Deferred revenue recognition refers to the accounting process where revenue is recorded only when it is earned, despite cash being received earlier, ensuring compliance with the revenue recognition principle under GAAP or IFRS. Unearned revenue represents the liability account that captures advance payments from customers for goods or services yet to be delivered or performed. Explore further to understand how these concepts impact financial statements and revenue management strategies.
Why it is important
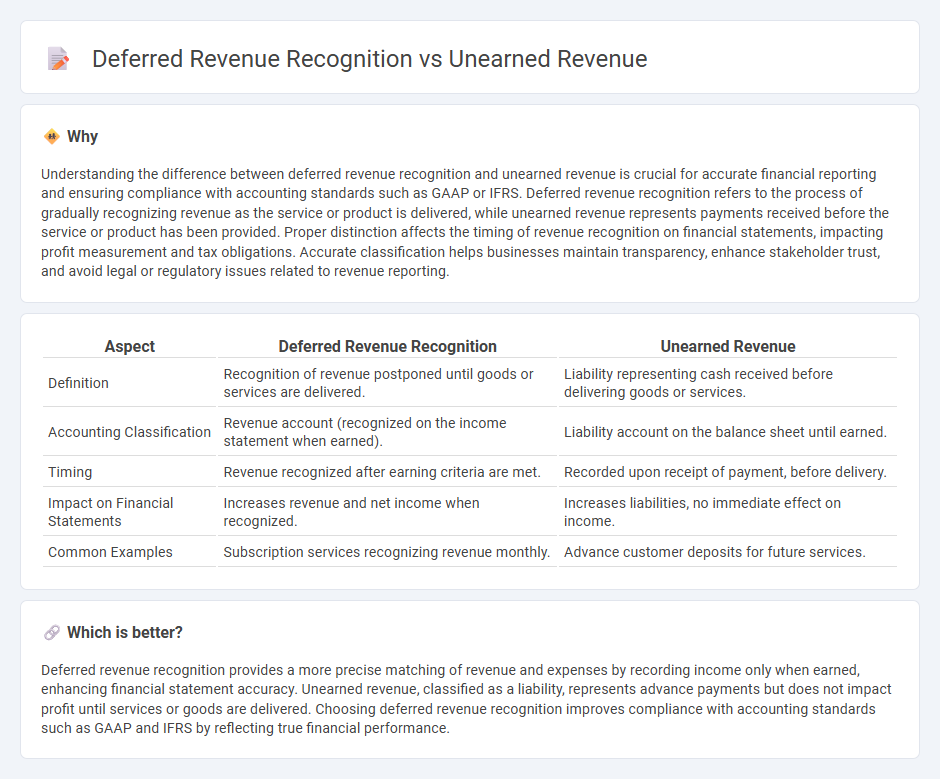
Understanding the difference between deferred revenue recognition and unearned revenue is crucial for accurate financial reporting and ensuring compliance with accounting standards such as GAAP or IFRS. Deferred revenue recognition refers to the process of gradually recognizing revenue as the service or product is delivered, while unearned revenue represents payments received before the service or product has been provided. Proper distinction affects the timing of revenue recognition on financial statements, impacting profit measurement and tax obligations. Accurate classification helps businesses maintain transparency, enhance stakeholder trust, and avoid legal or regulatory issues related to revenue reporting.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Deferred Revenue Recognition | Unearned Revenue |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recognition of revenue postponed until goods or services are delivered. | Liability representing cash received before delivering goods or services. |
| Accounting Classification | Revenue account (recognized on the income statement when earned). | Liability account on the balance sheet until earned. |
| Timing | Revenue recognized after earning criteria are met. | Recorded upon receipt of payment, before delivery. |
| Impact on Financial Statements | Increases revenue and net income when recognized. | Increases liabilities, no immediate effect on income. |
| Common Examples | Subscription services recognizing revenue monthly. | Advance customer deposits for future services. |
Which is better?
Deferred revenue recognition provides a more precise matching of revenue and expenses by recording income only when earned, enhancing financial statement accuracy. Unearned revenue, classified as a liability, represents advance payments but does not impact profit until services or goods are delivered. Choosing deferred revenue recognition improves compliance with accounting standards such as GAAP and IFRS by reflecting true financial performance.
Connection
Deferred revenue recognition and unearned revenue are interconnected accounting concepts representing payments received for goods or services not yet delivered. Unearned revenue appears as a liability on the balance sheet until the company fulfills its obligations, at which point deferred revenue is recognized as earned revenue on the income statement. This process ensures accurate matching of revenue with the period in which it is earned, adhering to accrual accounting principles.
Key Terms
Liability
Unearned revenue and deferred revenue are both liabilities representing payments received before delivering goods or services, reflecting an obligation to fulfill future performance. While unearned revenue broadly indicates advance payments, deferred revenue emphasizes the timing of revenue recognition in accordance with accounting standards like GAAP or IFRS. Explore detailed guidelines on how these liabilities impact financial statements and revenue recognition practices.
Accrual Basis
Unearned revenue and deferred revenue both represent liabilities on the accrual basis of accounting, arising when cash is received before services are performed or goods delivered. Unearned revenue is recognized as revenue only when the earnings process is complete, while deferred revenue specifically refers to postponing revenue recognition until the related expenses or obligations are fulfilled. Explore the distinctions and implications of these revenue recognition concepts for precise financial reporting.
Revenue Recognition
Unearned revenue refers to payments received by a company before delivering goods or services, classified as a liability until earned. Deferred revenue recognition occurs when the company gradually recognizes this revenue in the income statement as performance obligations are fulfilled over time. Explore the distinctions and implications of revenue recognition standards to optimize financial reporting.
Source and External Links
Unearned Revenue | Formula + Calculation Example - Unearned revenue is money received by a company before delivering a product or service, recorded as a liability until the obligation is fulfilled and revenue is earned according to accrual accounting principles.
What is unearned revenue? - Unearned revenue, also known as deferred revenue, is an advance payment for goods or services not yet delivered, initially recorded as a liability and gradually recognized as revenue as the company fulfills its obligations.
Adjusting Entry for Unearned Revenue - Unearned revenue represents customer payments collected in advance for goods or services not yet provided, treated as a liability until the company earns the revenue by delivering the promised goods or services.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com