ESG reporting focuses on environmental, social, and governance factors that influence corporate performance and investor decisions, emphasizing measurable metrics and risk management. Sustainability reporting covers a broader scope, highlighting long-term environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and economic impact aligned with global sustainability goals. Discover how these frameworks drive transparent and accountable business practices in accounting.
Why it is important
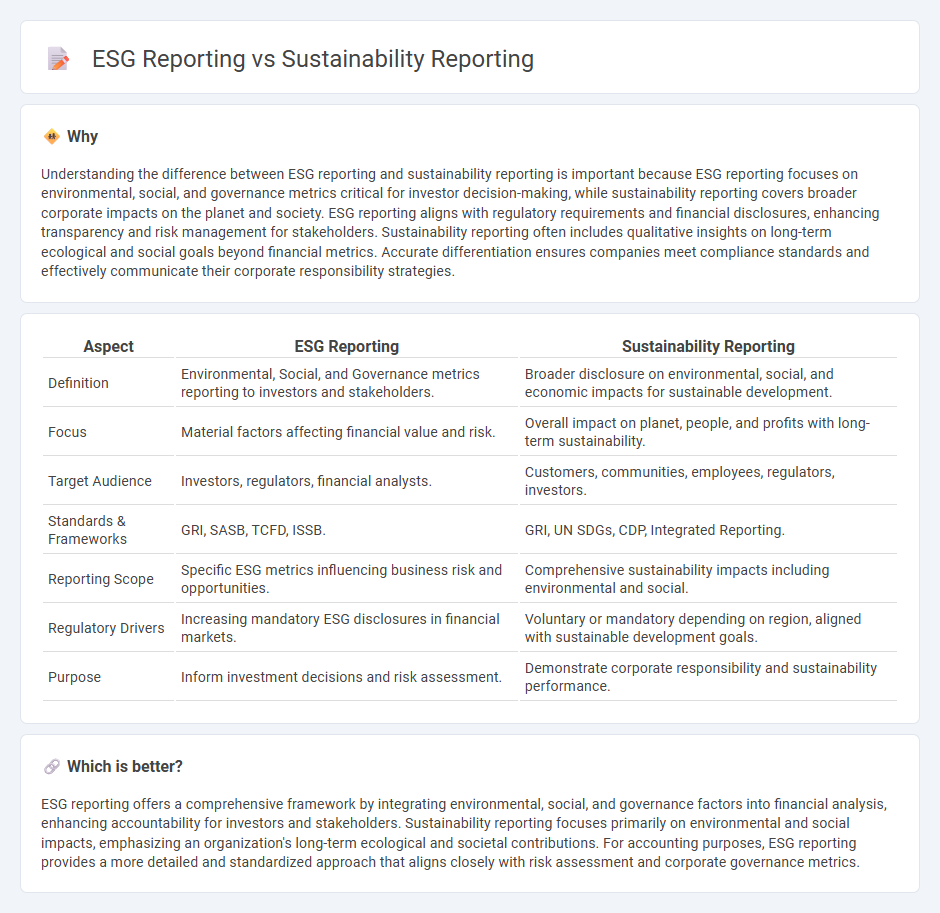
Understanding the difference between ESG reporting and sustainability reporting is important because ESG reporting focuses on environmental, social, and governance metrics critical for investor decision-making, while sustainability reporting covers broader corporate impacts on the planet and society. ESG reporting aligns with regulatory requirements and financial disclosures, enhancing transparency and risk management for stakeholders. Sustainability reporting often includes qualitative insights on long-term ecological and social goals beyond financial metrics. Accurate differentiation ensures companies meet compliance standards and effectively communicate their corporate responsibility strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | ESG Reporting | Sustainability Reporting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Environmental, Social, and Governance metrics reporting to investors and stakeholders. | Broader disclosure on environmental, social, and economic impacts for sustainable development. |
| Focus | Material factors affecting financial value and risk. | Overall impact on planet, people, and profits with long-term sustainability. |
| Target Audience | Investors, regulators, financial analysts. | Customers, communities, employees, regulators, investors. |
| Standards & Frameworks | GRI, SASB, TCFD, ISSB. | GRI, UN SDGs, CDP, Integrated Reporting. |
| Reporting Scope | Specific ESG metrics influencing business risk and opportunities. | Comprehensive sustainability impacts including environmental and social. |
| Regulatory Drivers | Increasing mandatory ESG disclosures in financial markets. | Voluntary or mandatory depending on region, aligned with sustainable development goals. |
| Purpose | Inform investment decisions and risk assessment. | Demonstrate corporate responsibility and sustainability performance. |
Which is better?
ESG reporting offers a comprehensive framework by integrating environmental, social, and governance factors into financial analysis, enhancing accountability for investors and stakeholders. Sustainability reporting focuses primarily on environmental and social impacts, emphasizing an organization's long-term ecological and societal contributions. For accounting purposes, ESG reporting provides a more detailed and standardized approach that aligns closely with risk assessment and corporate governance metrics.
Connection
ESG reporting and sustainability reporting are interconnected as both focus on evaluating a company's environmental, social, and governance impacts to ensure transparency and accountability. ESG reporting provides a structured framework with measurable criteria, while sustainability reporting broadly covers a company's initiatives to promote long-term ecological balance and social responsibility. Integrating ESG metrics into sustainability reporting enhances the accuracy and comparability of corporate performance assessments for investors and stakeholders.
Key Terms
Materiality
Sustainability reporting emphasizes a broad range of environmental, social, and governance factors, capturing a company's overall impact on sustainable development. ESG reporting specifically targets material issues that affect financial performance and investor decisions, prioritizing transparency and risk management in these areas. Explore further to understand how materiality shapes effective sustainability and ESG strategies.
Non-financial disclosure
Sustainability reporting emphasizes the comprehensive disclosure of a company's environmental, social, and governance (ESG) impacts, focusing on long-term value creation beyond financial metrics. ESG reporting specifically targets measurable criteria related to environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and governance practices that influence investor decisions and risk assessments. Explore the distinctions and advantages of each approach to enhance your understanding of non-financial disclosures.
Stakeholder engagement
Sustainability reporting emphasizes comprehensive disclosure on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors with a strong focus on stakeholder engagement to foster transparency and accountability. ESG reporting specifically targets measurable metrics aligned with investor interests, prioritizing data that reflect financial risks and opportunities related to sustainability practices. Explore how integrating robust stakeholder engagement enhances both reporting approaches for improved corporate responsibility and long-term value creation.
Source and External Links
What is Sustainability Reporting? - This page explains that sustainability reporting is a non-financial reporting method that allows companies to communicate their progress toward various sustainability goals, including environmental, social, and governance metrics.
Sustainability Reporting: Frameworks, Benefits & Challenges - This article discusses the importance and benefits of sustainability reporting, including its role in enhancing corporate reputation and compliance with regulations, using frameworks like GRI and ESRS.
Sustainability reporting - This Wikipedia page provides an overview of sustainability reporting, which involves disclosing non-financial performance information about environmental, social, economic, and governance issues to stakeholders.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com