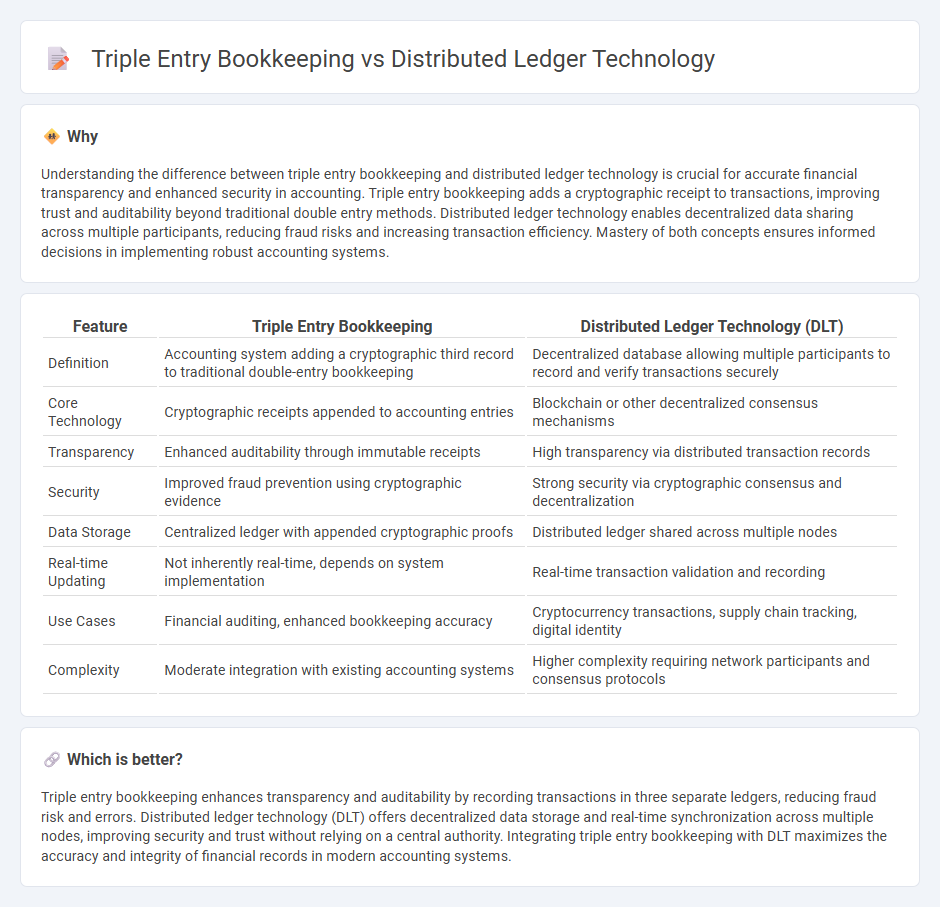
Understanding the difference between triple entry bookkeeping and distributed ledger technology is crucial for accurate financial transparency and enhanced security in accounting. Triple entry bookkeeping adds a cryptographic receipt to transactions, improving trust and auditability beyond traditional double entry methods. Distributed ledger technology enables decentralized data sharing across multiple participants, reducing fraud risks and increasing transaction efficiency. Mastery of both concepts ensures informed decisions in implementing robust accounting systems.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Triple Entry Bookkeeping | Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Accounting system adding a cryptographic third record to traditional double-entry bookkeeping | Decentralized database allowing multiple participants to record and verify transactions securely |
| Core Technology | Cryptographic receipts appended to accounting entries | Blockchain or other decentralized consensus mechanisms |
| Transparency | Enhanced auditability through immutable receipts | High transparency via distributed transaction records |
| Security | Improved fraud prevention using cryptographic evidence | Strong security via cryptographic consensus and decentralization |
| Data Storage | Centralized ledger with appended cryptographic proofs | Distributed ledger shared across multiple nodes |
| Real-time Updating | Not inherently real-time, depends on system implementation | Real-time transaction validation and recording |
| Use Cases | Financial auditing, enhanced bookkeeping accuracy | Cryptocurrency transactions, supply chain tracking, digital identity |
| Complexity | Moderate integration with existing accounting systems | Higher complexity requiring network participants and consensus protocols |
Which is better?
Triple entry bookkeeping enhances transparency and auditability by recording transactions in three separate ledgers, reducing fraud risk and errors. Distributed ledger technology (DLT) offers decentralized data storage and real-time synchronization across multiple nodes, improving security and trust without relying on a central authority. Integrating triple entry bookkeeping with DLT maximizes the accuracy and integrity of financial records in modern accounting systems.
Connection
Triple entry bookkeeping integrates distributed ledger technology by recording each financial transaction as a cryptographically secured third entry, enhancing transparency and auditability. Distributed ledgers provide an immutable, decentralized record that reduces fraud risks and reconciliation errors in accounting processes. This synergy ensures real-time verification and trust among multiple stakeholders in financial reporting.
Key Terms
Immutable Records
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) ensures immutable records by maintaining decentralized and cryptographically secured data across multiple nodes, preventing unauthorized alterations. Triple entry bookkeeping enhances traditional double entry systems by incorporating a cryptographic receipt verified on a blockchain, creating a tamper-proof third entry that guarantees data integrity. Explore how these innovations transform record-keeping and financial transparency.
Cryptographic Signature
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) leverages decentralized databases across multiple nodes to ensure data integrity through cryptographic signatures that authenticate transactions securely. Triple entry bookkeeping enhances traditional double-entry systems by adding a cryptographically signed third ledger, creating an immutable and transparent audit trail. Explore how cryptographic signatures drive trust and accountability in modern financial systems to learn more.
Shared Ledger
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) enhances shared ledger systems by enabling decentralized, transparent, and immutable record-keeping across multiple participants, ensuring data consistency without intermediaries. Triple entry bookkeeping extends traditional double entry by incorporating cryptographic proofs, recorded on a shared ledger, which strengthens auditability and fraud prevention. Explore how integration of DLT and triple entry bookkeeping revolutionizes financial transparency and security in shared ledgers.
Source and External Links
Distributed ledger - Wikipedia - A distributed ledger technology (DLT) is a system where replicated, shared, and synchronized digital data is distributed across many sites or institutions, operating on a peer-to-peer network without a central authority and relying on consensus algorithms to ensure data integrity and security through cryptographic methods.
What is distributed ledger technology (DLT)? - TechTarget - Distributed ledger technology is a decentralized digital system that records asset transactions simultaneously across multiple nodes using consensus algorithms, cryptography, and peer-to-peer networking to create a secure, immutable, and transparent ledger without centralized control.
What are distributed ledger technologies? | Hedera - Distributed ledgers are databases shared among multiple participants who maintain synchronized copies of data, enabling secure and efficient transactions without intermediaries, thereby reducing costs and enhancing trust through a tamper-evident, trustless network architecture.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com